Organizational compliance ensures that your business adheres to legal standards and regulatory requirements, minimizing risks of penalties and reputational damage. Effective compliance programs foster a culture of integrity and accountability across all levels of the organization. Explore the rest of the article to learn how to implement robust compliance strategies that protect and enhance your organization.
Table of Comparison
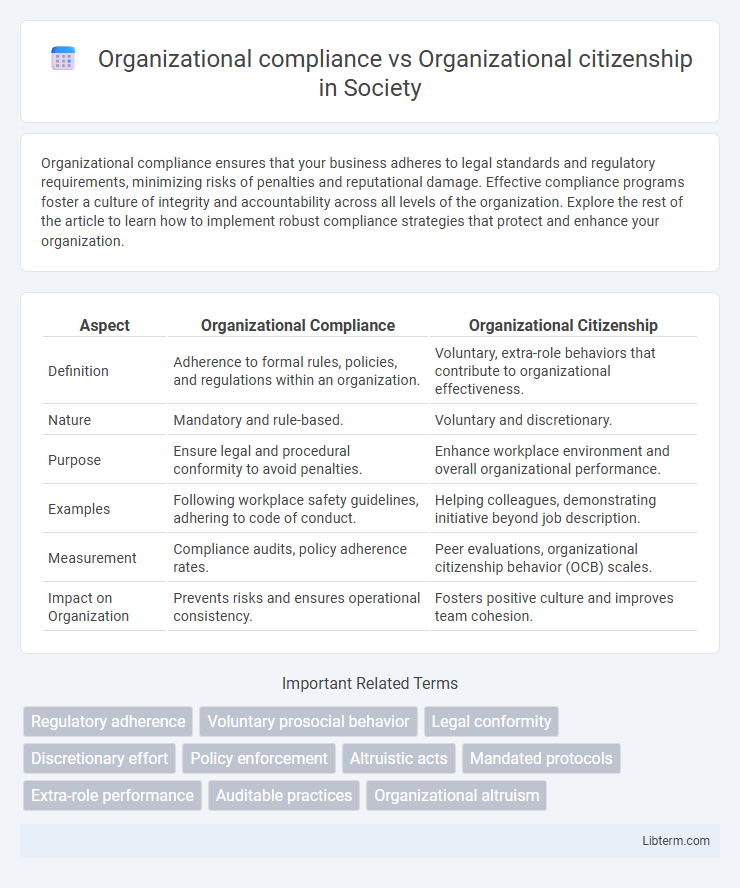
| Aspect | Organizational Compliance | Organizational Citizenship |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Adherence to formal rules, policies, and regulations within an organization. | Voluntary, extra-role behaviors that contribute to organizational effectiveness. |
| Nature | Mandatory and rule-based. | Voluntary and discretionary. |
| Purpose | Ensure legal and procedural conformity to avoid penalties. | Enhance workplace environment and overall organizational performance. |
| Examples | Following workplace safety guidelines, adhering to code of conduct. | Helping colleagues, demonstrating initiative beyond job description. |
| Measurement | Compliance audits, policy adherence rates. | Peer evaluations, organizational citizenship behavior (OCB) scales. |
| Impact on Organization | Prevents risks and ensures operational consistency. | Fosters positive culture and improves team cohesion. |
Understanding Organizational Compliance: Definition and Scope
Organizational compliance refers to the adherence of employees and management to established laws, regulations, policies, and ethical standards within a company, ensuring lawful and risk-free operations. It encompasses formal rules, mandatory practices, and audits that maintain organizational integrity and prevent legal penalties. Understanding organizational compliance involves recognizing its scope as a foundational framework that mandates behavior aligned with external requirements and internal controls.
Exploring Organizational Citizenship: Meaning and Key Traits
Organizational citizenship refers to voluntary employee behaviors that contribute to a positive work environment beyond formal job requirements. Key traits include altruism, conscientiousness, sportsmanship, courtesy, and civic virtue, which enhance team cooperation and organizational effectiveness. These behaviors foster trust and collaboration, leading to improved organizational performance and employee satisfaction.
Core Differences Between Compliance and Citizenship
Organizational compliance involves adhering to rules, policies, and regulations set by the company or external authorities, emphasizing mandatory behavior to avoid penalties. Organizational citizenship refers to voluntary actions employees take to support the workplace environment beyond formal job requirements, fostering cooperation and goodwill. The core difference lies in compliance being obligation-driven and enforced, while citizenship is discretionary and motivated by individual commitment to organizational well-being.
Importance of Compliance in Organizational Success
Organizational compliance ensures adherence to laws, regulations, and internal policies, mitigating risks and fostering a culture of accountability essential for sustainable success. Effective compliance programs reduce legal liabilities and enhance corporate reputation, directly impacting financial performance and stakeholder trust. While organizational citizenship promotes discretionary behavior that benefits the workplace, compliance forms the foundational framework safeguarding operational integrity and long-term viability.
The Role of Citizenship Behaviors in Workplace Culture
Organizational citizenship behaviors (OCBs) enhance workplace culture by promoting voluntary actions that go beyond formal job requirements, fostering collaboration, trust, and a positive work environment. While organizational compliance ensures adherence to rules and policies essential for operational stability, OCBs drive discretionary efforts that improve team cohesion and organizational effectiveness. Integrating citizenship behaviors into corporate culture encourages employee engagement, reduces conflicts, and supports sustained organizational success.
Legal and Ethical Frameworks Guiding Compliance
Organizational compliance strictly adheres to established legal and ethical frameworks, ensuring companies meet regulatory requirements and avoid penalties. In contrast, organizational citizenship involves voluntary behaviors that exceed formal obligations, promoting a positive ethical culture without explicit legal mandates. Both concepts contribute to corporate governance, but compliance centers on adherence to laws such as Sarbanes-Oxley and GDPR, while citizenship fosters internal ethical standards and social responsibility beyond legal frameworks.
Motivational Drivers Behind Citizenship Behaviors
Organizational citizenship behaviors (OCBs) are primarily driven by intrinsic motivational factors such as individual values, job satisfaction, and perceived organizational support, contrasting with organizational compliance, which relies on extrinsic motivators like rules and formal policies. Employees demonstrating high levels of OCB often engage in discretionary actions that go beyond formal job requirements, motivated by a sense of belonging and commitment to organizational goals. Research indicates that fostering a supportive work environment and aligning organizational values with personal beliefs significantly enhances citizenship behaviors among employees.
Impact of Compliance vs. Citizenship on Employee Engagement
Organizational compliance involves employees adhering strictly to rules and policies, ensuring mandatory standards are met but often fostering a transactional relationship with the employer. Organizational citizenship behavior (OCB) reflects voluntary, discretionary actions that go beyond formal requirements, significantly enhancing employee engagement by promoting a positive work environment and stronger commitment. Research shows that while compliance ensures baseline performance, OCB drives higher engagement levels, creativity, and organizational loyalty, ultimately contributing more to long-term productivity and workplace satisfaction.
Aligning Compliance and Citizenship for Sustainable Growth
Aligning organizational compliance with organizational citizenship fosters a culture where employees not only adhere to rules but also voluntarily contribute to collective goals, enhancing sustainable growth. Embedding compliance within a framework of citizenship behaviors encourages ethical practices and proactive engagement, driving innovation and long-term value creation. This integration supports resilient business operations by balancing regulatory adherence with discretionary efforts that promote collaboration and continuous improvement.
Best Practices for Balancing Compliance and Citizenship in Organizations
Best practices for balancing organizational compliance and organizational citizenship include fostering a culture that emphasizes both adherence to legal regulations and the encouragement of voluntary, positive employee behaviors. Implementing clear policies and training programs ensures employees understand compliance requirements while promoting engagement initiatives cultivates discretionary efforts that support organizational goals. Regular assessments and open communication channels help maintain equilibrium, aligning compliance obligations with the development of proactive employee contributions.
Organizational compliance Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com