Culture shapes identities, influences behaviors, and fosters community connections across diverse societies. Understanding cultural dynamics enhances your ability to navigate social interactions and appreciate global perspectives. Explore the rest of the article to discover how culture impacts everyday life and personal growth.
Table of Comparison
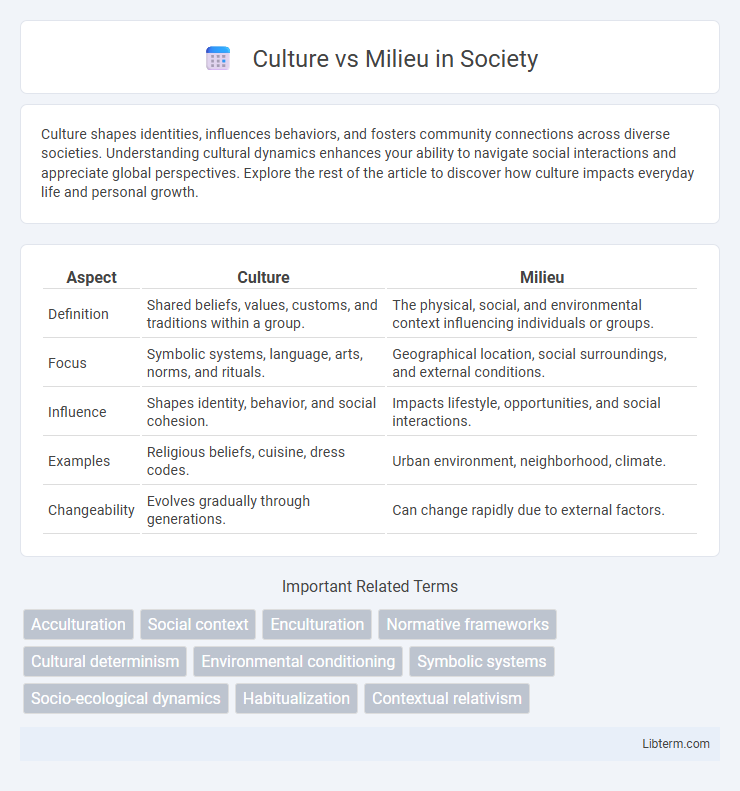
| Aspect | Culture | Milieu |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Shared beliefs, values, customs, and traditions within a group. | The physical, social, and environmental context influencing individuals or groups. |
| Focus | Symbolic systems, language, arts, norms, and rituals. | Geographical location, social surroundings, and external conditions. |
| Influence | Shapes identity, behavior, and social cohesion. | Impacts lifestyle, opportunities, and social interactions. |
| Examples | Religious beliefs, cuisine, dress codes. | Urban environment, neighborhood, climate. |
| Changeability | Evolves gradually through generations. | Can change rapidly due to external factors. |
Defining Culture and Milieu
Culture encompasses the shared beliefs, behaviors, values, customs, and artifacts that characterize a group or society, shaping individual identities and social norms. Milieu refers to the social environment or setting in which individuals live and interact, influencing their experiences and perceptions through external conditions and contexts. Understanding culture involves analyzing internalized, symbolic systems, while milieu emphasizes the external, situational factors impacting social behavior.
Historical Perspectives on Culture and Milieu
Historical perspectives on culture emphasize the shared beliefs, values, customs, and artistic expressions that define a group, evolving through traditions and collective experiences over time. Milieu refers to the immediate social and physical environment influencing individual behavior and social interactions, shaped by historical events and socio-economic conditions. Understanding the interplay between culture and milieu reveals how historical contexts shape both collective identities and the surrounding circumstances impacting daily life.
Key Differences Between Culture and Milieu
Culture encompasses the shared beliefs, values, customs, and social behaviors of a group, shaping identities and traditions over time. Milieu refers to the immediate social environment or setting influencing an individual's daily experiences and interactions. The key difference lies in culture being a broader, enduring framework, while milieu is the specific contextual backdrop affecting behavior in the moment.
The Role of Culture in Shaping Identity
Culture shapes identity by providing shared symbols, norms, and values that individuals internalize, influencing their worldview and behavior patterns. Unlike milieu, which refers to the immediate physical and social environment, culture encompasses historical traditions and collective meanings that persist across contexts. This deep cultural framework serves as a foundation for personal and group identity formation, guiding social interaction and self-perception.
Milieu: Environment, Context, and Influence
Milieu encompasses the physical environment, social context, and external influences that shape an individual's experiences and behaviors. It includes factors such as geographic location, socioeconomic status, and community dynamics that interact to form the immediate setting in which a person lives. Understanding the milieu is crucial for analyzing how environmental conditions and contextual factors influence psychological development and social interactions.
Interactions Between Culture and Milieu
Culture shapes social behaviors, values, and norms, while milieu refers to the physical and social environment influencing individual experiences. Interactions between culture and milieu occur as cultural practices adapt to environmental conditions, and the milieu simultaneously affects the transmission and evolution of cultural traits. This dynamic interplay highlights how changing social settings can reinforce or transform cultural identities over time.
Cultural Transmission vs. Environmental Adaptation
Cultural transmission involves the passing of knowledge, beliefs, and customs from one generation to another, ensuring the preservation and evolution of social norms within a community. Environmental adaptation refers to the ways humans adjust their behaviors and technologies to survive and thrive in diverse ecological settings. While cultural transmission emphasizes continuity and learning, environmental adaptation focuses on practical changes imposed by physical surroundings.
Case Studies: Culture vs Milieu in Practice
Case studies of Culture vs Milieu demonstrate how cultural norms influence individual behaviors differently than environmental conditions, revealing unique patterns in social interactions and decision-making. For example, studies in organizational settings show that corporate culture shapes work styles and communication more strongly than physical workspace layout or geographic location. Research on immigrant communities further highlights how cultural values persist despite changes in milieu, emphasizing the resilience of cultural identity amid varying external environments.
Impact on Social Behavior and Norms
Culture shapes social behavior and norms through shared values, beliefs, and customs that guide individual and group interactions within a society. Milieu, referring to the immediate social environment or context, influences behavior by providing situational cues and localized norms that individuals adapt to in real-time. The dynamic interplay between overarching cultural frameworks and specific milieus determines how social expectations are internalized and enacted in daily life.
Bridging the Gap: Integrating Culture and Milieu
Bridging the gap between culture and milieu involves understanding culture as the shared values, beliefs, and practices that shape individual behavior, while milieu refers to the immediate social and physical environment influencing interactions. Integrating culture and milieu enhances social cohesion by aligning cultural norms with environmental contexts, fostering adaptive responses in diverse settings. This synergy supports effective communication and collaboration, particularly in multicultural communities and organizational frameworks.
Culture Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com