Technocracy emphasizes governance by experts and specialists, ensuring decisions are based on knowledge and scientific data rather than politics. This system aims to optimize efficiency, innovation, and problem-solving within society's various sectors. Explore the full article to understand how technocracy could impact Your future governance and daily life.
Table of Comparison
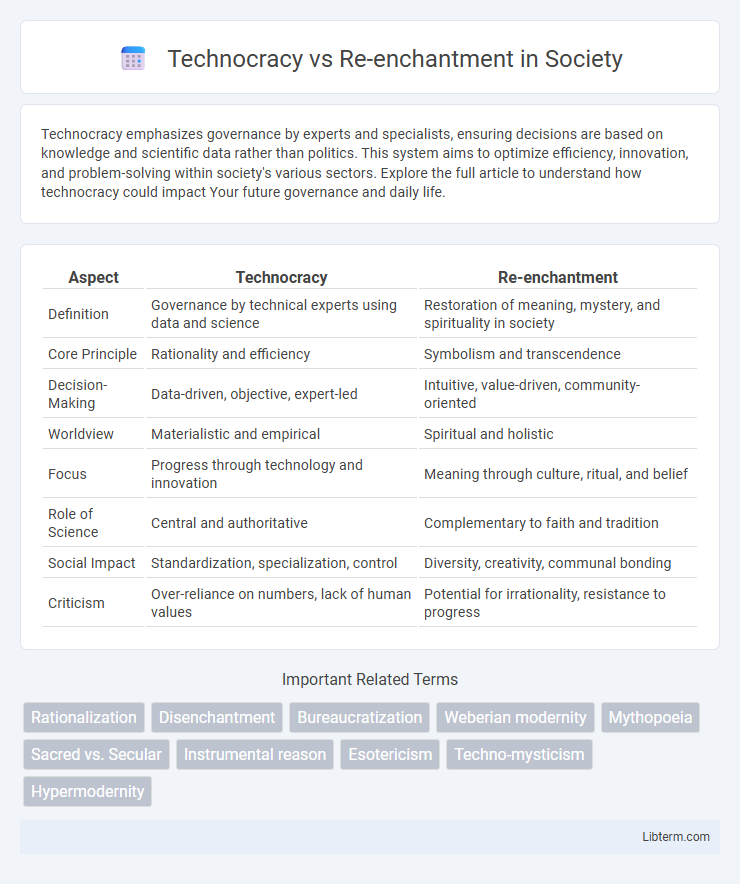
| Aspect | Technocracy | Re-enchantment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Governance by technical experts using data and science | Restoration of meaning, mystery, and spirituality in society |
| Core Principle | Rationality and efficiency | Symbolism and transcendence |
| Decision-Making | Data-driven, objective, expert-led | Intuitive, value-driven, community-oriented |
| Worldview | Materialistic and empirical | Spiritual and holistic |
| Focus | Progress through technology and innovation | Meaning through culture, ritual, and belief |
| Role of Science | Central and authoritative | Complementary to faith and tradition |
| Social Impact | Standardization, specialization, control | Diversity, creativity, communal bonding |
| Criticism | Over-reliance on numbers, lack of human values | Potential for irrationality, resistance to progress |
Understanding Technocracy: Definition and Origins
Technocracy is a system of governance emphasizing decision-making by technical experts and scientists, rooted in early 20th-century movements advocating efficient management of society through scientific principles. Originating during the Great Depression, it aimed to replace political and economic elites with engineers and specialists to optimize resource allocation and production. The concept contrasts with re-enchantment, which values symbolic meaning and cultural narratives over empirical data and utilitarian rationality.
The Philosophy of Re-enchantment: Revisiting Wonder
The philosophy of re-enchantment challenges the dominance of technocracy by reinvigorating a sense of wonder and mystery in contemporary life, emphasizing qualitative experience over purely rational, technical control. It advocates for a worldview where meaningful connections and symbolic interpretations reintroduce depth and value beyond mechanistic explanations. This perspective seeks to balance the precision of technological progress with an enriched appreciation for existential and spiritual dimensions.
Historical Roots: Technocratic Progress vs Mystical Worldviews
Technocratic progress traces its roots to the early 20th century, emphasizing scientific management, efficiency, and rational control over society, influenced by industrialization and Enlightenment ideals. Mystical worldviews arise from ancient spiritual traditions, valuing intuition, sacredness, and interconnectedness as fundamental to understanding reality. The historical tension between these perspectives reflects a broader conflict between measurable, objective advancement and the search for meaning through symbolic and spiritual experiences.
Rationalization of Society: The Rise of Technocratic Governance
Technocratic governance represents the rationalization of society by prioritizing expert knowledge and data-driven decision-making over traditional political processes. This shift emphasizes efficiency, scientific management, and technological solutions to complex social problems, contrasting sharply with the re-enchantment movement's focus on restoring meaning, spirituality, and cultural narratives. The rise of technocracy highlights a societal paradigm deeply rooted in rationalization, where administrative expertise replaces charismatic authority and emotional values in shaping public policy.
The Loss of Meaning: Disenchantment in Modernity
Disenchantment in modernity manifests through the rise of technocracy, where rationalization and bureaucratic governance prioritize efficiency over spiritual or cultural significance, leading to a pervasive loss of meaning in everyday life. Max Weber's concept of disenchantment highlights how scientific rationality and technological control diminish the role of mythology, religion, and mysticism, resulting in a fragmented sense of purpose. This process contrasts sharply with efforts toward re-enchantment, which seek to restore meaning by integrating symbolic, emotional, and experiential dimensions into social and political structures.
Re-enchantment Movements: Calls for Spiritual Renewal
Re-enchantment movements emphasize a revival of spiritual values and deeper connection to nature as a response to the rational, technocratic dominance in modern society. These movements advocate for incorporating mystical experience, ritual, and ecological awareness to counterbalance mechanistic worldviews. They seek to restore meaning and purpose through spirituality, fostering holistic well-being in contrast to the impersonal efficiency of technocracy.
Technology and the Sacred: Can They Coexist?
Technocracy emphasizes rationality, efficiency, and control through technology, often sidelining spiritual or sacred values. Re-enchantment seeks to restore a sense of wonder and meaning by integrating technology with deeper, sacred narratives. Balancing advanced technological innovation with ethical and spiritual principles can enable a coexistence where progress respects human transcendence.
Impacts on Culture: Art, Science, and Human Experience
Technocracy emphasizes empirical science and technological control, shaping culture through efficiency-driven innovation and often marginalizing artistic expression and subjective human experiences. Re-enchantment restores a sense of wonder and meaning by integrating myth, spirituality, and creativity, enriching art and broadening scientific inquiry to include holistic and experiential dimensions. The tension between these worldviews influences cultural narratives, impacting how societies value rationality versus emotional and symbolic engagement in shaping human identity.
Navigating the Divide: Integrative Approaches for the Future
Navigating the divide between technocracy and re-enchantment involves blending rational data-driven governance with cultural and spiritual values to create holistic policies. Integrative approaches emphasize the use of advanced technologies such as AI and big data analytics alongside participatory decision-making and community engagement methods. This synthesis fosters sustainable innovation, ensuring that technological progress aligns with human well-being and ecological balance.
Technocracy vs Re-enchantment: Charting a Path Forward
Technocracy emphasizes governance through scientific expertise and data-driven decision-making, prioritizing efficiency and rationality in addressing societal challenges. Re-enchantment advocates for restoring meaning, spirituality, and human connection within modern systems, countering the sterile, mechanistic tendencies of technocratic approaches. Charting a path forward requires integrating empirical knowledge with holistic values to create sustainable, inclusive policies that resonate with both reason and human experience.
Technocracy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com