Liberal nationalism blends the principles of individual freedom and collective national identity, emphasizing democratic governance and the protection of civil rights within a sovereign state. It advocates for a nation built on shared values and inclusive citizenship, promoting both cultural unity and political liberty. Explore the full article to understand how liberal nationalism shapes modern political landscapes and influences your sense of belonging.
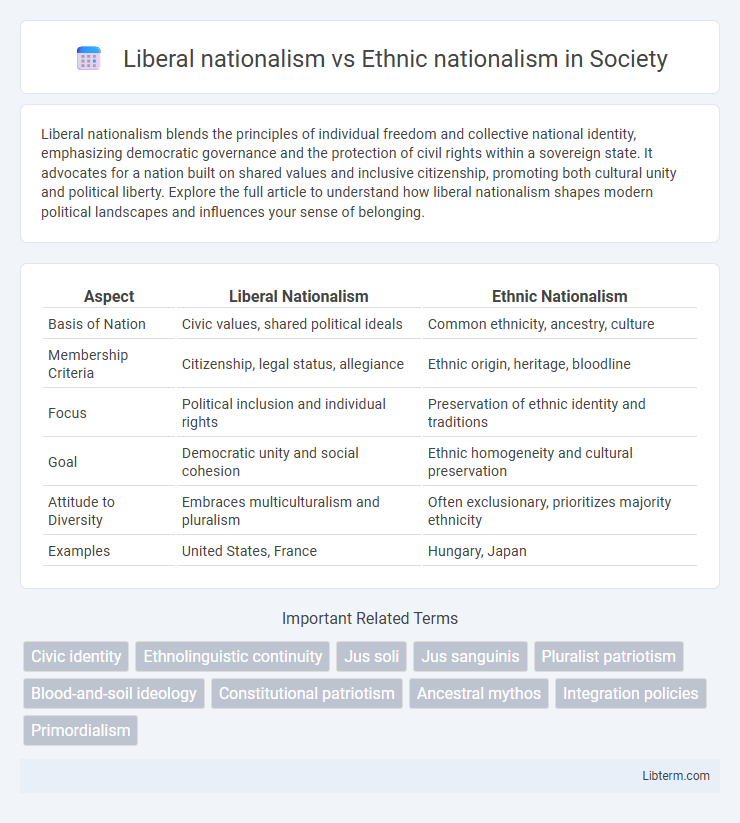
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Liberal Nationalism | Ethnic Nationalism |
|---|---|---|
| Basis of Nation | Civic values, shared political ideals | Common ethnicity, ancestry, culture |
| Membership Criteria | Citizenship, legal status, allegiance | Ethnic origin, heritage, bloodline |
| Focus | Political inclusion and individual rights | Preservation of ethnic identity and traditions |
| Goal | Democratic unity and social cohesion | Ethnic homogeneity and cultural preservation |
| Attitude to Diversity | Embraces multiculturalism and pluralism | Often exclusionary, prioritizes majority ethnicity |
| Examples | United States, France | Hungary, Japan |
Defining Liberal Nationalism
Liberal nationalism emphasizes individual rights, democratic governance, and inclusive citizenship, promoting a nation defined by shared political values rather than ethnic identity. It supports the integration of diverse cultural groups under a common legal and social framework, ensuring equal participation regardless of ethnicity. This form of nationalism contrasts with ethnic nationalism, which prioritizes ancestry, language, and cultural heritage as the basis for national belonging.
Understanding Ethnic Nationalism
Ethnic nationalism centers on shared heritage, language, culture, and ancestry as the foundation of national identity, often emphasizing exclusivity based on lineage. It contrasts with liberal nationalism, which bases nationhood on civic values, political institutions, and individual rights regardless of ethnicity. Understanding ethnic nationalism involves recognizing its role in fostering group cohesion by promoting a collective identity tied to descent and historical narratives.
Historical Foundations of Each Ideology
Liberal nationalism, rooted in the Enlightenment and the American and French Revolutions, emphasizes individual rights, civic participation, and the idea of nationhood based on shared political values and citizenship. Ethnic nationalism traces its origins to 19th-century Romanticism and the rise of national identity based on common ancestry, language, culture, and historical heritage, often emphasizing ethnic homogeneity. These differing historical foundations shape liberal nationalism's inclusive political framework versus ethnic nationalism's focus on cultural and ethnic unity.
Key Philosophical Differences
Liberal nationalism emphasizes individual rights, political freedom, and inclusion based on shared civic values, while ethnic nationalism prioritizes common ancestry, culture, and ethnicity as the foundation of national identity. The former advocates for a pluralistic society where membership is voluntary and inclusive; the latter often seeks homogeneity and exclusive belonging tied to ethnic heritage. These philosophical differences influence policies on citizenship, minority rights, and the state's role in preserving national identity.
Political Expression and Policy Implications
Liberal nationalism promotes political expression based on shared citizenship, individual rights, and inclusive state policies that emphasize equal participation regardless of ethnicity, leading to multicultural and civic-oriented governance. Ethnic nationalism centers political expression on a common heritage, language, and ancestry, influencing policies that prioritize the interests of a dominant ethnic group and often result in exclusionary practices or preferential treatment. These divergent foundations affect immigration laws, minority rights, and national identity framing, shaping the political landscape and state legitimacy in distinct ways.
Inclusivity vs Exclusivity in National Identity
Liberal nationalism emphasizes inclusivity in national identity, promoting citizenship based on shared values, legal rights, and political participation regardless of ethnic background. Ethnic nationalism prioritizes exclusivity by defining national identity through common ancestry, language, culture, or heritage, often resulting in exclusion of those outside the dominant ethnic group. This fundamental difference shapes policies on immigration, minority rights, and social cohesion, influencing national unity and multicultural integration.
Social Cohesion and Minority Rights
Liberal nationalism emphasizes social cohesion through inclusive citizenship and equal rights, fostering a shared national identity that respects minority rights and cultural diversity. Ethnic nationalism, by prioritizing a common ancestry, language, or culture, can strengthen in-group solidarity but often marginalizes minorities and undermines social cohesion. Balancing national unity with minority protections remains a critical challenge in diverse, multi-ethnic societies.
Case Studies: Examples Around the World
Liberal nationalism emphasizes inclusive citizenship and individual rights, as seen in Canada's multicultural policies promoting unity despite ethnic diversity. Ethnic nationalism prioritizes shared heritage and cultural identity, exemplified by Hungary's emphasis on ethnic Hungarians in national policy, often excluding minorities. South Africa's post-apartheid nation-building blends liberal nationalism's inclusivity with recognition of ethnic identities, illustrating complex dynamics in multi-ethnic states.
Liberal Nationalism and Globalization
Liberal nationalism emphasizes shared values, individual rights, and civic participation, promoting an inclusive national identity compatible with globalization's interconnected economies and multicultural societies. It supports open borders, international cooperation, and the protection of human rights, enabling nations to thrive in global networks while maintaining political sovereignty. This approach contrasts with ethnic nationalism, which prioritizes cultural homogeneity and often resists globalization due to perceived threats to traditional ethnic identities.
Contemporary Challenges and Future Trends
Liberal nationalism emphasizes individual rights, inclusivity, and civic identity, confronting contemporary challenges such as multicultural integration and global migration pressures. Ethnic nationalism centers on shared heritage and cultural homogeneity, facing issues like ethnic conflict and exclusion in increasingly diverse societies. Future trends suggest a potential rise in hybrid models that balance national identity with pluralism to address global interconnectedness and social cohesion.
Liberal nationalism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com