Organizational commitment reflects the emotional attachment and loyalty employees feel toward their company, influencing job satisfaction and retention rates. High organizational commitment drives productivity and enhances workplace culture by fostering trust and alignment with company goals. Discover how strengthening your organizational commitment can transform your business in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
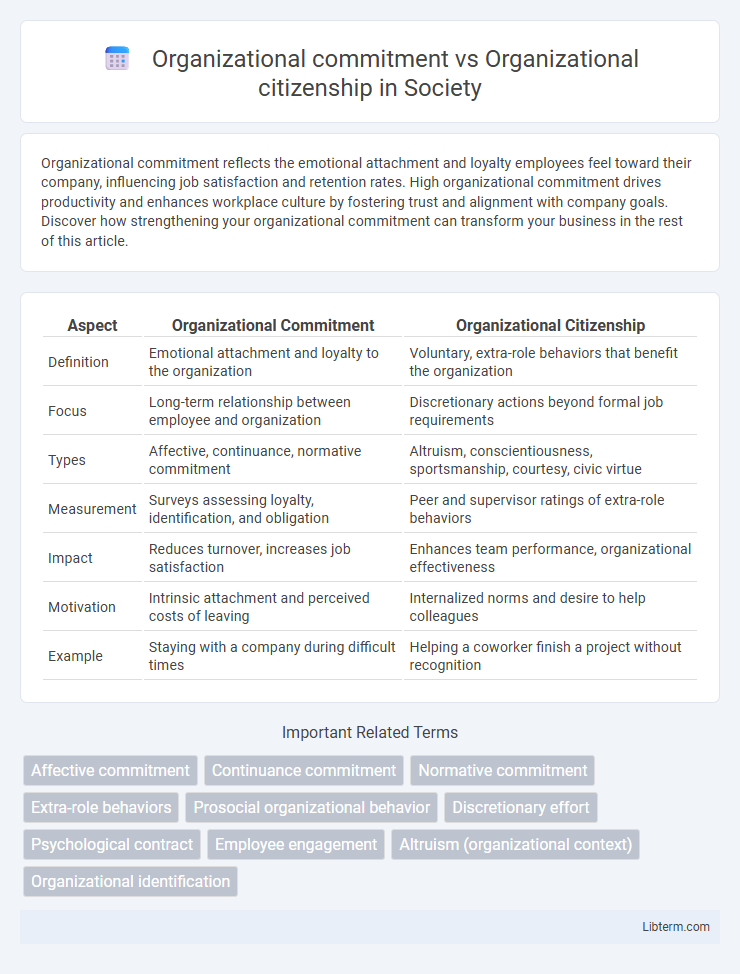
| Aspect | Organizational Commitment | Organizational Citizenship |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Emotional attachment and loyalty to the organization | Voluntary, extra-role behaviors that benefit the organization |
| Focus | Long-term relationship between employee and organization | Discretionary actions beyond formal job requirements |
| Types | Affective, continuance, normative commitment | Altruism, conscientiousness, sportsmanship, courtesy, civic virtue |
| Measurement | Surveys assessing loyalty, identification, and obligation | Peer and supervisor ratings of extra-role behaviors |
| Impact | Reduces turnover, increases job satisfaction | Enhances team performance, organizational effectiveness |
| Motivation | Intrinsic attachment and perceived costs of leaving | Internalized norms and desire to help colleagues |
| Example | Staying with a company during difficult times | Helping a coworker finish a project without recognition |
Defining Organizational Commitment
Organizational commitment represents an employee's psychological attachment and loyalty to their organization, reflecting their willingness to remain and exert effort on its behalf. It encompasses affective commitment, which relates to emotional connection, continuance commitment based on the costs of leaving, and normative commitment driven by a sense of obligation. This concept differs from organizational citizenship behavior, which involves discretionary, extra-role activities that support organizational effectiveness without explicit rewards.
Understanding Organizational Citizenship
Organizational citizenship refers to voluntary, discretionary behaviors employees engage in that go beyond formal job requirements and contribute to the overall effectiveness of the organization. Unlike organizational commitment, which measures an employee's emotional attachment and loyalty to the company, organizational citizenship emphasizes proactive actions such as helping colleagues, supporting organizational initiatives, and promoting a positive work environment. Understanding organizational citizenship helps organizations foster a culture of cooperation and enhances performance by encouraging employees to participate beyond their prescribed roles.
Key Dimensions of Organizational Commitment
Organizational commitment primarily encompasses affective, continuance, and normative dimensions, reflecting employees' emotional attachment, perceived costs of leaving, and feelings of obligation, respectively. In contrast, organizational citizenship behavior refers to voluntary, discretionary actions that go beyond formal job requirements to benefit the organization. Understanding these key dimensions of organizational commitment helps differentiate it from organizational citizenship by highlighting the motivational bases behind employee loyalty versus extra-role behaviors.
Core Elements of Organizational Citizenship
Organizational citizenship centers on voluntary, discretionary behaviors that go beyond formal job requirements, including altruism, conscientiousness, sportsmanship, courtesy, and civic virtue as its core elements. These behaviors enhance organizational functioning by promoting a positive workplace environment and facilitating cooperation among employees. Unlike organizational commitment, which reflects an employee's emotional attachment, organizational citizenship focuses on proactive contributions that support organizational goals without direct compensation.
Differences Between Organizational Commitment and Citizenship
Organizational commitment refers to an employee's psychological attachment and loyalty to their organization, often measured by their willingness to stay and contribute to organizational goals. Organizational citizenship behavior (OCB) involves discretionary actions beyond formal job requirements that promote the overall functioning and environment of the workplace. The key difference lies in commitment representing an emotional and attitudinal bond, whereas citizenship encompasses voluntary, extra-role behaviors that benefit the organization.
Impact on Employee Performance
Organizational commitment significantly enhances employee performance by fostering loyalty, reducing turnover, and increasing dedication to achieving company goals. Organizational citizenship behavior (OCB) further boosts performance through voluntary, extra-role actions that improve team dynamics and workplace environment without direct rewards. Together, these elements create a synergistic effect, driving higher productivity, collaboration, and overall organizational effectiveness.
Influence on Organizational Culture
Organizational commitment significantly shapes organizational culture by fostering a strong sense of loyalty and adherence to shared values, which enhances employee engagement and reduces turnover rates. Organizational citizenship behavior, characterized by voluntary, discretionary actions that go beyond formal job requirements, promotes a collaborative and supportive culture that boosts team cohesion and overall productivity. Both elements synergistically influence organizational culture by embedding dedication and cooperative behaviors into daily workplace practices, driving sustainable organizational success.
Factors Influencing Commitment and Citizenship
Factors influencing organizational commitment include job satisfaction, perceived organizational support, and alignment with company values, which enhance employees' emotional attachment and loyalty. Organizational citizenship behavior is driven by positive workplace relationships, recognition, and employee empowerment, encouraging voluntary, extra-role actions that benefit the organization. Both constructs are shaped by leadership style, organizational culture, and effective communication, reinforcing dedication and proactive behaviors within the workforce.
Measuring Commitment and Citizenship Behaviors
Measuring organizational commitment involves assessing employees' psychological attachment through tools like the Organizational Commitment Questionnaire (OCQ), which evaluates affective, continuance, and normative commitment dimensions. Organizational citizenship behaviors (OCBs) are quantified by frequency and quality of discretionary actions benefiting the organization, often using scales such as the Organizational Citizenship Behavior Checklist (OCB-C). Accurate measurement of both constructs provides insight into employee engagement, predicting retention, productivity, and positive workplace dynamics.
Strategies to Foster Both Commitment and Citizenship
Implementing transparent communication, recognizing employee contributions, and aligning individual values with organizational goals enhance organizational commitment and citizenship behaviors. Training programs that emphasize teamwork, ethical conduct, and role clarity promote a culture of cooperation and voluntary effort beyond job requirements. Leadership styles such as transformational and servant leadership effectively foster engagement, motivation, and discretionary behaviors essential for organizational success.
Organizational commitment Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com