Localization ensures your content resonates with target audiences by adapting language, cultural nuances, and regional preferences to deliver a seamless user experience. This process goes beyond translation, enhancing engagement and boosting brand loyalty in diverse markets. Explore the article to discover how effective localization can transform your global outreach.
Table of Comparison
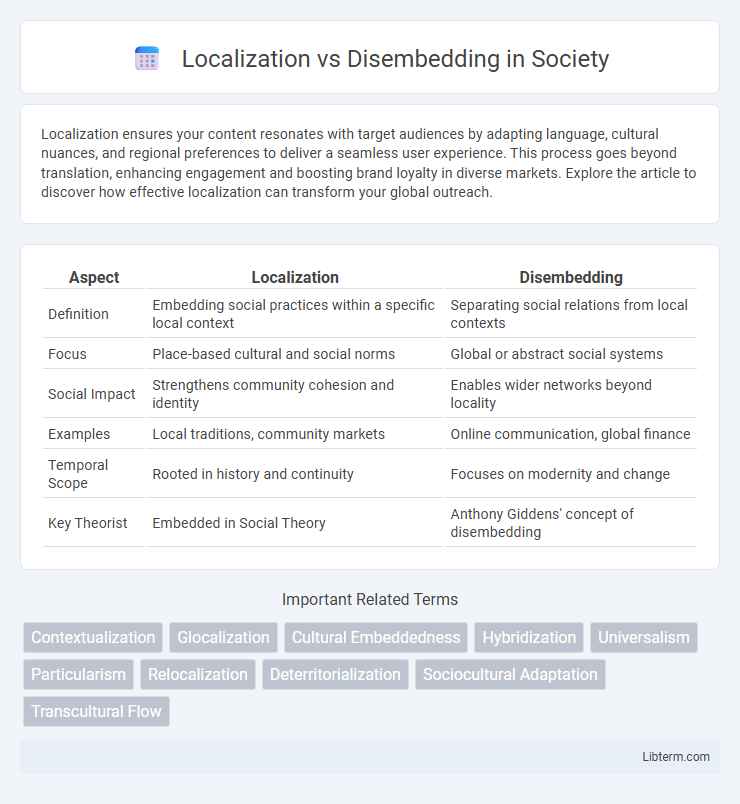
| Aspect | Localization | Disembedding |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Embedding social practices within a specific local context | Separating social relations from local contexts |
| Focus | Place-based cultural and social norms | Global or abstract social systems |
| Social Impact | Strengthens community cohesion and identity | Enables wider networks beyond locality |
| Examples | Local traditions, community markets | Online communication, global finance |
| Temporal Scope | Rooted in history and continuity | Focuses on modernity and change |
| Key Theorist | Embedded in Social Theory | Anthony Giddens' concept of disembedding |
Understanding Localization and Disembedding
Localization involves adapting products or content to meet the linguistic, cultural, and regulatory requirements of a specific target market, ensuring relevance and user engagement. Disembedding refers to the process of extracting ideas, practices, or products from their original context to apply them universally across different environments. Understanding localization requires recognizing its emphasis on cultural nuance and context-specific customization, while disembedding focuses on generalization and broader applicability beyond initial settings.
Historical Context of Localization and Disembedding
Localization refers to the adaptation of content, products, or services to fit the cultural, linguistic, and regional nuances of a specific area, a concept that gained prominence with the rise of global trade and communication in the late 20th century. Disembedding, a term popularized by sociologist Anthony Giddens, describes the process by which social relations are lifted out of local contexts and restructured across extended time-space dimensions, becoming significant in the context of modernity and globalization. Historically, localization preserved cultural identity and consumer relevance within particular localities, while disembedding facilitated the spread of social, economic, and technological systems beyond localized settings, shaping contemporary globalization dynamics.
Key Differences Between Localization and Disembedding
Localization emphasizes adapting products, services, or content to fit the cultural, linguistic, and regional specifics of a particular market, enhancing relevance and user experience. Disembedding involves extracting social or economic activities from a localized context to operate on a broader, often global, scale, reducing dependency on specific cultural or geographic factors. The key difference lies in localization's focus on cultural integration and customization, whereas disembedding prioritizes detachment and scalability across diverse environments.
Localization: Definition and Real-World Examples
Localization involves adapting products, services, or content to meet the linguistic, cultural, and societal preferences of a specific target market or region, ensuring relevance and user engagement. For example, software companies tailor interfaces and support documentation to local languages and compliance standards, while global brands modify advertising campaigns to align with local customs and values. This process enhances market penetration and customer satisfaction by addressing regional nuances and expectations effectively.
Disembedding: Meaning and Applications
Disembedding refers to the process of separating information or content from its original context to allow more flexible use and analysis across different platforms or regions. This technique is widely applied in global marketing, software development, and data management to enable customization and adaptation without altering the core content. Its applications include enhancing user experience by providing culturally neutral content and improving workflow efficiency through standardized, context-independent data modules.
Impact of Globalization on Localization and Disembedding
Globalization intensifies the interplay between localization and disembedding by increasing cross-cultural interactions and economic interdependencies, which challenge traditional local practices while promoting standardized processes. Localization adapts global products and services to meet specific cultural, linguistic, and regulatory requirements, enhancing relevance and acceptance in diverse markets. Disembedding separates social and economic activities from local contexts, enabling global networks to operate beyond geographical constraints, thus accelerating the flow of information, capital, and goods worldwide.
Cultural Implications of Localization vs Disembedding
Localization enhances user experience by adapting products and content to specific cultural norms, languages, and societal values, fostering deeper emotional connections and market relevance. Disembedding operational processes or content removes them from their local context, which can lead to cultural misunderstandings and reduced effectiveness due to the lack of alignment with local customs and expectations. Balancing localization with global efficiency ensures cultural sensitivity while maintaining scalable business operations, ultimately influencing brand perception and customer loyalty.
Economic Effects of Localization and Disembedding
Localization enhances economic resilience by fostering local production, creating jobs, and reducing dependency on global supply chains, which often results in increased community wealth and sustainable growth. Disembedding, characterized by the detachment of economic activities from local contexts, facilitates global trade and capital flow but can lead to economic disparities, job displacement, and vulnerability to external market shocks. The economic effects of localization promote stability and equitable development, while disembedding drives efficiency and globalization at the expense of local economic cohesion.
Challenges and Benefits: Localization vs Disembedding
Localization enhances user experience by adapting content to specific cultural and linguistic contexts, improving engagement and relevance across global markets. Challenges include the complexity of maintaining consistency and managing diverse regional regulations, which can increase costs and extend timelines. Disembedding offers scalability and uniformity by separating content from presentation, enabling faster updates and easier maintenance, but may struggle with personalizing user experience effectively in varied cultural environments.
Future Trends in Localization and Disembedding
Future trends in localization emphasize the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning to enhance cultural adaptation and real-time language translation, driving more personalized user experiences. Disembedding will increasingly leverage blockchain technology and decentralized networks to facilitate secure, transparent cross-border transactions and asset transfers. The convergence of these technologies is expected to reshape global business models by balancing hyper-local relevance with seamless global connectivity.
Localization Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com