Agenda-setting influences which topics dominate public discourse by shaping media focus and framing issues. This process directs your attention toward specific subjects, affecting perceptions and priorities. Discover how agenda-setting impacts what you see and think in the following article.
Table of Comparison
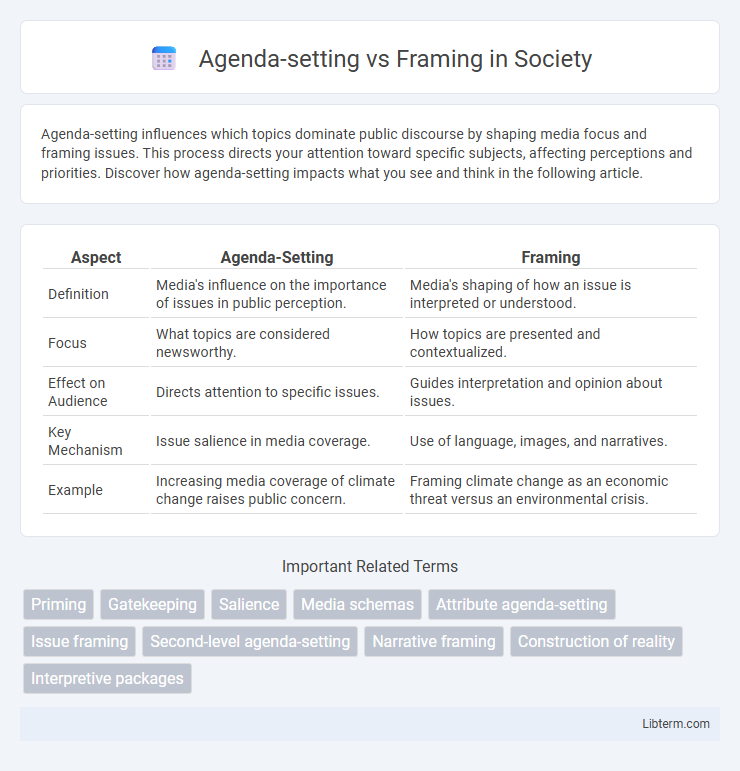
| Aspect | Agenda-Setting | Framing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Media's influence on the importance of issues in public perception. | Media's shaping of how an issue is interpreted or understood. |
| Focus | What topics are considered newsworthy. | How topics are presented and contextualized. |
| Effect on Audience | Directs attention to specific issues. | Guides interpretation and opinion about issues. |
| Key Mechanism | Issue salience in media coverage. | Use of language, images, and narratives. |
| Example | Increasing media coverage of climate change raises public concern. | Framing climate change as an economic threat versus an environmental crisis. |
Understanding Agenda-Setting Theory
Agenda-setting theory explains how media prioritize certain topics, influencing public perception by highlighting specific issues over others. This process shapes the public agenda by determining which subjects receive attention, affecting the perceived importance of those issues. Framing complements agenda-setting by shaping how information is presented, influencing interpretation rather than just the prominence of topics.
Defining Framing in Media Studies
Framing in media studies refers to the process by which media outlets shape the perception of an issue by highlighting specific aspects while omitting others, thereby influencing audience interpretation. Unlike agenda-setting, which determines what topics are important, framing controls how those topics are presented and understood. This technique involves the selection, emphasis, exclusion, and elaboration of information to guide public opinion and discourse.
Historical Origins of Agenda-Setting and Framing
The historical origins of agenda-setting trace back to the 1968 study by Maxwell McCombs and Donald Shaw, which demonstrated how media influence the public's perception of important issues by highlighting certain topics. Framing theory originated from Erving Goffman's work in the 1970s, emphasizing how media shapes the interpretation and meaning of news through specific presentation and context. Both theories reveal distinct processes: agenda-setting controls what gets attention, while framing controls how issues are understood.
Key Differences Between Agenda-Setting and Framing
Agenda-setting influences the public by determining which issues are considered important, while framing shapes how those issues are interpreted and understood. Agenda-setting operates through media highlighting specific topics, whereas framing involves selecting certain angles, language, and context around those topics. The key difference lies in agenda-setting emphasizing issue salience, and framing focusing on issue interpretation.
How Agenda-Setting Shapes Public Priorities
Agenda-setting influences public priorities by determining which issues receive media attention, thereby signaling their importance to the audience and impacting what topics people consider most urgent. Research shows that increased media coverage of specific subjects leads to greater public concern and policy focus on those issues. This process shapes the collective agenda by filtering information and elevating certain topics over others, guiding societal discourse and decision-making.
The Role of Framing in Influencing Perception
Framing shapes public perception by selecting specific aspects of a topic and emphasizing particular interpretations, which guides audiences in understanding complex issues. Unlike agenda-setting that determines what topics are discussed, framing controls how those topics are presented, affecting attitudes and emotional responses. Media frames, such as conflict or human interest, profoundly impact opinion formation and decision-making processes.
Case Studies: Agenda-Setting vs Framing in News
Research in media studies reveals that agenda-setting influences public perception by prioritizing certain news topics, as seen in the 2008 U.S. presidential election coverage where media emphasis shaped voter focus on the economy and healthcare. Framing, on the other hand, affects interpretation by shaping how issues are presented; for example, coverage of the COVID-19 pandemic often framed health measures as either public safety or economic threats, influencing public attitudes. Case studies illustrate that while agenda-setting determines what issues are discussed, framing shapes the context and emotional undertones, both critically impacting public discourse and policy responses.
Effects on Public Opinion and Policy
Agenda-setting determines which issues capture public and policymaker attention, significantly influencing the prioritization of topics in political discourse and legislative agendas. Framing shapes how these issues are interpreted by emphasizing particular aspects, thereby affecting public attitudes and emotional responses toward policy options. The combined effect of agenda-setting and framing guides public opinion formation and can drive policy decisions by highlighting specific problems and solutions.
Challenges and Criticisms of Each Approach
Agenda-setting faces challenges in distinguishing cause and effect between media emphasis and public opinion shifts, often criticized for oversimplifying complex media influence processes. Framing encounters criticism due to its subjective nature, as interpretations of frames vary among audiences, complicating measurement and empirical validation. Both approaches struggle with isolating media effects from other social and psychological factors, limiting their explanatory power in real-world communication dynamics.
Integrating Agenda-Setting and Framing for Comprehensive Analysis
Integrating agenda-setting and framing offers a comprehensive analysis by combining the identification of salient issues with the interpretation of those issues' meanings, enhancing the understanding of media influence on public opinion. Agenda-setting highlights which topics receive attention, while framing shapes how those topics are perceived, creating a dynamic interplay that drives media effects. This integration allows researchers to capture both the prominence and the contextual nuances of media messages for more effective communication strategies.
Agenda-setting Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com