Community-centric approaches focus on fostering strong relationships, shared values, and active participation among members to create a supportive and thriving environment. These strategies prioritize local needs and empower individuals to contribute meaningfully to collective goals. Explore the rest of the article to discover how a community-centric mindset can transform Your organization or neighborhood.
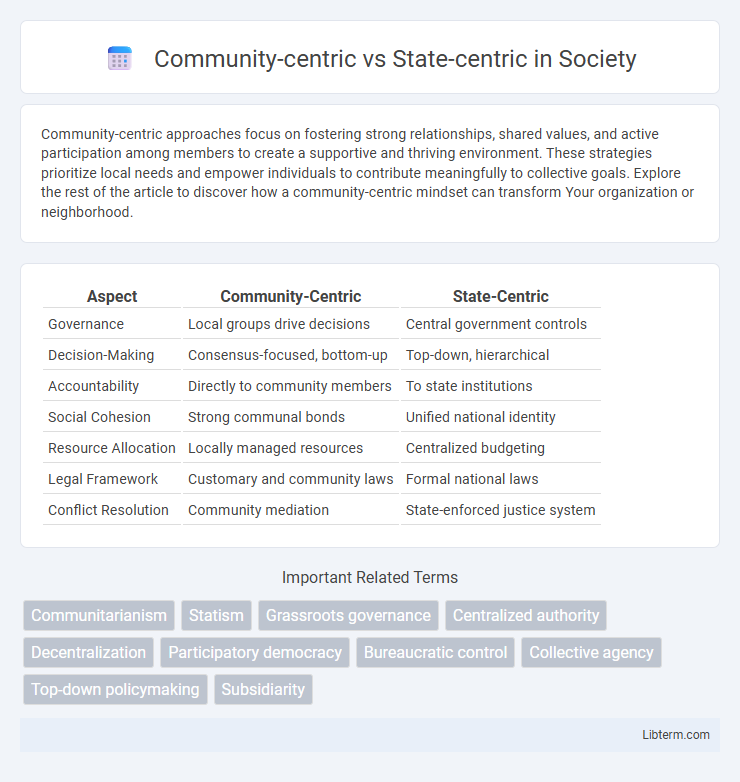
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Community-Centric | State-Centric |
|---|---|---|
| Governance | Local groups drive decisions | Central government controls |
| Decision-Making | Consensus-focused, bottom-up | Top-down, hierarchical |
| Accountability | Directly to community members | To state institutions |
| Social Cohesion | Strong communal bonds | Unified national identity |
| Resource Allocation | Locally managed resources | Centralized budgeting |
| Legal Framework | Customary and community laws | Formal national laws |
| Conflict Resolution | Community mediation | State-enforced justice system |
Understanding Community-Centric Approaches
Community-centric approaches prioritize local knowledge, participation, and empowerment in decision-making processes, fostering sustainable development and social cohesion. These methods emphasize collaborative problem-solving and resource management grounded in the specific cultural and social contexts of the community. Understanding community-centric approaches reveals their effectiveness in building trust, resilience, and long-term impact compared to state-centric models that centralize authority and policy implementation.
Defining State-Centric Systems
State-centric systems prioritize the central government's authority in decision-making, resource allocation, and enforcement of laws, ensuring uniform policies across regions. These systems emphasize centralized institutions, hierarchical governance structures, and the monopoly of legitimate power by the state. Key features include concentrated political control, standardized administrative procedures, and a focus on national unity and security.
Historical Context: Community vs State Focus
Historical context reveals that community-centric models prioritize localized governance, cultural traditions, and collective identity, often rooted in indigenous and tribal societies. In contrast, state-centric systems emphasize centralized authority, legal frameworks, and bureaucratic institutions developed through the evolution of nation-states from feudal and colonial eras. The shift from community to state focus reflects broader socio-political transformations shaped by industrialization, modernization, and the rise of sovereign governance structures.
Core Principles of Community-Centric Models
Community-centric models prioritize local participation, collective decision-making, and empowerment of community members, emphasizing shared responsibility and social cohesion. These models foster trust, enhance cultural relevance, and ensure responsiveness to specific community needs by leveraging indigenous knowledge and local resources. Core principles include inclusivity, transparency, collaboration, and sustainability, which drive more effective and equitable outcomes compared to state-centric approaches.
Fundamental Tenets of State-Centric Governance
State-centric governance emphasizes centralized authority where the state holds primary control over political power, decision-making, and resource allocation. Fundamental tenets include sovereignty, rule of law, and the monopoly on legitimate use of force within a defined territory. This approach prioritizes institutional stability, national security, and uniform policy implementation across diverse populations.
Impact on Social Cohesion and Identity
Community-centric approaches strengthen social cohesion by fostering local participation, shared values, and collective identities rooted in everyday interactions and cultural practices. State-centric models emphasize national identity and uniform policies, often prioritizing centralized control over diverse local identities, which can lead to weaker bonds at the community level. Empirical studies show that community-driven initiatives enhance trust and resilience, whereas state-centric frameworks may struggle to accommodate pluralism and local distinctiveness.
Policy Development: Bottom-up vs Top-down
Community-centric policy development emphasizes bottom-up approaches, where local stakeholders actively participate in decision-making, ensuring policies reflect grassroots needs and priorities. State-centric frameworks prioritize top-down strategies, with centralized authorities designing and implementing policies to maintain uniformity and control at the national level. The effectiveness of either approach depends on governance structures, stakeholder engagement, and the specific policy domains involved.
Case Studies: Global Examples and Outcomes
Community-centric approaches in case studies from Kerala, India, and Porto Alegre, Brazil demonstrate improved local governance, enhanced social inclusion, and equitable resource distribution by enabling grassroots participation. State-centric models, observed in Singapore and China, emphasize centralized control to achieve rapid economic growth and infrastructural development but often face challenges in addressing local needs and participatory governance. Comparative outcomes highlight that community-centric frameworks foster sustainability and social cohesion, whereas state-centric systems excel in efficiency and large-scale project implementation.
Challenges and Criticisms of Each Paradigm
Community-centric approaches face challenges such as limited scalability, potential exclusion of marginalized groups, and difficulty in achieving consensus across diverse stakeholders. State-centric paradigms often struggle with bureaucratic inefficiencies, centralized power leading to authoritarian tendencies, and reduced responsiveness to local needs. Both frameworks are criticized for either underrepresenting local voices or over-consolidating control, highlighting the need for hybrid models that balance grassroots participation with effective governance.
Future Directions: Integrating Community and State Approaches
Future directions in governance emphasize integrating community-centric and state-centric approaches to enhance policy effectiveness and social cohesion. Leveraging community knowledge and state resources fosters participatory decision-making and sustainable development. Innovations in digital platforms and decentralized technologies enable real-time collaboration between local communities and government institutions, driving inclusive growth and resilience.
Community-centric Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com