Multiracialism celebrates the coexistence and blending of diverse racial identities, enriching societies with cultural variety and greater understanding. It challenges rigid racial classifications by promoting inclusivity and acknowledging the complexity of individual heritage. Explore the rest of this article to understand how multiracialism shapes social dynamics and personal identity in today's world.
Table of Comparison
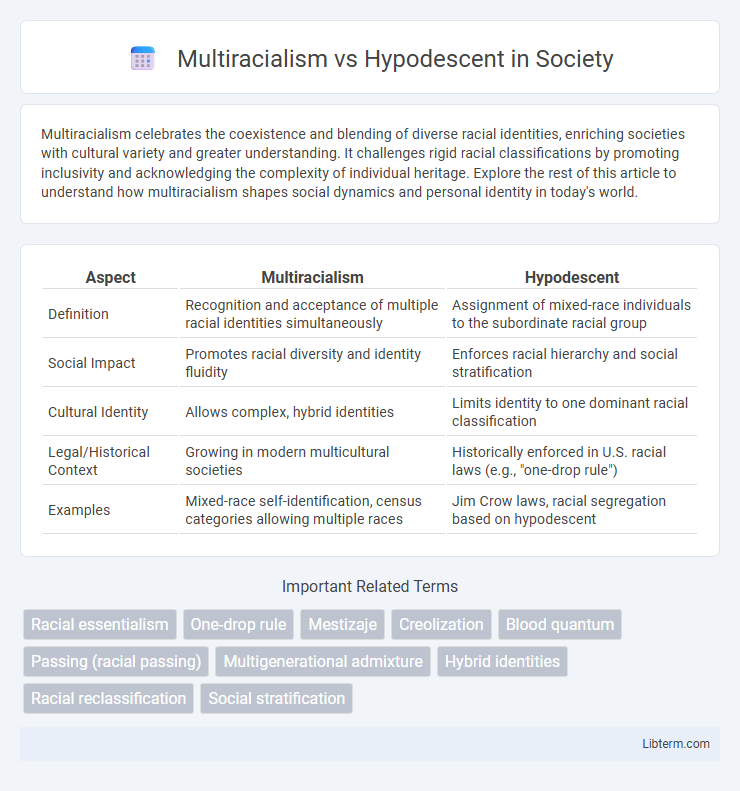
| Aspect | Multiracialism | Hypodescent |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Recognition and acceptance of multiple racial identities simultaneously | Assignment of mixed-race individuals to the subordinate racial group |
| Social Impact | Promotes racial diversity and identity fluidity | Enforces racial hierarchy and social stratification |
| Cultural Identity | Allows complex, hybrid identities | Limits identity to one dominant racial classification |
| Legal/Historical Context | Growing in modern multicultural societies | Historically enforced in U.S. racial laws (e.g., "one-drop rule") |
| Examples | Mixed-race self-identification, census categories allowing multiple races | Jim Crow laws, racial segregation based on hypodescent |
Understanding Multiracialism: Definitions and Origins
Multiracialism refers to the recognition and identification of individuals with ancestry from two or more racial groups, promoting a fluid and inclusive understanding of racial identity. Hypodescent, often known as the "one-drop rule," historically classifies individuals with any trace of minority ancestry into the subordinate racial group, reinforcing rigid racial boundaries. The origins of multiracialism stem from social movements advocating for the acceptance of complex identities, contrasting with hypodescent's roots in legal and social systems designed to maintain racial hierarchies.
The Hypodescent Principle: Historical Context and Meaning
The Hypodescent Principle, historically rooted in U.S. racial classification laws such as the One-Drop Rule, mandated that individuals with any African ancestry be classified as Black, reinforcing racial boundaries and social hierarchy. This principle emerged during slavery and segregation eras to maintain white supremacy by legally and socially assigning mixed-race individuals to the subordinate group. Its legacy persists in social identity and census practices, contrasting with multiracialism, which embraces mixed heritage and challenges rigid racial categories.
Multiracial Identity Formation in Contemporary Society
Multiracial identity formation in contemporary society reflects the growing recognition of individuals with diverse racial backgrounds, challenging traditional categorical boundaries imposed by hypodescent, which historically assigned mixed-race individuals to a single subordinate racial group. Sociological research indicates that multiracial identity development involves complex processes of self-identification, community affiliation, and negotiation of social perceptions in a context of increasing demographic diversity and racial fluidity. This evolving multiracial identity contributes to reshaping societal understandings of race, promoting inclusivity and the deconstruction of rigid racial hierarchies embedded in hypodescent practices.
Hypodescent in Practice: Real-World Impacts
Hypodescent, a social and legal principle assigning individuals of mixed race to the subordinate racial group, perpetuates systemic inequalities by reinforcing racial hierarchies and limiting access to resources. This practice impacts education, employment, and legal outcomes by maintaining racial classifications that influence societal treatment and opportunities. Real-world consequences include reduced social mobility and the endurance of discriminatory policies tied to rigid racial categorizations.
Cultural Representation: Multiracialism vs Hypodescent
Multiracialism promotes the acknowledgment and celebration of multiple racial identities, fostering inclusive cultural representation that reflects diverse heritages. Hypodescent, often known as the "one-drop rule," historically assigns individuals to the subordinate racial group, limiting cultural representation and reinforcing monoracial categorizations. This dichotomy influences media portrayals, societal recognition, and the preservation of multicultural identities within communities.
Legal and Institutional Frameworks Shaping Racial Categorization
Legal and institutional frameworks have historically reinforced hypodescent by assigning individuals with any minority ancestry to subordinate racial categories, thus maintaining rigid boundaries in racial classification. Multiracialism challenges these frameworks by advocating for recognition of mixed heritage identities, promoting legal reforms that allow for self-identification rather than imposed categories. Government policies, such as the U.S. Census's evolving racial categories, reflect ongoing tensions between hypodescent's legacy and emergent multiracial identities within institutional systems.
Personal Narratives: Multiracial Experiences Across Generations
Multiracialism emphasizes the complex identities formed by individuals with diverse racial backgrounds, capturing a broad spectrum of experiences and self-identifications. Hypodescent, often known as the "one-drop rule," historically categorizes multiracial individuals based on the lowest racial status in their lineage, influencing identity formation and social perceptions. Personal narratives reveal how multiracial individuals navigate generational shifts, challenging hypodescent norms while embracing multifaceted heritage and cultural connections.
The Role of Hypodescent in Social and Political Systems
Hypodescent plays a crucial role in reinforcing racial hierarchies by assigning mixed-race individuals to the subordinate group, often impacting their social status and legal rights. This principle influences policies related to citizenship, education, and affirmative action, perpetuating systemic inequalities. Multiracialism challenges hypodescent by promoting recognition of diverse identities, but hypodescent remains embedded in many political and social institutions, shaping identity and power dynamics.
Breaking Stereotypes: Challenging Racial Boundaries
Multiracialism promotes embracing multiple racial identities, challenging traditional racial boundaries and stereotypes by recognizing the complexity of individual heritage. Hypodescent, often called the "one-drop rule," assigns mixed-race individuals to the racial minority group, reinforcing rigid social divisions and limiting identity expression. Breaking stereotypes involves rejecting hypodescent's strict categorization in favor of multiracialism's inclusive understanding, fostering social acceptance and dismantling systemic racial boundaries.
Moving Forward: Advocating for Multiracial Recognition and Inclusion
Multiracial recognition and inclusion promote a more accurate representation of diverse identities beyond the limitations of hypodescent, which historically assigns mixed-race individuals to a single racial category, often marginalizing their complex heritage. Emphasizing multiracialism acknowledges the fluidity of identity, encourages policy changes that reflect self-identification, and supports social systems that validate multiple racial backgrounds simultaneously. Advancing this approach fosters equity, reduces racial stigmatization, and cultivates a society that respects and embraces the intersectionality of all racial experiences.
Multiracialism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com