Culture shapes the way communities express their identities, values, and traditions through language, art, and customs. Understanding cultural diversity enhances your ability to connect with people from different backgrounds and appreciate unique perspectives. Dive deeper into this article to explore the rich complexities of culture and its impact on society.
Table of Comparison
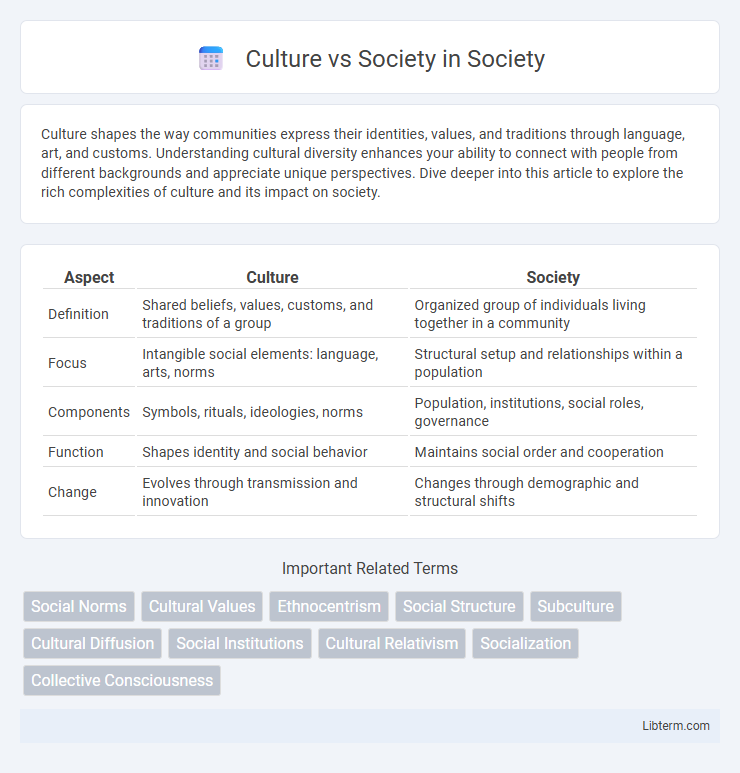
| Aspect | Culture | Society |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Shared beliefs, values, customs, and traditions of a group | Organized group of individuals living together in a community |
| Focus | Intangible social elements: language, arts, norms | Structural setup and relationships within a population |
| Components | Symbols, rituals, ideologies, norms | Population, institutions, social roles, governance |
| Function | Shapes identity and social behavior | Maintains social order and cooperation |
| Change | Evolves through transmission and innovation | Changes through demographic and structural shifts |
Defining Culture and Society
Culture encompasses the beliefs, customs, arts, and social behaviors of a particular group, representing the shared symbolic systems that shape identity and worldview. Society refers to an organized group of individuals who share a defined territory and interact through established institutions, creating a structured community. While culture forms the intangible framework of meanings and practices, society provides the physical and social environment where these cultural elements are expressed and maintained.
Key Differences Between Culture and Society
Culture encompasses the shared beliefs, values, customs, arts, and social behaviors of a particular group, while society refers to an organized group of individuals who live together within a defined territory and interact under a shared legal and political structure. Key differences include that culture is intangible, representing the learned behaviors and symbolic expressions of a group, whereas society is tangible, consisting of individuals and institutions that make up the social system. Culture shapes social norms and identity, whereas society provides the framework for social relationships and collective governance.
Historical Evolution of Culture and Society
Culture and society have evolved through complex historical processes where early human groups formed social structures to organize communal life and shared cultural practices. The development of agriculture, technological innovations, and the rise of civilizations accelerated cultural diversification and social stratification, shaping institutions, norms, and belief systems. Over centuries, this interplay between cultural values and societal organization influenced political systems, economic frameworks, and collective identities across regions.
Components of Culture: Language, Beliefs, and Values
Language, beliefs, and values form the core components of culture that shape human interactions and societal norms. Language serves as a critical communication tool, enabling the transmission of cultural knowledge and social customs across generations. Beliefs and values establish a framework for interpreting experiences, guiding behavior, and reinforcing the collective identity within a society.
Social Structures: Roles and Institutions
Social structures in society organize individuals into distinct roles and institutions that regulate behavior and maintain order. Culture shapes these roles and institutions by providing the shared values, norms, and symbols that guide social interactions and define group identity. Roles such as family members, professionals, and community leaders operate within institutional frameworks like education, government, and religion, reflecting the underlying cultural meaning and societal expectations.
How Culture Shapes Identity
Culture profoundly influences identity by providing shared values, beliefs, and customs that shape individuals' perceptions and behaviors. It forms the framework within which people interpret their experiences, fostering a sense of belonging and continuity across generations. Cultural identity affects language, traditions, and social norms, playing a crucial role in personal and collective self-understanding.
The Influence of Society on Behavior
Society shapes individual behavior through established norms, laws, and social expectations, influencing how people interact and make decisions. Social institutions such as family, education, and media play a critical role in reinforcing acceptable behaviors and shaping collective values. The pressure to conform within a society often drives individuals to adopt behaviors that align with cultural practices and societal standards.
Interaction Between Culture and Society
Culture shapes societal norms, beliefs, and behaviors, influencing how individuals and groups interact within a community. Society provides the structural framework where cultural values are expressed, transmitted, and modified through social institutions like family, education, and religion. Continuous interaction between culture and society drives social change, adapts traditions, and fosters collective identity.
Cultural Change vs Social Change
Cultural change refers to the transformation of beliefs, values, norms, and symbols within a society, often driven by innovation, diffusion, or cultural contact. Social change involves shifts in the organization, structure, and institutions of society, impacting social roles, relationships, and power dynamics. While cultural change influences social attitudes and behaviors, social change modifies the frameworks within which culture operates, making both processes interconnected yet distinct in sociological analysis.
Impact of Globalization on Culture and Society
Globalization accelerates cultural exchange, leading to the blending and sometimes the erosion of indigenous traditions and languages within societies. It promotes the spread of global consumer culture, influencing social norms, values, and lifestyle choices across diverse populations. The resulting cultural homogenization challenges societal identities while fostering increased interconnectedness and economic integration worldwide.
Culture Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com