Physical space plays a crucial role in shaping our environment, influencing productivity, comfort, and overall well-being. Designing functional and aesthetically pleasing spaces can enhance how you interact with your surroundings and improve daily experiences. Explore the rest of the article to discover practical tips and insights on optimizing your physical space effectively.
Table of Comparison
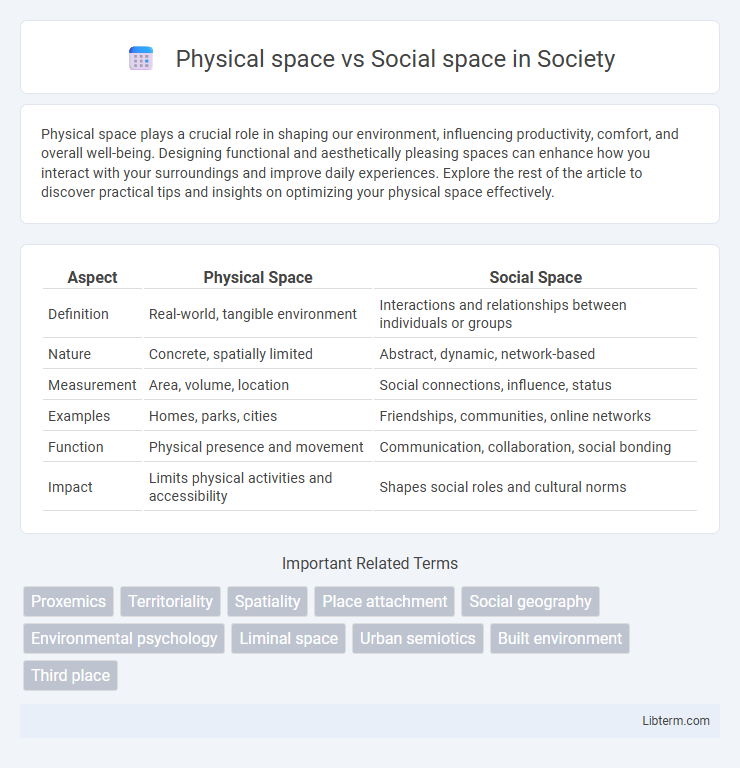
| Aspect | Physical Space | Social Space |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Real-world, tangible environment | Interactions and relationships between individuals or groups |
| Nature | Concrete, spatially limited | Abstract, dynamic, network-based |
| Measurement | Area, volume, location | Social connections, influence, status |
| Examples | Homes, parks, cities | Friendships, communities, online networks |
| Function | Physical presence and movement | Communication, collaboration, social bonding |
| Impact | Limits physical activities and accessibility | Shapes social roles and cultural norms |
Defining Physical Space and Social Space
Physical space refers to tangible, measurable environments characterized by geographical boundaries, structures, and objects that occupy specific locations. Social space encompasses the dynamic relationships, interactions, and cultural meanings that individuals and groups create within or across these physical environments. While physical space provides the concrete setting, social space is shaped by human behavior, communication, and societal norms influencing how individuals experience and organize their surroundings.
Historical Evolution of Physical and Social Spaces
Physical space has evolved from rudimentary shelters and open landscapes to complex urban environments shaped by technological advances and architectural innovation. Social space, historically intertwined with physical space, reflects changing human interactions, community structures, and cultural norms influenced by economic and political developments. The transition from agrarian societies to industrial and post-industrial eras dramatically redefined both physical layouts and social dynamics, emphasizing the interdependence of spatial design and social organization.
Key Differences Between Physical and Social Spaces
Physical space refers to tangible, measurable environments characterized by geographic boundaries, structures, and material elements, while social space encompasses the relational and symbolic interactions between individuals or groups within or across those physical settings. Key differences include the observation that physical space is static and quantified using dimensions like distance and area, whereas social space is dynamic, shaped by social norms, power relations, and cultural meanings. Furthermore, physical spaces can be directly mapped and navigated, but social spaces require analysis of social networks, communication patterns, and collective behaviors to understand their influence on human interactions.
The Role of Technology in Shaping Spaces
Technology transforms physical spaces into dynamic social environments by enabling virtual interactions, blurring the boundaries between location and connectivity. Digital platforms and smart devices foster social spaces that transcend geographic limitations, creating communities based on shared interests rather than proximity. Augmented reality and IoT technologies further integrate physical and social dimensions, enhancing user experiences and redefining how spaces are perceived and utilized.
Interactions and Behaviors in Each Space
Physical space influences interactions by providing tangible settings that shape behaviors through proximity, sensory experiences, and environmental cues, fostering direct communication and immediate feedback. Social space, defined by relational and cultural contexts, governs behaviors via shared norms, symbolic meanings, and social roles, guiding interactions beyond physical presence. Understanding the distinctions between these spaces highlights how physical arrangements affect face-to-face dynamics, while social constructs drive patterns of behavior and connection in virtual or abstract environments.
Impact of Physical Design on Social Dynamics
Physical space layout directly influences social dynamics by shaping interaction patterns and movement flow within environments. Open floor plans and communal areas encourage collaboration and spontaneous communication, enhancing social cohesion. Conversely, segmented or cluttered physical designs can inhibit engagement, leading to reduced social connectivity and isolated behaviors.
Accessibility and Inclusion in Both Spaces
Physical space accessibility relies on universal design principles such as ramps, tactile paving, and braille signage to ensure inclusivity for individuals with mobility, visual, or sensory impairments. Social space accessibility emphasizes equitable participation, fostering inclusive environments through policies, communication norms, and cultural sensitivity that address diverse identities and needs. Both spaces require intentional adaptations to remove barriers and promote the full engagement of people regardless of physical ability or social background.
Challenges in Integrating Physical and Social Spaces
Integrating physical and social spaces presents challenges such as aligning architectural design with social interaction patterns and addressing diverse user needs within shared environments. Spatial constraints often limit the flexibility required for dynamic social activities, while technological solutions may struggle to capture the nuances of human behavior. Balancing privacy with community engagement remains a critical issue in creating cohesive environments that support both physical presence and social connectivity.
Future Trends: Blending Physical and Social Environments
Advancements in augmented reality and smart city technologies are driving the fusion of physical and social spaces, creating immersive environments where digital interactions seamlessly integrate with real-world settings. Future urban designs are prioritizing interactive public spaces that harness IoT sensors and AI to enhance social connectivity and personalized experiences. This convergence enables dynamic community engagement while optimizing spatial utility and fostering inclusive social ecosystems.
Conclusion: Striking a Balance Between Spaces
Striking a balance between physical space and social space is essential for fostering productivity and well-being, as physical environments influence social interactions and vice versa. Integrating flexible layouts with communal areas enhances collaboration while respecting personal boundaries, promoting both focus and connectivity. Prioritizing adaptive design creates harmonious spaces that support diverse needs and evolving social dynamics.
Physical space Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com