Direct democracy empowers citizens to participate actively in decision-making processes by voting on laws and policies without intermediaries. This system fosters transparency and accountability, ensuring that Your voice directly influences governmental actions. Explore the rest of the article to understand how direct democracy shapes modern governance and affects your community.
Table of Comparison
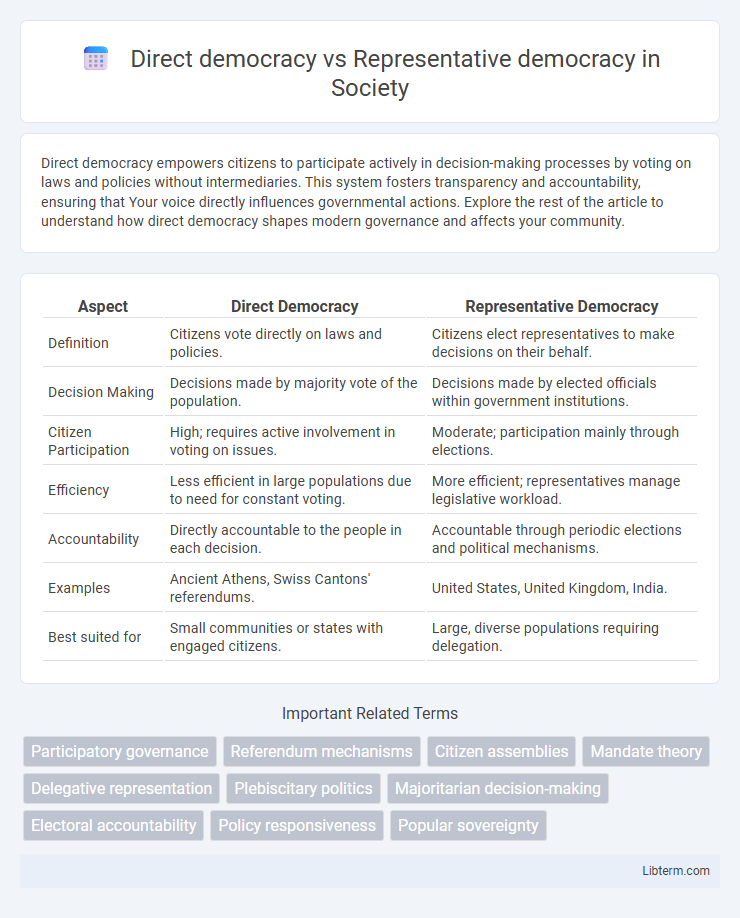
| Aspect | Direct Democracy | Representative Democracy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Citizens vote directly on laws and policies. | Citizens elect representatives to make decisions on their behalf. |
| Decision Making | Decisions made by majority vote of the population. | Decisions made by elected officials within government institutions. |
| Citizen Participation | High; requires active involvement in voting on issues. | Moderate; participation mainly through elections. |
| Efficiency | Less efficient in large populations due to need for constant voting. | More efficient; representatives manage legislative workload. |
| Accountability | Directly accountable to the people in each decision. | Accountable through periodic elections and political mechanisms. |
| Examples | Ancient Athens, Swiss Cantons' referendums. | United States, United Kingdom, India. |
| Best suited for | Small communities or states with engaged citizens. | Large, diverse populations requiring delegation. |
Introduction to Democracy: Definitions and Types
Direct democracy allows citizens to participate actively in decision-making by voting on laws and policies without intermediaries, ensuring maximum public involvement. Representative democracy delegates decision-making authority to elected officials who act on behalf of the people, balancing efficiency and citizen representation. Both systems embody core democratic principles but differ in methods of public participation and governance structure.
What is Direct Democracy?
Direct democracy is a political system where citizens participate firsthand in decision-making processes, voting directly on laws and policies rather than electing representatives to decide on their behalf. It emphasizes citizen involvement through referendums, initiatives, and recalls, enabling immediate influence over government actions. This form of democracy contrasts with representative democracy, where elected officials deliberate and make decisions, highlighting direct democracy's focus on direct public control and accountability.
Understanding Representative Democracy
Representative democracy enables citizens to elect officials who make policy decisions on their behalf, ensuring efficient governance in large populations. It balances popular sovereignty with practical administration by allowing elected representatives to deliberate, create laws, and oversee government functions. This system fosters accountability through regular elections and encourages political stability by providing a structured decision-making process.
Key Differences Between Direct and Representative Democracy
Direct democracy allows citizens to vote on laws and policies directly, ensuring immediate participation in decision-making processes. Representative democracy entrusts elected officials to make legislative decisions on behalf of the populace, promoting efficiency in managing complex governmental functions. Key differences include the scale of public involvement, with direct democracy demanding active voter engagement and representative democracy relying on periodic elections to delegate authority.
Advantages of Direct Democracy
Direct democracy allows citizens to participate actively in decision-making, ensuring policies directly reflect the will of the people and enhancing political accountability. It reduces the risk of corruption and elite manipulation by minimizing intermediary representatives. Voter engagement and civic responsibility increase as individuals have a direct role in shaping laws and public policies.
Advantages of Representative Democracy
Representative democracy offers more efficient decision-making compared to direct democracy by delegating governance to elected officials who possess expertise and accountability. It enables broader participation through elected representatives, ensuring diverse interests are balanced and minority rights protected within a structured political framework. This system reduces the logistical challenges of frequent voting and allows for more informed policy development in complex societies.
Challenges Faced by Direct Democracy
Direct democracy faces significant challenges such as scalability issues in large, populous nations where direct citizen participation becomes logistically complex and inefficient. The risk of misinformation and manipulation in public decision-making processes can undermine informed voting and lead to populist outcomes. Furthermore, the time and resource demands on citizens to engage continuously in policy-making can result in low participation rates and governance fatigue.
Challenges Faced by Representative Democracy
Representative democracy faces challenges including voter disengagement, where citizens feel disconnected from elected officials who make decisions on their behalf. The system often struggles with issues like political polarization, lobbying influence, and slow legislative processes that can hinder responsive governance. Furthermore, the risk of misrepresentation arises when elected representatives prioritize party agendas or special interests over the electorate's diverse needs.
Real-World Examples of Each System
Switzerland exemplifies direct democracy through regular referendums allowing citizens to directly vote on policy issues. The United States represents representative democracy, where elected officials make decisions on behalf of voters in local, state, and federal legislatures. Both systems demonstrate distinct approaches to citizen participation and governance in modern political frameworks.
Which System is Better for Modern Societies?
Direct democracy offers citizens direct involvement in decision-making through referendums and initiatives, promoting transparency and responsiveness in political processes. Representative democracy relies on elected officials to make policy decisions, enabling efficient governance and expertise in managing complex modern issues. Modern societies often benefit from a hybrid approach that balances direct citizen participation with the practicality and scalability of representative institutions.
Direct democracy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com