Egalitarianism promotes the belief in equal rights, opportunities, and treatment for all individuals, regardless of their background or status. It challenges social hierarchies and advocates for fairness in economic, political, and social spheres. Discover how embracing egalitarian principles can transform your perspective on justice and equality throughout this article.
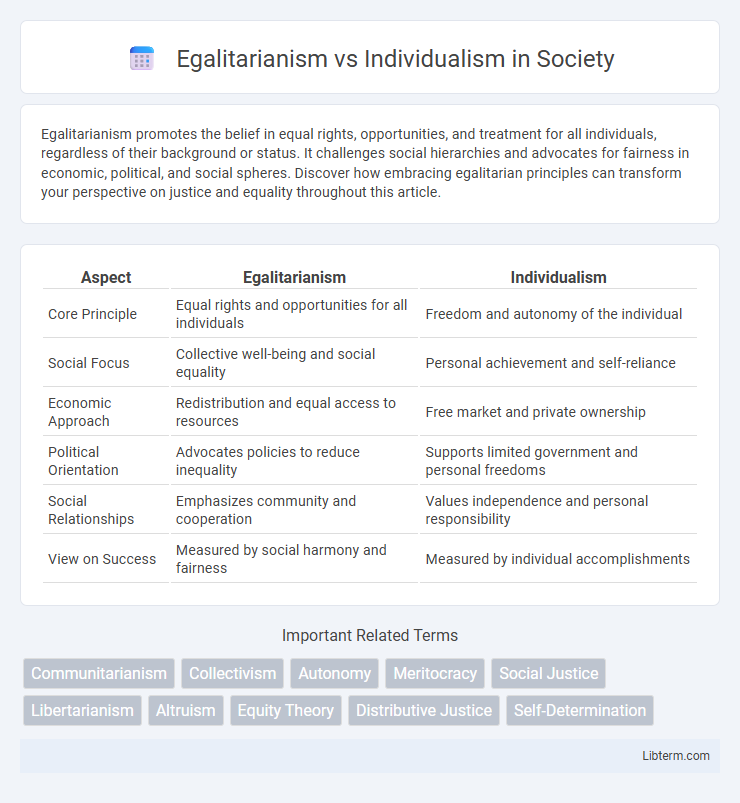
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Egalitarianism | Individualism |
|---|---|---|
| Core Principle | Equal rights and opportunities for all individuals | Freedom and autonomy of the individual |
| Social Focus | Collective well-being and social equality | Personal achievement and self-reliance |
| Economic Approach | Redistribution and equal access to resources | Free market and private ownership |
| Political Orientation | Advocates policies to reduce inequality | Supports limited government and personal freedoms |
| Social Relationships | Emphasizes community and cooperation | Values independence and personal responsibility |
| View on Success | Measured by social harmony and fairness | Measured by individual accomplishments |
Understanding Egalitarianism: Core Principles
Egalitarianism emphasizes equal rights, opportunities, and treatment for all individuals, advocating for the reduction of social, economic, and political inequalities. It prioritizes collective well-being and social justice, often supporting redistributive policies to achieve fairness. Key principles include equity, inclusion, and the belief that no person or group should have undue privileges over others.
Defining Individualism: Key Concepts
Individualism emphasizes personal autonomy, self-reliance, and the primacy of individual rights over collective goals. Core concepts include self-expression, freedom of choice, and the pursuit of personal interests without undue interference. This philosophy values the unique qualities and decisions of each person as fundamental to societal progress.
Historical Roots of Egalitarianism
Egalitarianism traces its historical roots to ancient philosophies such as those of the Greek Stoics and early Christian teachings that emphasized the intrinsic equality of all individuals. The Enlightenment period further shaped egalitarian thought by promoting ideas of equal rights and social justice, challenging hierarchical structures. Key movements like the French and American revolutions institutionalized principles of equality in political frameworks, reflecting the deep historical evolution of egalitarian ideals.
The Evolution of Individualism in Society
The evolution of individualism in society traces its roots to the Renaissance and Enlightenment periods, emphasizing personal autonomy and self-expression as core values. This shift challenged traditional egalitarian norms by prioritizing individual rights, freedom, and responsibility over collective equality. Contemporary individualism drives innovation and diversity but also raises debates about social cohesion and economic disparities.
Egalitarianism vs Individualism: Philosophical Differences
Egalitarianism emphasizes equality in social, political, and economic rights, advocating for equal opportunities and redistribution of resources to reduce disparities. Individualism prioritizes personal autonomy, self-reliance, and individual rights, asserting that individuals should be free to pursue their own interests without excessive external interference. Philosophically, egalitarianism challenges hierarchical structures, promoting collective well-being, while individualism underscores personal freedom and responsibility as foundational ethical principles.
Social Impacts: Equality versus Autonomy
Egalitarianism promotes social equality by advocating for equal access to resources, opportunities, and rights, reducing disparities and fostering social cohesion. Individualism emphasizes personal autonomy and self-reliance, encouraging innovation and personal freedom but often leading to social stratification and reduced collective responsibility. Balancing these concepts impacts social policies, shaping whether societies prioritize collective welfare or individual liberties.
Economic Perspectives: Wealth Distribution and Opportunity
Egalitarianism promotes equal wealth distribution through progressive taxation and robust social welfare systems to reduce economic disparities. Individualism emphasizes the importance of personal responsibility and free-market mechanisms, advocating minimal government intervention to allow wealth accumulation based on merit and innovation. Economic opportunity under egalitarianism prioritizes universal access to education and healthcare, while individualism focuses on incentivizing entrepreneurship and competition for wealth creation.
Political Systems: Collective Governance vs Personal Freedom
Egalitarianism emphasizes collective governance by promoting equal distribution of power and resources to ensure social justice and reduce disparities in political influence. Individualism prioritizes personal freedom, advocating for minimal government intervention to protect individual rights and foster self-reliance. Political systems grounded in egalitarianism often support robust social welfare programs and participatory democracy, whereas individualistic frameworks favor free-market capitalism and limited state control.
Challenges and Critiques of Both Ideologies
Challenges of egalitarianism include difficulties in balancing equality with individual freedom, often leading to debates over government intervention and resource distribution. Individualism faces critiques related to social fragmentation and neglect of collective responsibility, sometimes resulting in increased inequality and reduced social cohesion. Both ideologies struggle to reconcile personal rights with broader societal goals, presenting ongoing tensions in political and ethical discourse.
Finding Balance: Harmonizing Equality and Individual Rights
Egalitarianism emphasizes equal rights and opportunities for all individuals, promoting social justice and fairness by reducing disparities. Individualism values personal freedom, autonomy, and self-expression, advocating for the protection of individual rights even when they conflict with collective goals. Finding balance requires policies that ensure equal access to resources while respecting personal liberties, fostering a society where social equity coexists with individual empowerment.
Egalitarianism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com