Social segregation significantly impacts community cohesion by creating divisions based on race, class, or ethnicity, leading to unequal access to resources and opportunities. This separation often results in disparities in education, employment, and healthcare, reinforcing cycles of poverty and social exclusion. Explore the rest of this article to understand how social segregation affects your environment and what measures can address these challenges.
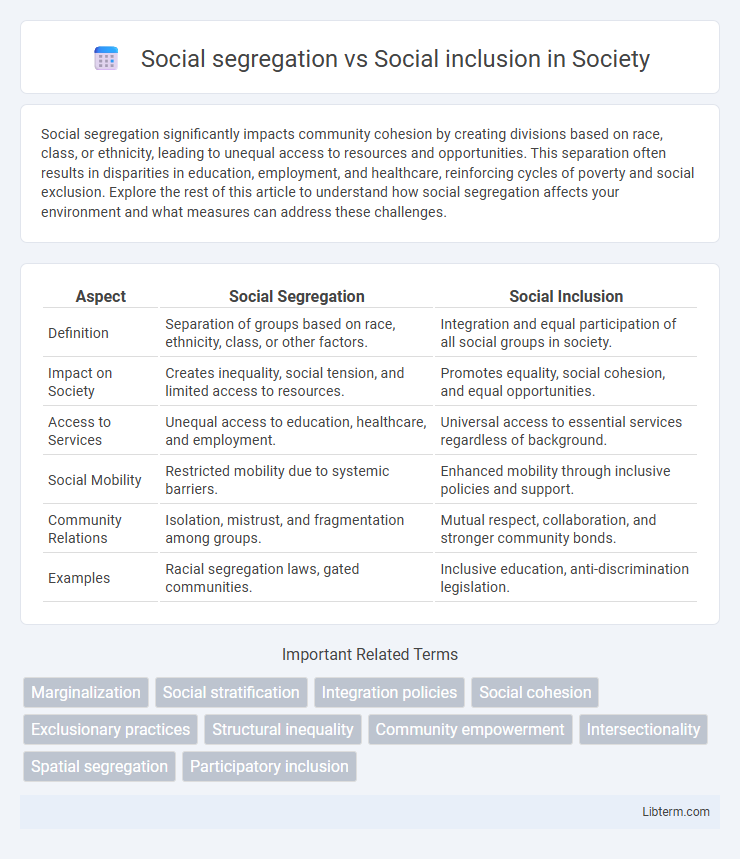
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Social Segregation | Social Inclusion |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Separation of groups based on race, ethnicity, class, or other factors. | Integration and equal participation of all social groups in society. |
| Impact on Society | Creates inequality, social tension, and limited access to resources. | Promotes equality, social cohesion, and equal opportunities. |
| Access to Services | Unequal access to education, healthcare, and employment. | Universal access to essential services regardless of background. |
| Social Mobility | Restricted mobility due to systemic barriers. | Enhanced mobility through inclusive policies and support. |
| Community Relations | Isolation, mistrust, and fragmentation among groups. | Mutual respect, collaboration, and stronger community bonds. |
| Examples | Racial segregation laws, gated communities. | Inclusive education, anti-discrimination legislation. |
Understanding Social Segregation
Social segregation refers to the systematic separation of groups in society based on characteristics such as race, ethnicity, socioeconomic status, or religion, leading to unequal access to resources, opportunities, and social networks. This segregation manifests in residential patterns, education, employment, and social interactions, reinforcing disparities and limiting social mobility. Understanding social segregation involves analyzing structural factors like discriminatory policies, economic inequalities, and cultural barriers that perpetuate division and hinder social cohesion.
Defining Social Inclusion
Social inclusion refers to the process of improving the terms of participation in society for all individuals, especially marginalized groups, by enhancing opportunities, access to resources, and respect for rights. It aims to dismantle barriers related to race, gender, disability, and socioeconomic status, fostering equal involvement in economic, social, and political life. Unlike social segregation, which separates and isolates groups, social inclusion promotes cohesion and equitable relationships within diverse communities.
Historical Context of Social Segregation
Historical social segregation emerged from institutionalized systems such as apartheid in South Africa and Jim Crow laws in the United States, enforcing racial divides in housing, education, and public facilities. These systemic barriers created long-lasting socio-economic disparities by limiting access to resources and opportunities for marginalized groups. Social inclusion efforts today aim to dismantle these historical inequalities by promoting equitable access and fostering diverse, integrated communities.
Causes and Drivers of Social Segregation
Social segregation stems primarily from economic disparities, discriminatory policies, and cultural divisions that limit interaction between different social groups. Factors such as residential segregation, unequal access to education, and employment discrimination reinforce social exclusion and marginalization. Systemic inequality and social stratification act as critical drivers perpetuating social segregation, hindering social cohesion and inclusion.
Impact of Social Segregation on Communities
Social segregation fragments communities, limiting access to resources, education, and employment opportunities for marginalized groups, which perpetuates inequality and poverty cycles. This division fosters social tensions and reduces social cohesion, weakening community resilience and collective problem-solving capabilities. Persistent social segregation undermines economic growth by restricting diversity and innovation within neighborhoods and workplaces.
Benefits of Social Inclusion
Social inclusion promotes equal access to opportunities, resources, and rights, leading to improved social cohesion and reduced disparities. It fosters a sense of belonging and participation among marginalized groups, enhancing mental health and community well-being. Economies benefit from diverse contributions and innovation driven by inclusive practices in workplaces and education systems.
Barriers to Achieving Social Inclusion
Barriers to achieving social inclusion include systemic inequalities, such as discriminatory policies and unequal access to education, healthcare, and employment opportunities, which perpetuate social segregation. Cultural prejudices and stereotypes further hinder marginalized groups from fully participating in society, limiting social cohesion and economic mobility. Overcoming these obstacles requires targeted policy interventions, community engagement, and inclusive practices that promote equity and respect for diversity.
Strategies for Promoting Social Inclusion
Strategies for promoting social inclusion involve creating equitable access to education, employment, and healthcare, which help bridge gaps caused by social segregation. Community engagement initiatives and inclusive policy-making foster environments where marginalized groups can participate fully in social, economic, and political activities. Implementing diversity training programs and anti-discrimination laws further supports the dismantling of social barriers and encourages cohesive, integrated societies.
Case Studies: Social Segregation vs Social Inclusion
Case studies on social segregation reveal patterns of exclusion based on race, class, or ethnicity that limit access to resources and opportunities, often resulting in marginalized communities facing poverty and limited education. In contrast, social inclusion initiatives documented in urban areas and schools demonstrate the effectiveness of policies promoting diversity, equitable access, and community participation, which enhance social cohesion and reduce disparities. Evidence from programs such as inclusive housing projects and integrative educational curricula highlight measurable improvements in social mobility and cross-cultural understanding.
Future Directions for Inclusive Societies
Future directions for inclusive societies emphasize leveraging technology and policy reforms to bridge gaps caused by social segregation, promoting equal access to education, employment, and healthcare. Embracing diversity through community-driven initiatives and inclusive urban planning aims to dismantle systemic barriers and foster social cohesion. Advancements in data analytics and AI support targeted interventions that address marginalization and enhance participatory governance for sustained social inclusion.
Social segregation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com