Localization adapts products and content to meet the cultural, linguistic, and regional preferences of your target audience, ensuring relevance and engagement. Effective localization enhances user experience and drives market expansion by respecting local customs and language nuances. Discover how to optimize your localization strategy and boost your global reach in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
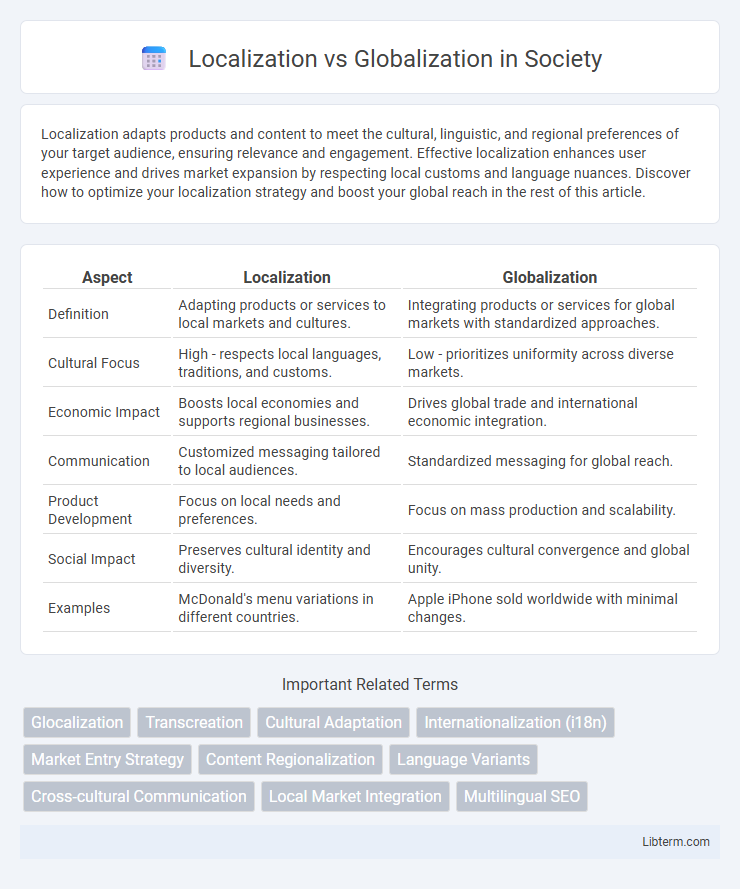
| Aspect | Localization | Globalization |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Adapting products or services to local markets and cultures. | Integrating products or services for global markets with standardized approaches. |
| Cultural Focus | High - respects local languages, traditions, and customs. | Low - prioritizes uniformity across diverse markets. |
| Economic Impact | Boosts local economies and supports regional businesses. | Drives global trade and international economic integration. |
| Communication | Customized messaging tailored to local audiences. | Standardized messaging for global reach. |
| Product Development | Focus on local needs and preferences. | Focus on mass production and scalability. |
| Social Impact | Preserves cultural identity and diversity. | Encourages cultural convergence and global unity. |
| Examples | McDonald's menu variations in different countries. | Apple iPhone sold worldwide with minimal changes. |
Defining Localization and Globalization
Localization involves customizing products or content to meet the language, cultural, and regulatory requirements of a specific target market, ensuring relevance and user engagement within that locale. Globalization is the comprehensive process of designing and developing products or services so they can be easily adapted for various international markets without the need for extensive reengineering. Effective globalization strategies facilitate seamless localization by enabling scalable adaptations that respect diverse cultural nuances and compliance standards.
Key Differences Between Localization and Globalization
Localization tailors products or content to meet the linguistic, cultural, and regulatory requirements of a specific target market, ensuring relevance and user satisfaction at a local level. Globalization involves designing and developing products or services that function universally across multiple regions, enabling efficient international expansion by integrating diverse market needs from the outset. The key difference lies in localization's market-specific customization versus globalization's broad, scalable approach to reach a worldwide audience.
Benefits of Localization for Businesses
Localization enhances customer engagement by tailoring products and marketing strategies to specific cultural preferences, improving brand loyalty and market relevance. It increases penetration in diverse markets through language adaptation, legal compliance, and culturally appropriate content, leading to higher conversion rates. Businesses gain competitive advantage and boost revenue by overcoming regional barriers and delivering personalized user experiences.
Advantages of Globalization in Today’s Market
Globalization enhances market access by enabling businesses to reach a broader, international customer base, increasing sales potential. It fosters innovation through exposure to diverse cultures, ideas, and technologies, driving competitive advantage and product development. Economies of scale are achievable as companies optimize production and distribution across global supply chains, reducing costs and improving efficiency.
Challenges of Implementing Localization Strategies
Implementing localization strategies presents challenges such as managing diverse cultural preferences, ensuring accurate translation and adaptation of content, and maintaining brand consistency across different markets. Companies often struggle with the complexity of local regulations, varying consumer behaviors, and technological infrastructure that can impede seamless localization efforts. Effective localization requires significant investment in local expertise, continuous market research, and scalable processes to address these multifaceted challenges efficiently.
Obstacles Faced During Global Expansion
Localization requires adapting products and marketing to specific cultural, linguistic, and legal contexts, which can significantly increase costs and complexity during global expansion. Globalization efforts face challenges such as regulatory compliance across diverse markets, differing consumer behaviors, and logistical hurdles including supply chain management and local partnerships. Overcoming language barriers, inconsistent infrastructure, and varying technological adoption rates are also critical obstacles that must be managed to achieve successful international growth.
Impact on Consumer Experience
Localization enhances consumer experience by tailoring products, services, and content to meet the cultural, linguistic, and regional preferences of specific markets, resulting in higher customer satisfaction and engagement. Globalization offers a consistent brand experience across diverse markets, enabling scalability and broader reach but may overlook unique local nuances that affect consumer perceptions. Balancing localization and globalization strategies ensures businesses deliver both personalized experiences and cohesive brand messaging, driving loyalty and market penetration effectively.
Case Studies: Localization vs Globalization Success Stories
Successful localization case studies highlight companies like Netflix, which tailored content to regional languages and preferences, resulting in significant subscriber growth in markets like India and Korea. In contrast, globalization success stories such as Coca-Cola demonstrate the power of maintaining a consistent global brand image while adapting marketing campaigns to local cultures, driving widespread brand loyalty. These examples emphasize the strategic balance between global brand consistency and local market customization for optimal international expansion.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Brand
Choosing between localization and globalization depends on your brand's target market, goals, and resources. Localization tailors products and marketing to specific cultural preferences, increasing relevance and engagement in distinct regions. Globalization emphasizes a unified brand message and consistent experience worldwide, maximizing efficiency and brand recognition across diverse markets.
Future Trends in Localization and Globalization
Future trends in localization emphasize the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning to enhance real-time language translation and cultural adaptation, enabling personalized user experiences across diverse markets. Globalization strategies are increasingly focusing on sustainable practices and ethical considerations to meet the demands of socially conscious consumers and international regulations. The convergence of digital transformation and localization technologies is driving seamless global customer engagement, fostering deeper market penetration and competitive advantage.
Localization Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com