Social influence shapes your behaviors, attitudes, and decisions through the impact of others in your environment. Understanding the mechanisms behind conformity, compliance, and persuasion can empower you to navigate complex social dynamics effectively. Discover how these principles affect daily interactions and transform relationships by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
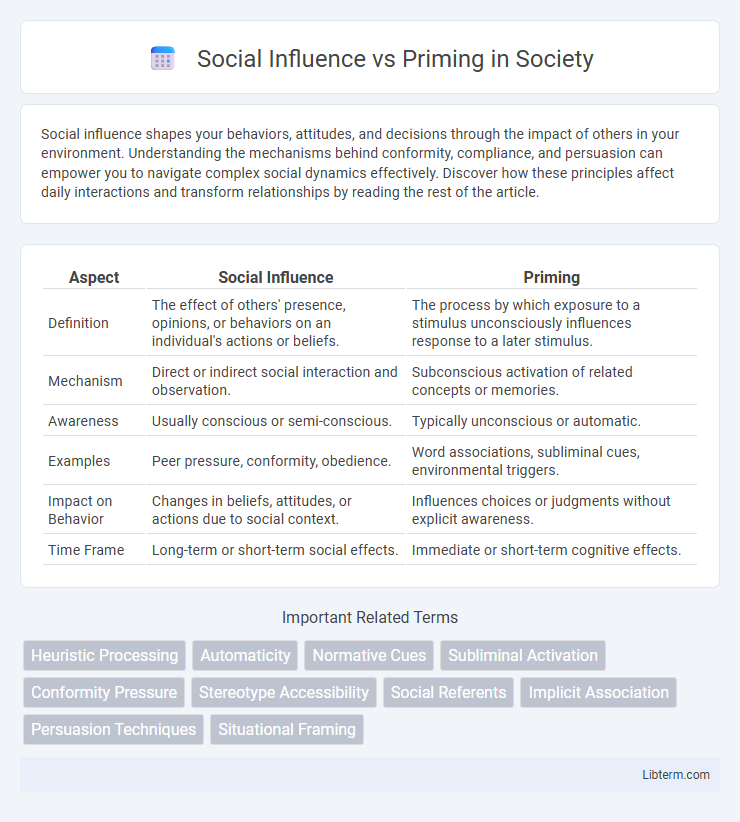
| Aspect | Social Influence | Priming |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The effect of others' presence, opinions, or behaviors on an individual's actions or beliefs. | The process by which exposure to a stimulus unconsciously influences response to a later stimulus. |
| Mechanism | Direct or indirect social interaction and observation. | Subconscious activation of related concepts or memories. |
| Awareness | Usually conscious or semi-conscious. | Typically unconscious or automatic. |
| Examples | Peer pressure, conformity, obedience. | Word associations, subliminal cues, environmental triggers. |
| Impact on Behavior | Changes in beliefs, attitudes, or actions due to social context. | Influences choices or judgments without explicit awareness. |
| Time Frame | Long-term or short-term social effects. | Immediate or short-term cognitive effects. |
Understanding Social Influence: Core Concepts
Social influence encompasses techniques like conformity, compliance, and obedience, which shape individual behavior based on group dynamics and authority. Key concepts include normative influence, where people conform to gain social approval, and informational influence, where individuals accept information from others as evidence of reality. Understanding these mechanisms reveals how social contexts and perceived social pressures drive behavior modification.
What Is Priming? Definitions and Mechanisms
Priming is a psychological mechanism where exposure to a stimulus influences responses to subsequent stimuli, often operating below conscious awareness. It functions by activating specific neural pathways, which can alter perception, memory, and behavior based on prior exposure. This process contrasts with social influence, which involves direct interactions and external pressures shaping attitudes and actions.
Social Influence vs Priming: Key Differences
Social influence involves changes in behavior or attitudes resulting from real or perceived social pressure, while priming refers to the activation of specific concepts or associations in memory, influencing responses without conscious awareness. Social influence operates through direct interaction or communication within groups, whereas priming is an internal cognitive process triggered by exposure to stimuli. Key differences include the source of effect--external social context for social influence versus internal mental activation for priming--and the level of conscious awareness involved in modifying behavior or judgments.
Types of Social Influence in Everyday Life
Social influence manifests in everyday life through conformity, compliance, and obedience, shaping behavior in diverse social contexts. Conformity involves adjusting actions to align with group norms, while compliance refers to yielding to explicit requests, and obedience entails following authoritative commands. These types of social influence profoundly impact decision-making, group dynamics, and individual behavior in settings ranging from workplaces to social gatherings.
The Science Behind Priming Effects
Priming effects are grounded in cognitive psychology, where exposure to a stimulus influences responses to subsequent related stimuli without conscious awareness. Research shows neural pathways activated by initial primes facilitate faster recognition and behavioral responses, demonstrating associative memory networks at work. Experiments using lexical decision tasks and semantic priming reveal measurable reaction time differences, confirming priming's role in shaping perception and judgment independently from overt social influence mechanisms.
Real-World Examples of Social Influence
Social influence manifests in real-world scenarios such as peer pressure driving teenagers to adopt certain fashion trends or social media platforms shaping consumer behavior through endorsements and viral challenges. Workplace dynamics often reveal social influence when employees conform to group norms to foster team cohesion or gain approval from supervisors. Political campaigns leverage social influence by utilizing endorsements from trusted public figures to sway voter opinions and increase turnout.
How Priming Shapes Our Behavior
Priming subtly activates specific mental pathways by exposing individuals to particular stimuli, which then shapes their subsequent behavior and decision-making processes. Research in cognitive psychology demonstrates how environmental cues, such as words or images, can unconsciously influence attitudes, perceptions, and actions, often without the person's awareness. This automatic activation contrasts with social influence, which typically involves direct interactions or explicit social pressures guiding behavior.
Social Influence and Priming in Decision Making
Social influence significantly shapes decision making by altering individuals' preferences and behaviors through group norms, authority, and peer pressure, often leading to conformity or changes in risk assessment. Priming affects decision making by subtly activating specific memories or associations, thereby influencing choices without conscious awareness. Both mechanisms operate through different cognitive pathways, with social influence relying on external social cues and priming leveraging implicit memory activation.
Applications in Marketing and Advertising
Social influence leverages peer pressure and social proof to shape consumer behavior, enhancing brand credibility through testimonials, influencer collaborations, and user-generated content in marketing campaigns. Priming subtly triggers consumers' subconscious associations by exposing them to specific stimuli such as colors, words, or images, which can increase brand recall and purchase intent in advertising. Combining social influence with priming strategies optimizes engagement and conversion rates by aligning consumer emotions and social context with targeted messaging.
Future Research Directions: Social Influence and Priming
Future research directions in social influence and priming emphasize exploring neural mechanisms underlying behavior changes and the temporal dynamics of priming effects. Investigating individual differences in susceptibility to social influence and the interaction between implicit priming and explicit social cues can enhance intervention strategies. Advanced neuroimaging and longitudinal studies are critical for mapping the cognitive processes and long-term impacts on decision-making.
Social Influence Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com