Elites often hold significant influence in political, economic, and social spheres, shaping policies and public opinion to maintain their status. Understanding the dynamics of elite power helps reveal the underlying mechanisms that impact your daily life and societal structure. Explore the rest of the article to discover how elites affect global systems and individual opportunities.
Table of Comparison
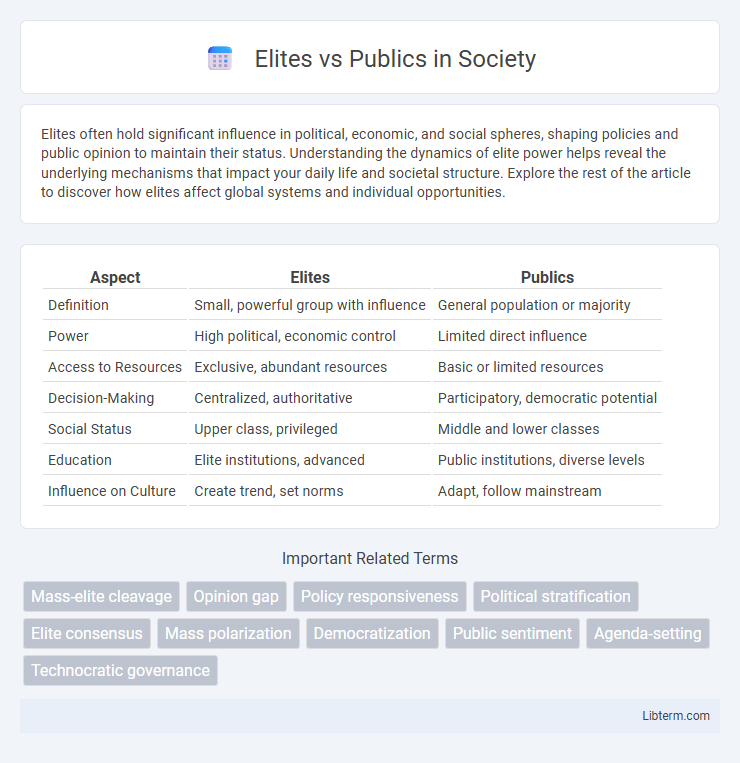
| Aspect | Elites | Publics |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Small, powerful group with influence | General population or majority |
| Power | High political, economic control | Limited direct influence |
| Access to Resources | Exclusive, abundant resources | Basic or limited resources |
| Decision-Making | Centralized, authoritative | Participatory, democratic potential |
| Social Status | Upper class, privileged | Middle and lower classes |
| Education | Elite institutions, advanced | Public institutions, diverse levels |
| Influence on Culture | Create trend, set norms | Adapt, follow mainstream |
Defining Elites and Publics
Elites are individuals or groups holding concentrated power, influence, and resources within political, economic, or social spheres, often shaping policy and decision-making processes. Publics consist of the broader population or general citizenry who engage with political systems primarily through voting, public opinion, and grassroots activism. The distinction centers on access to authority and capacity to impact governance versus the collective role of public participation and consent.
Historical Context of Elite-Public Divide
The historical context of the elite-public divide traces back to ancient civilizations where ruling classes, such as monarchs and aristocrats, held concentrated political and economic power distinct from the general populace. During the Enlightenment, philosophical critiques of absolute authority emphasized the need for political representation and accountability, highlighting systemic inequalities between elites and ordinary citizens. Industrialization further widened this divide as emerging capitalist elites controlled resources and labor, prompting social movements advocating for democratization and workers' rights.
Power Dynamics: Who Holds Influence?
Elites predominantly hold influence through concentrated economic resources, political positions, and strategic networks that shape major policy decisions and societal norms. In contrast, the public exerts power more diffusely via collective actions such as voting, protests, and grassroots movements, which can pressure elites to respond or adjust policies. Power dynamics continuously evolve as elites aim to maintain control while publics seek increased representation and accountability.
Elite Interests vs Public Needs
Elite interests often prioritize economic growth, political power, and policy stability, benefiting a narrow segment of society. Public needs typically emphasize social welfare, healthcare, education, and equitable resource distribution that address broader community well-being. Conflicts arise when elite-driven policies overlook or undermine essential public services and social equity.
Communication Barriers Between Elites and Publics
Communication barriers between elites and publics often stem from differences in language complexity, access to information, and trust levels. Elites use specialized jargon and assume familiarity with policy details, which creates understanding gaps for the general public. Limited media access and perceived elitism further hinder effective dialogue and mutual comprehension.
Representation and Accountability
Elites often hold disproportionate influence over political decision-making, undermining the principle of equal representation for the public. Public accountability suffers when elite interests dominate, as policies may prioritize narrow agendas over broader societal needs. Enhancing transparency and mechanisms for public participation strengthens democratic accountability and ensures that diverse voices are effectively represented.
Media’s Role in Shaping Perceptions
Media plays a crucial role in shaping public perceptions by framing elite narratives and selectively highlighting issues that align with elite interests, often marginalizing grassroots voices. News outlets and social platforms act as gatekeepers, determining which stories gain visibility and influencing opinion formation through agenda-setting and framing effects. This dynamic reinforces power structures by amplifying elite perspectives while limiting the diversity of viewpoints accessible to the general public.
Democracy and Populism: Bridging the Gap
Democracy thrives when elites and publics engage in mutual respect and effective communication, balancing expertise with popular will to foster inclusive governance. Populism emerges as a response to perceived elite detachment, amplifying public voices but sometimes risking oversimplification of complex issues. Bridging the gap requires transparent institutions, participatory mechanisms, and informed public discourse to harmonize elite knowledge with popular aspirations.
Social Movements and Public Mobilization
Social movements emerge as powerful forces challenging established elites by mobilizing public grievances through collective action and grassroots organizing. The dynamic between elites and publics is shaped by the ability of movements to frame issues, leverage social networks, and utilize media to amplify their demands, influencing policy and societal change. Public mobilization hinges on resource availability, leadership charisma, and strategic use of digital platforms to disrupt elite dominance and foster inclusive participation.
Future Trends in Elite-Public Relations
Future trends in elite-public relations indicate increasing reliance on digital platforms for direct communication, enhancing transparency but also amplifying misinformation risks. The rise of data analytics enables elites to tailor messages more precisely, fostering personalized engagement yet raising privacy concerns. Shifts toward participatory governance models suggest a growing demand for accountability and inclusion from diverse public segments.
Elites Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com