Rural traditionalism preserves customs, values, and lifestyles rooted in agricultural communities, often emphasizing family bonds, religious practices, and respect for nature. These traditions shape social norms and provide a sense of identity and continuity amid changing times. Discover how rural traditionalism influences modern society and what it means for your community by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
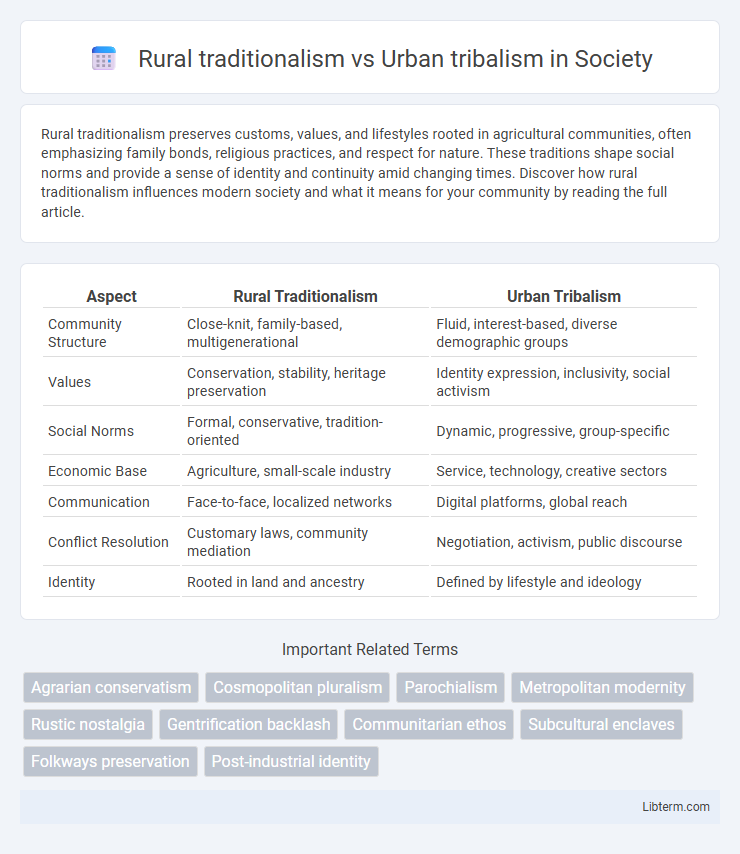
| Aspect | Rural Traditionalism | Urban Tribalism |
|---|---|---|
| Community Structure | Close-knit, family-based, multigenerational | Fluid, interest-based, diverse demographic groups |
| Values | Conservation, stability, heritage preservation | Identity expression, inclusivity, social activism |
| Social Norms | Formal, conservative, tradition-oriented | Dynamic, progressive, group-specific |
| Economic Base | Agriculture, small-scale industry | Service, technology, creative sectors |
| Communication | Face-to-face, localized networks | Digital platforms, global reach |
| Conflict Resolution | Customary laws, community mediation | Negotiation, activism, public discourse |
| Identity | Rooted in land and ancestry | Defined by lifestyle and ideology |
Understanding Rural Traditionalism
Rural traditionalism centers on preserving long-standing cultural values, agricultural practices, and community-based social structures often rooted in kinship and historical continuity. This worldview emphasizes self-reliance, close family ties, and adherence to established moral codes, contrasting sharply with urban tribalism's fluid group identities based on shared interests or ideologies rather than heritage. Understanding rural traditionalism requires recognizing its role in maintaining social cohesion through rituals, localized governance, and resistance to rapid social change.
Defining Urban Tribalism
Urban tribalism refers to social groupings in metropolitan areas where individuals form close-knit communities based on shared interests, lifestyles, or identities, rather than geographical or familial ties. These tribes often manifest through subcultures, niche hobbies, and collective experiences that foster a sense of belonging amidst the anonymity of city life. Distinct from rural traditionalism's emphasis on heritage and long-standing customs, urban tribalism thrives on fluidity, diversity, and the blending of cultural influences.
Historical Roots of Rural and Urban Divides
Rural traditionalism stems from long-established agricultural practices, close-knit communities, and a reliance on local customs that date back centuries. Urban tribalism, however, is rooted in the rapid industrialization and diverse migration patterns of cities, fostering subcultures and identity-based groups. These historical divides have shaped distinct social values, economic structures, and political attitudes between rural and urban populations.
Cultural Values: Preservation vs Progress
Rural traditionalism emphasizes the preservation of cultural values, prioritizing historical customs, heritage, and community continuity as essential to identity. Urban tribalism drives cultural progress through innovation, diversity, and adaptive social norms, reflecting dynamic, multi-ethnic urban environments. These contrasting cultural values shape societal behaviors, influencing everything from social cohesion to policy attitudes in rural versus urban settings.
Social Structures and Community Bonds
Rural traditionalism emphasizes tightly-knit social structures where kinship, long-established customs, and shared histories form the foundation of community bonds. In contrast, urban tribalism is characterized by fluid, interest-based networks often centered around cultural, professional, or ideological affiliations rather than familial ties. These differing community dynamics influence social cohesion, identity formation, and collective behavior within rural and urban contexts.
Economic Dynamics in Rural and Urban Settings
Rural traditionalism often emphasizes agriculture-based economies, local craftsmanship, and resource-dependent livelihoods, which foster stable but slower economic growth due to limited market access and infrastructure. Urban tribalism, characterized by diverse social networks and localized economic clusters, drives innovation and rapid economic development by leveraging technology, service industries, and dynamic labor markets. Economic dynamics in rural areas prioritize sustainability and community cohesion, while urban settings focus on competitiveness and scalability within globalized markets.
Political Tendencies and Voting Patterns
Rural traditionalism often aligns with conservative political tendencies, emphasizing values like self-reliance, family, and resistance to rapid societal change, which typically results in consistent support for right-leaning parties. Urban tribalism, by contrast, tends to reflect progressive or left-leaning political preferences, driven by diverse, identity-based groups that prioritize social justice, environmental issues, and inclusive policies, influencing voting patterns toward liberal candidates. These contrasting political dynamics highlight how geographic and cultural contexts shape electoral behavior and party allegiance in significant ways.
Communication Styles and Conflict Resolution
Rural traditionalism emphasizes face-to-face communication, valuing directness, respect, and long-established social roles to maintain harmony and resolve conflicts through community consensus and mediation. Urban tribalism often involves rapid, technology-driven interactions within diverse social groups, where conflict resolution can be fragmented, relying on digital platforms and informal peer networks to address disputes. The contrasting communication styles reflect deeper cultural values: rural communities prioritize stability and collective well-being, whereas urban tribes focus on identity expression and dynamic social negotiation.
Impact of Media on Rural and Urban Identities
Media plays a crucial role in shaping rural traditionalism by reinforcing long-standing cultural values and community cohesion through local news and regional programming. In contrast, urban tribalism is amplified by social media platforms and niche online communities that facilitate identity formation based on lifestyle, interests, and social networks. The divergence in media consumption patterns results in distinct identity constructions, influencing political attitudes, social behaviors, and cultural expressions in rural and urban areas.
Bridging the Gap: Towards Mutual Understanding
Rural traditionalism emphasizes established customs, community values, and a deep connection to the land, while urban tribalism centers on identity-based groups and dynamic social networks within metropolitan environments. Bridging the gap requires fostering open dialogue, cultural exchange programs, and inclusive policymaking that acknowledges the legitimacy of rural heritage and urban diversity. Collaborative initiatives focused on shared goals such as sustainable development and education can enhance mutual respect and reduce polarization between these distinct social paradigms.
Rural traditionalism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com