Civic nationalism emphasizes shared values, citizenship, and political rights over ethnicity or culture, fostering unity based on inclusive participation in the state. This form of nationalism promotes democracy, equality, and civic responsibility, allowing diverse populations to coexist under common laws and institutions. Explore the rest of the article to understand how civic nationalism shapes modern societies and your role within it.
Table of Comparison
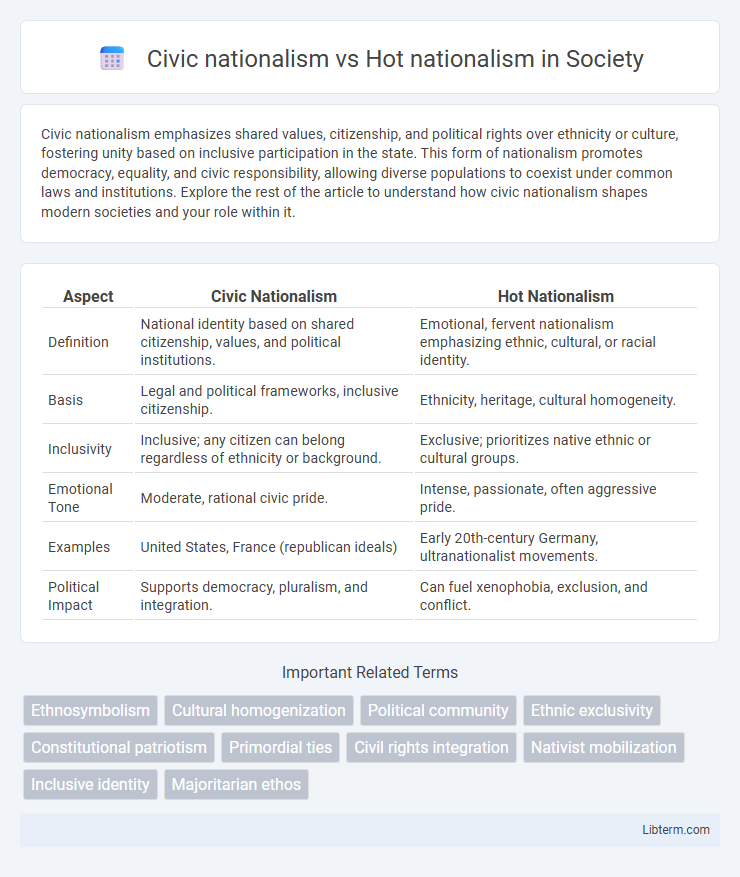
| Aspect | Civic Nationalism | Hot Nationalism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | National identity based on shared citizenship, values, and political institutions. | Emotional, fervent nationalism emphasizing ethnic, cultural, or racial identity. |
| Basis | Legal and political frameworks, inclusive citizenship. | Ethnicity, heritage, cultural homogeneity. |
| Inclusivity | Inclusive; any citizen can belong regardless of ethnicity or background. | Exclusive; prioritizes native ethnic or cultural groups. |
| Emotional Tone | Moderate, rational civic pride. | Intense, passionate, often aggressive pride. |
| Examples | United States, France (republican ideals) | Early 20th-century Germany, ultranationalist movements. |
| Political Impact | Supports democracy, pluralism, and integration. | Can fuel xenophobia, exclusion, and conflict. |
Defining Civic Nationalism
Civic nationalism defines national identity based on shared citizenship, legal rights, and political participation rather than ethnic, racial, or cultural origins. It promotes inclusive values that emphasize equality, individual freedoms, and commitment to democratic institutions as the foundation of national unity. This form of nationalism contrasts sharply with hot nationalism, which is often characterized by ethnic exclusivity, intense patriotism, and emotional loyalty to a distinct cultural or ethnic group.
Understanding Hot Nationalism
Hot nationalism centers on intense emotional loyalty and often manifests through aggressive patriotism, prioritizing cultural, ethnic, or racial identity over political values. It contrasts with civic nationalism, which emphasizes inclusive citizenship and shared political principles regardless of ethnic background. Understanding hot nationalism requires analyzing its potential to fuel exclusionary policies, social polarization, and conflicts driven by identity politics.
Historical Origins of Both Ideologies
Civic nationalism traces its origins to the Enlightenment period and the French Revolution, emphasizing shared values, citizenship, and political rights as the basis for national identity. Hot nationalism, often linked to 19th and early 20th-century Romanticism and ethno-nationalist movements, prioritizes ethnic heritage, cultural homogeneity, and emotional attachment to the nation. These historical roots reveal contrasting foundations: civic nationalism centers on inclusive legal frameworks, while hot nationalism derives legitimacy from ancestral ethnicity and perceived cultural purity.
Key Philosophies and Values Compared
Civic nationalism emphasizes inclusive citizenship, shared values, and political participation regardless of ethnic background, promoting equality, individual rights, and adherence to democratic principles. Ethnic nationalism, often referred to as "hot nationalism," prioritizes a common heritage, language, and ethnicity, fostering strong group identity and loyalty tied to ancestral and cultural origins. While civic nationalism supports a pluralistic society with legal equality, ethnic nationalism centers on preserving a homogeneous national identity and cultural unity.
Civic vs Hot Nationalism: Political Implications
Civic nationalism emphasizes inclusive political identity based on shared values, laws, and citizenship, promoting democratic participation and multiculturalism. Hot nationalism, often characterized by emotional intensity and ethnocentric loyalty, can lead to exclusionary policies and heightened ethnic tensions. The political implications diverge as civic nationalism fosters institutional stability and integration, while hot nationalism risks polarization and authoritarian tendencies.
Social Cohesion and National Identity
Civic nationalism emphasizes social cohesion through shared values, legal frameworks, and inclusive citizenship regardless of ethnicity, fostering a unified national identity based on common rights and responsibilities. Hot nationalism, driven by ethnic or cultural exclusivity, often prioritizes a homogeneous national identity that can intensify social divisions and reduce cohesion among diverse populations. Social cohesion in civic nationalism supports integration and collective belonging, while hot nationalism risks fragmentation by emphasizing ethnic or cultural superiority.
Effects on Immigration and Integration Policies
Civic nationalism promotes inclusive immigration policies emphasizing legal frameworks and cultural assimilation to foster social cohesion, often supporting multiculturalism and equal rights for immigrants. In contrast, hot nationalism drives restrictive immigration policies focused on ethnic identity and cultural homogeneity, frequently resulting in stricter border controls and limited integration efforts. These differing approaches significantly impact how immigrant communities are accepted and integrated within the host society.
Case Studies: Civic and Hot Nationalism in Practice
Civic nationalism, exemplified by Canada's multicultural policies, emphasizes inclusive citizenship and shared values over ethnic identity, promoting social cohesion through legal frameworks and political participation. In contrast, Hungary's hot nationalism showcases ethnic-based identity politics, driven by exclusionary rhetoric and policies prioritizing ethnic homogeneity, leading to increased social polarization. Case studies reveal that civic nationalism fosters democratic resilience and integration, whereas hot nationalism often correlates with authoritarian tendencies and intergroup conflict.
Challenges and Criticisms of Each Approach
Civic nationalism faces challenges related to defining inclusive citizenship without eroding national identity, often criticized for being overly idealistic and neglecting cultural cohesion. Hot nationalism, driven by intense emotional and cultural fervor, encounters criticism for promoting exclusion, xenophobia, and sometimes authoritarian tendencies. Both approaches struggle to balance unity and diversity while addressing fears of societal fragmentation and identity loss.
Future Trends in Nationalism Discourse
Future trends in nationalism discourse suggest a growing emphasis on civic nationalism, which prioritizes inclusive citizenship and shared political values over ethnic or cultural identity. As globalization and migration increase, civic nationalism offers a framework for integrating diverse populations while maintaining national cohesion. Conversely, hot nationalism--characterized by intense ethnic loyalty and exclusion--faces challenges due to its potential to exacerbate social divisions and conflict in increasingly interconnected societies.
Civic nationalism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com