Strong corporate governance ensures accountability, transparency, and ethical decision-making within organizations, driving long-term success and investor confidence. Effective governance frameworks help mitigate risks and align the interests of stakeholders and management. Discover how implementing robust corporate governance can enhance Your company's performance and reputation in the full article.
Table of Comparison
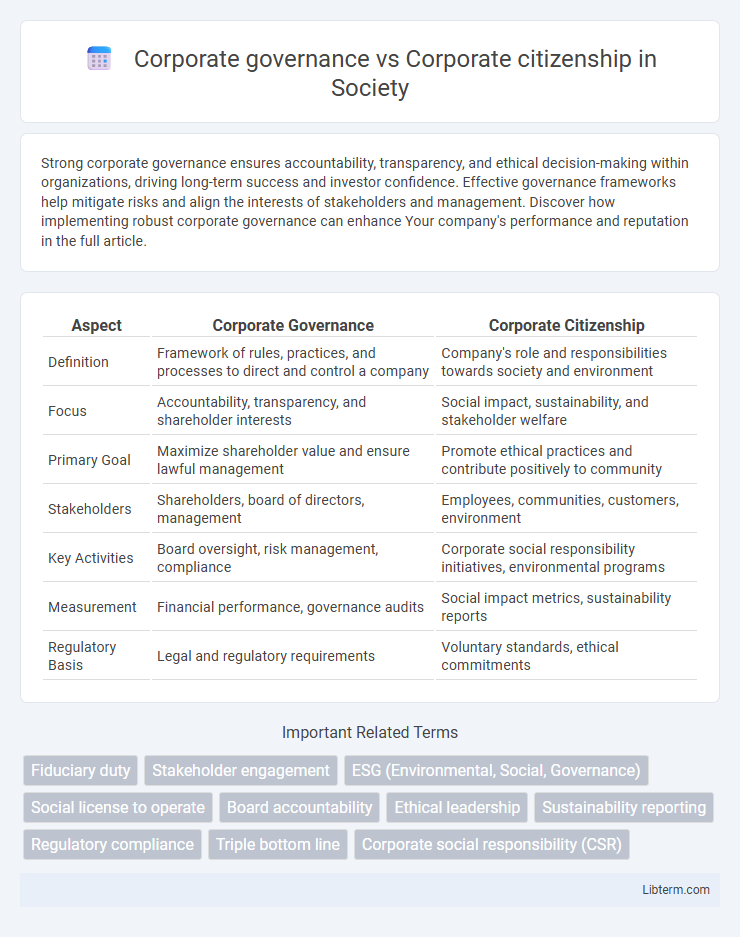
| Aspect | Corporate Governance | Corporate Citizenship |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Framework of rules, practices, and processes to direct and control a company | Company's role and responsibilities towards society and environment |
| Focus | Accountability, transparency, and shareholder interests | Social impact, sustainability, and stakeholder welfare |
| Primary Goal | Maximize shareholder value and ensure lawful management | Promote ethical practices and contribute positively to community |
| Stakeholders | Shareholders, board of directors, management | Employees, communities, customers, environment |
| Key Activities | Board oversight, risk management, compliance | Corporate social responsibility initiatives, environmental programs |
| Measurement | Financial performance, governance audits | Social impact metrics, sustainability reports |
| Regulatory Basis | Legal and regulatory requirements | Voluntary standards, ethical commitments |
Introduction to Corporate Governance and Corporate Citizenship
Corporate governance defines the framework of rules, practices, and processes by which a company is directed and controlled, emphasizing accountability, transparency, and shareholder rights. Corporate citizenship refers to a company's responsibility towards society, encompassing ethical behavior, social contributions, and environmental sustainability. Both concepts are integral to modern business strategy, aligning organizational goals with stakeholder expectations and societal impact.
Defining Corporate Governance: Structure and Principles
Corporate governance refers to the system of rules, practices, and processes by which a company is directed and controlled, emphasizing accountability, transparency, and ethical decision-making. Its structure typically includes the board of directors, executive management, and shareholders, each playing a critical role in balancing interests and ensuring regulatory compliance. Fundamental principles such as fairness, responsibility, and independence guide corporate governance to promote sustainable business performance and stakeholder trust.
Understanding Corporate Citizenship: Scope and Responsibilities
Corporate citizenship encompasses a company's commitment to ethical behavior, social responsibility, and sustainable development beyond legal compliance, integrating stakeholder interests into core business strategies. Its scope includes environmental stewardship, community engagement, employee welfare, and transparent governance practices that foster long-term value creation. Understanding corporate citizenship entails recognizing the broader societal impact of business decisions, emphasizing accountability and proactive contributions to social and economic well-being.
Key Differences Between Corporate Governance and Corporate Citizenship
Corporate governance primarily focuses on the system of rules, practices, and processes by which a company is directed and controlled, emphasizing accountability, transparency, and shareholder interests. Corporate citizenship encompasses a company's responsibilities toward society and the environment, highlighting ethical behavior, social impact, and sustainable development. The key difference lies in corporate governance prioritizing internal oversight and regulatory compliance, whereas corporate citizenship extends to external social and environmental engagement.
The Interplay of Governance and Citizenship in Modern Corporations
Corporate governance establishes the framework of rules, practices, and processes by which a company is directed and controlled, ensuring accountability to shareholders and stakeholders. Corporate citizenship emphasizes a company's ethical responsibilities, including social, environmental, and community impacts, reflecting its commitment to sustainable and responsible business practices. The interplay in modern corporations integrates governance structures with citizenship principles to align strategic objectives with societal expectations, enhancing transparency, ethical conduct, and long-term value creation.
Benefits of Strong Corporate Governance Practices
Strong corporate governance practices enhance transparency, accountability, and risk management within organizations, leading to improved investor confidence and long-term financial performance. Effective governance frameworks ensure regulatory compliance and ethical decision-making, reducing the likelihood of corporate scandals and operational disruptions. Companies with robust governance structures often experience better access to capital, enhanced reputation, and sustainable competitive advantages in global markets.
The Impact of Corporate Citizenship on Stakeholder Trust
Corporate citizenship significantly enhances stakeholder trust by demonstrating a company's commitment to ethical practices, social responsibility, and sustainable development beyond mere compliance with corporate governance standards. Trust is cultivated through transparent communication, community engagement, and consistent actions that align with stakeholders' values and expectations. This positive perception strengthens stakeholder relationships, fosters loyalty, and supports long-term corporate success.
Regulatory Frameworks: Governance vs Citizenship Obligations
Corporate governance primarily focuses on regulatory frameworks that ensure compliance with legal standards, risk management, and accountability to shareholders through structured policies and oversight mechanisms. Corporate citizenship obligations extend beyond regulatory mandates, encompassing ethical responsibilities, social impact, and sustainable practices aligned with community and environmental expectations. Governance frameworks emphasize transparency and fiduciary duties, while citizenship frameworks integrate voluntary initiatives promoting corporate social responsibility and stakeholder engagement.
Integrating Corporate Governance and Citizenship Strategies
Integrating corporate governance and corporate citizenship strategies enhances organizational accountability and social responsibility by aligning ethical decision-making with stakeholder interests. Effective corporate governance frameworks incorporate citizenship principles, promoting transparency, sustainability, and community engagement alongside financial performance. This holistic approach creates long-term value by balancing regulatory compliance with proactive social impact initiatives.
Future Trends in Corporate Governance and Corporate Citizenship
Future trends in corporate governance emphasize integrating environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria to enhance transparency and accountability, driven by increasing regulatory demands and stakeholder expectations. Corporate citizenship is evolving towards proactive community engagement and sustainable business practices that align with global social responsibility goals. Both disciplines are converging, leveraging digital technologies and data analytics to measure impact and foster ethical, long-term value creation.
Corporate governance Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com