Philosophy explores fundamental questions about existence, knowledge, values, reason, and language, shaping the way we understand reality and our place within it. By examining different schools of thought and critical arguments, it challenges assumptions and encourages deeper reflection. Discover how philosophy can broaden your perspective and enrich your thinking by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
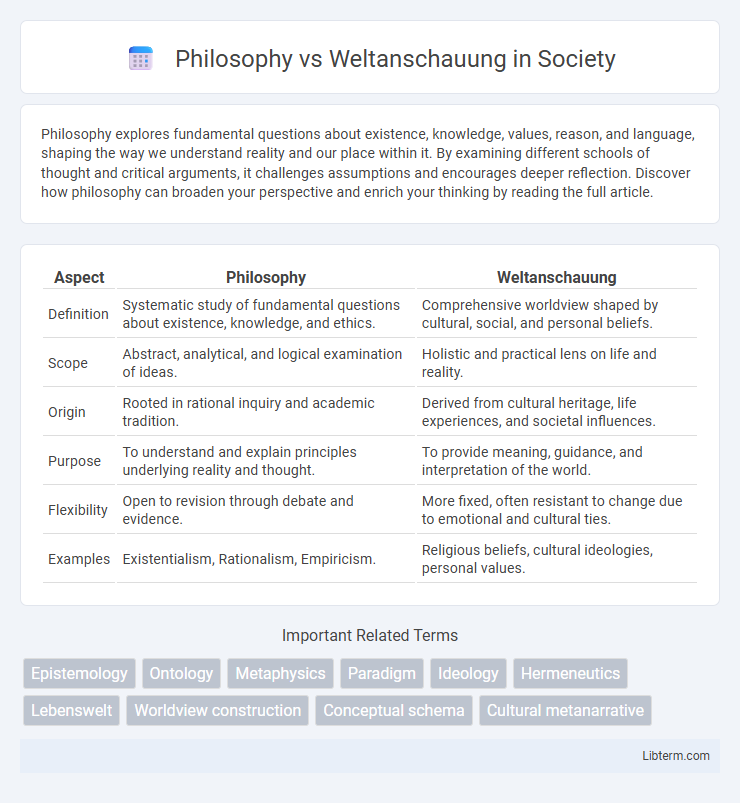
| Aspect | Philosophy | Weltanschauung |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Systematic study of fundamental questions about existence, knowledge, and ethics. | Comprehensive worldview shaped by cultural, social, and personal beliefs. |
| Scope | Abstract, analytical, and logical examination of ideas. | Holistic and practical lens on life and reality. |
| Origin | Rooted in rational inquiry and academic tradition. | Derived from cultural heritage, life experiences, and societal influences. |
| Purpose | To understand and explain principles underlying reality and thought. | To provide meaning, guidance, and interpretation of the world. |
| Flexibility | Open to revision through debate and evidence. | More fixed, often resistant to change due to emotional and cultural ties. |
| Examples | Existentialism, Rationalism, Empiricism. | Religious beliefs, cultural ideologies, personal values. |
Defining Philosophy: Scope and Methods
Philosophy encompasses the systematic study of fundamental questions related to existence, knowledge, ethics, and reality through critical analysis and rational argumentation. Its scope includes diverse branches such as metaphysics, epistemology, ethics, logic, and aesthetics, employing methods like dialectic, phenomenology, and analytic reasoning to explore abstract concepts. Unlike Weltanschauung, which represents a broader, often cultural or ideological worldview, philosophy rigorously challenges assumptions and seeks universal truths using structured methodologies.
Understanding Weltanschauung: Meaning and Origins
Weltanschauung, a German term translating to "worldview," represents an individual or collective's comprehensive perspective on life and existence, shaped by cultural, historical, and psychological factors. Unlike philosophy, which systematically explores fundamental questions through critical reasoning, Weltanschauung encompasses an implicit and often holistic framework informing beliefs, values, and experiences. Understanding its origins involves examining how personal experiences, social environments, and cultural narratives converge to form this deeply ingrained interpretive lens.
Key Differences Between Philosophy and Weltanschauung
Philosophy is a systematic study of fundamental questions about existence, knowledge, and ethics through critical reasoning, whereas Weltanschauung refers to an individual's or culture's comprehensive worldview shaped by beliefs, experiences, and values. Philosophy prioritizes logical analysis and theoretical frameworks, while Weltanschauung encompasses emotional and cultural dimensions influencing perception and interpretation of reality. Key differences include philosophy's emphasis on objective inquiry contrasted with Weltanschauung's subjective, experiential nature.
Historical Development of Philosophical Thought
Philosophy, rooted in ancient Greece with figures like Socrates and Plato, evolved through systematic inquiry into ethics, metaphysics, and epistemology, shaping the foundation of Western intellectual tradition. Weltanschauung, a German term popularized in the 19th century by philosophers such as Wilhelm Dilthey, refers to a comprehensive worldview encompassing cultural, historical, and existential perspectives that extend beyond formal philosophy. The historical development of philosophical thought intertwines with divergent Weltanschauungen, reflecting shifts from classical rationalism to existentialism and postmodern critiques, highlighting the interplay between abstract reasoning and lived human experience.
Evolution of Weltanschauung in Cultural Contexts
Weltanschauung, or world view, evolves dynamically within cultural contexts, reflecting the collective beliefs, values, and historical experiences of societies, whereas philosophy systematically analyzes fundamental questions through critical reasoning and abstract thought. Over time, cultural shifts, technological advancements, and intercultural interactions reshape Weltanschauung, embedding new symbols and meanings that guide social behavior and identity construction. This evolution contrasts with philosophy's more stable pursuit of universal truths, highlighting how Weltanschauung serves as a living, contextual framework anchoring human experience in cultural realities.
Influence of Philosophy on Worldviews
Philosophy shapes weltanschauung by providing structured frameworks for understanding existence, ethics, and knowledge, influencing how individuals interpret reality and their place within it. Key philosophical movements such as existentialism, rationalism, and pragmatism underpin varied worldviews by addressing fundamental questions about meaning, truth, and human purpose. The critical analysis and systematic inquiry characteristic of philosophy serve as the foundation for diverse cultural and personal perspectives, deeply affecting societal values and belief systems.
Core Functions: Explaining Reality vs. Shaping Perspective
Philosophy primarily serves to explain reality through systematic inquiry, logical analysis, and conceptual clarity, providing frameworks for understanding existence, knowledge, and values. Weltanschauung, or worldview, functions to shape perspective by integrating cultural, emotional, and existential dimensions that guide individual and collective interpretation of life's meaning. These core functions distinguish philosophy as analytical and descriptive, whereas Weltanschauung is holistic and prescriptive in influencing one's orientation toward the world.
Interactions: How Philosophy and Weltanschauung Intersect
Philosophy and Weltanschauung intersect by shaping an individual's framework for interpreting reality and guiding decision-making processes. Philosophy offers systematic methods for critical analysis and questioning, while Weltanschauung encompasses the totality of cultural, historical, and personal beliefs that inform one's worldview. Together, they interact dynamically, with philosophy refining and challenging Weltanschauung, and Weltanschauung grounding philosophical inquiry in lived experience.
Impacts on Society and Individual Belief Systems
Philosophy systematically explores fundamental questions about existence, knowledge, and ethics, shaping critical thinking and rational discourse within society, thereby influencing legal systems, education, and cultural norms. Weltanschauung, as a comprehensive worldview encompassing cultural, religious, and personal beliefs, deeply affects individual identity and collective behavior by framing how people interpret their experiences and moral values. Both philosophy and Weltanschauung significantly impact societal cohesion and personal belief systems, with philosophy promoting analytical evaluation and Weltanschauung providing an intuitive, often emotionally rooted framework.
Contemporary Relevance: Why the Distinction Matters
Contemporary relevance of philosophy versus Weltanschauung lies in their distinct approaches to understanding reality: philosophy employs critical analysis and systematic reasoning, while Weltanschauung represents a comprehensive worldview shaped by cultural and personal values. This distinction matters because philosophy fosters objective inquiry and dialogue necessary for addressing complex ethical, scientific, and social issues in a globalized world. Recognizing the difference helps individuals and societies balance analytical rigor with existential meaning, promoting more nuanced decision-making and intercultural understanding.
Philosophy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com