Conspicuous consumption refers to the act of purchasing goods or services to publicly display wealth and social status rather than to meet basic needs. This behavior often influences consumer trends and impacts economic patterns globally. Explore the article to understand how conspicuous consumption shapes your financial decisions and societal values.
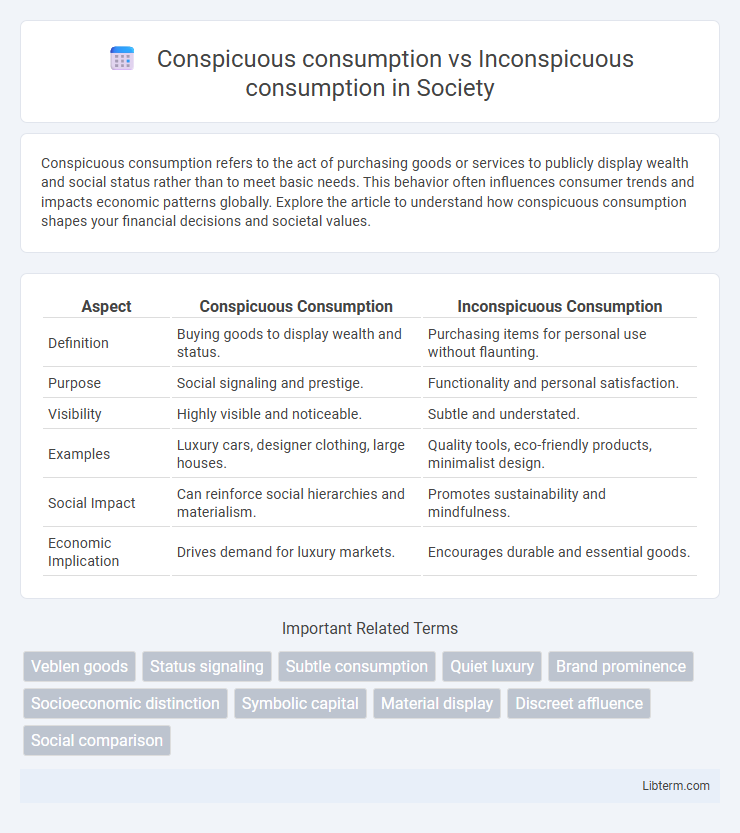
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Conspicuous Consumption | Inconspicuous Consumption |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Buying goods to display wealth and status. | Purchasing items for personal use without flaunting. |
| Purpose | Social signaling and prestige. | Functionality and personal satisfaction. |
| Visibility | Highly visible and noticeable. | Subtle and understated. |
| Examples | Luxury cars, designer clothing, large houses. | Quality tools, eco-friendly products, minimalist design. |
| Social Impact | Can reinforce social hierarchies and materialism. | Promotes sustainability and mindfulness. |
| Economic Implication | Drives demand for luxury markets. | Encourages durable and essential goods. |
Understanding Conspicuous Consumption
Conspicuous consumption involves purchasing goods or services to display wealth and social status, often characterized by luxury brands, expensive cars, and designer clothing. This behavior serves as a social signal, differentiating individuals within their peer groups and reinforcing social hierarchies. Understanding conspicuous consumption helps marketers target aspirational consumers and informs sociologists about patterns of social stratification and identity expression.
Defining Inconspicuous Consumption
Inconspicuous consumption involves purchasing goods and services that signal status through subtlety and discretion, rather than overt displays or luxury branding. It focuses on quality, experience, and ethical values, often emphasizing sustainability, artisanal craftsmanship, and personal well-being. This contrasts with conspicuous consumption, which seeks social recognition through highly visible, often extravagant purchases.
Historical Evolution of Consumption Patterns
Conspicuous consumption emerged prominently during the late 19th and early 20th centuries, driven by industrialization and the rise of the affluent middle class seeking to display wealth through luxury goods and lavish lifestyles. In contrast, inconspicuous consumption gained traction in the late 20th century as environmental awareness and social values shifted, emphasizing sustainable and meaningful spending on experiences or subtle, high-quality products rather than overt displays. The historical evolution reflects broader socioeconomic transformations, including changing cultural norms and the increasing importance of identity and ethics in consumer behavior.
Psychological Drivers Behind Consumption Choices
Conspicuous consumption is driven by psychological needs for status, social recognition, and self-expression, where individuals purchase luxury goods to signal wealth and prestige. Inconspicuous consumption is motivated by intrinsic values such as personal satisfaction, authenticity, and long-term utility, reflecting a preference for functional or sustainable products without the need for external validation. Both consumption types reveal underlying psychological drivers related to identity formation, social comparison, and the pursuit of well-being.
Social Status and the Influence of Visibility
Conspicuous consumption involves purchasing luxury goods or services to publicly display wealth and elevate social status, reinforcing visibility as a key social signal. Inconspicuous consumption, by contrast, emphasizes subtlety and privacy in spending choices, aiming to maintain or enhance status without overt displays. The influence of visibility determines how individuals navigate social hierarchies, balancing the desire for recognition with the risks of conspicuousness in different cultural or social contexts.
Cultural Perspectives on Consumption
Conspicuous consumption, popularized by Thorstein Veblen, highlights the display of wealth through visible luxury goods as a cultural status symbol, mainly prevalent in Western societies. Inconspicuous consumption, by contrast, emphasizes subtler forms of consumption such as experiences, education, and sustainable goods, reflecting cultural values of modesty and environmental awareness found in various Eastern and indigenous cultures. These contrasting consumption patterns reveal how cultural contexts shape consumer behavior, social identity, and the symbolic meaning attributed to goods and services.
Modern Manifestations in Digital Media
Conspicuous consumption in digital media manifests through social media platforms where users showcase luxury brands, expensive gadgets, and exclusive experiences to signal wealth and status. Inconspicuous consumption, by contrast, emerges as subtle displays of taste and values, such as promoting sustainable products or minimalist lifestyles that resonate with authenticity and social responsibility. These modern expressions reflect evolving social norms where digital visibility and identity construction drive consumption patterns beyond mere material acquisition.
Economic Impact of Consumption Trends
Conspicuous consumption drives economic growth by increasing demand for luxury goods and exclusive services, stimulating high-profit industries and creating jobs in premium sectors. In contrast, inconspicuous consumption emphasizes durability and sustainability, encouraging industries focused on quality, environmental responsibility, and long-term value, which can reduce waste and lower overall resource consumption. Both consumption trends shape market dynamics and influence economic policies, with conspicuous consumption boosting short-term economic activity and inconspicuous consumption fostering sustainable development and resilience.
Environmental Implications of Consumption Behaviors
Conspicuous consumption often leads to increased environmental degradation due to the demand for luxury goods that require excessive resource extraction and energy use. Inconspicuous consumption, characterized by subtle or minimalistic purchases, tends to have a smaller ecological footprint by promoting durability and reduced waste generation. Understanding these patterns helps inform sustainable consumption policies aimed at lowering global carbon emissions and resource depletion.
The Future of Consumption: Balancing Visibility and Value
Conspicuous consumption emphasizes status through visible, often luxury goods, while inconspicuous consumption focuses on discreet, value-driven purchases prioritizing quality and sustainability. The future of consumption lies in balancing these approaches by integrating ethical considerations and personal well-being into buying decisions. Emerging trends show increasing demand for products that offer long-term value without overt displays of wealth, reflecting a shift toward mindful consumer behavior.
Conspicuous consumption Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com