Common people form the backbone of every society, contributing to cultural richness and economic stability through their daily efforts. Understanding the challenges and aspirations of common people offers valuable insights into social dynamics and community development. Explore the rest of the article to discover how common people's experiences shape our world.
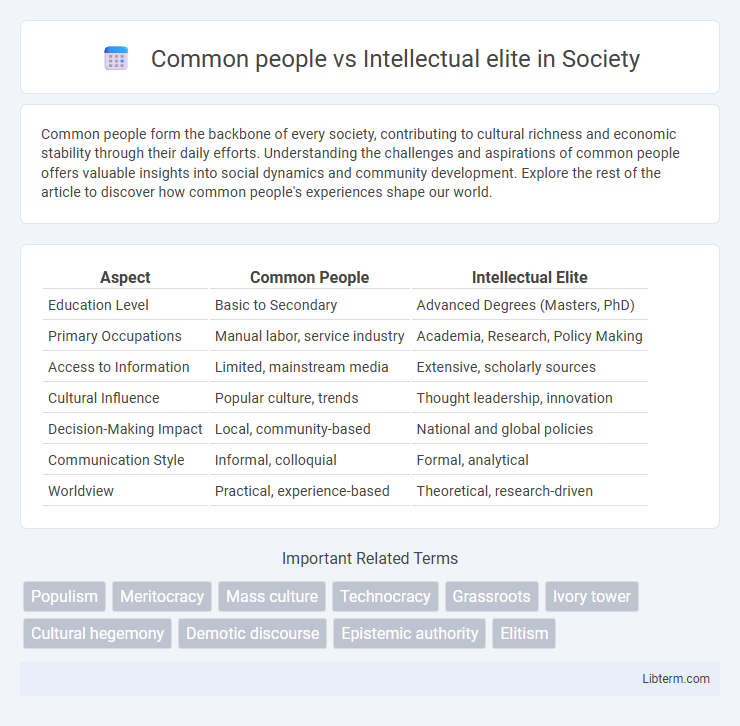
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Common People | Intellectual Elite |
|---|---|---|
| Education Level | Basic to Secondary | Advanced Degrees (Masters, PhD) |
| Primary Occupations | Manual labor, service industry | Academia, Research, Policy Making |
| Access to Information | Limited, mainstream media | Extensive, scholarly sources |
| Cultural Influence | Popular culture, trends | Thought leadership, innovation |
| Decision-Making Impact | Local, community-based | National and global policies |
| Communication Style | Informal, colloquial | Formal, analytical |
| Worldview | Practical, experience-based | Theoretical, research-driven |
Defining the Common People and the Intellectual Elite
Common people typically represent the majority of society, characterized by everyday occupations, diverse socioeconomic backgrounds, and practical knowledge rooted in daily experiences. The intellectual elite consist of individuals with advanced education, specialized expertise, and influence in shaping cultural, scientific, and political discourse. Defining these groups highlights the contrast between experiential wisdom and formal intellectual authority within social hierarchies.
Historical Context: Class Divides in Society
Historical class divides have consistently defined the tension between common people and the intellectual elite, often rooted in access to education, wealth, and political power. Social stratification in societies such as ancient Rome, feudal Europe, and modern industrial states highlights systemic barriers faced by the working class compared to the privileged intellectual elite. These divisions influenced cultural, economic, and political dynamics, shaping the evolution of social hierarchies and movements for equality throughout history.
Education and Access to Knowledge
Common people often face significant barriers in education due to limited resources, socioeconomic constraints, and lack of access to advanced learning materials. The intellectual elite typically benefit from elite educational institutions, extensive networks, and unrestricted access to cutting-edge research and knowledge databases. These disparities reinforce social stratification and influence career opportunities, innovation, and participation in cultural and political discourse.
Influence on Politics and Policy
Common people exert influence on politics and policy primarily through voting, grassroots movements, and public opinion, shaping electoral outcomes and pressing politicians to address widespread concerns. The intellectual elite impact politics by formulating theories, advising policymakers, and driving evidence-based legislation, often directing long-term strategic agendas. Together, these forces create a dynamic interplay where popular demands and expert insights converge to inform democratic governance and policy development.
Economic Disparities and Social Mobility
Economic disparities between common people and the intellectual elite often result in limited access to quality education and high-paying jobs for the former, reinforcing social stratification. The intellectual elite benefits from inherited wealth, advanced networks, and elite institutions that enhance social mobility barriers for lower socioeconomic groups. Policies targeting equitable education funding and workforce opportunities are critical to bridging the gap in economic status and promoting upward mobility across classes.
Cultural Representation and Media Narratives
Media narratives often frame the common people as rooted in tradition and practicality, emphasizing cultural representation that highlights everyday struggles and community values. The intellectual elite are portrayed as innovators or critics, shaping discourse with complex ideas and cultural critique, often depicted in elite publications or academic platforms. This dichotomy reinforces stereotypes that influence public perception and cultural identity, creating a divide between popular culture and high culture in media representation.
Common Stereotypes and Misconceptions
Common people are often stereotyped as lacking sophistication or critical thinking skills, whereas the intellectual elite are assumed to possess superior knowledge and rationality. Misconceptions include the belief that common people are intellectually inferior and resistant to new ideas, while intellectual elites are perceived as aloof or disconnected from everyday concerns. These stereotypes oversimplify complex social dynamics and overlook the diversity within both groups.
The Role of Intellectual Elites in Shaping Public Opinion
Intellectual elites play a pivotal role in shaping public opinion by interpreting complex issues and framing them within accessible narratives that influence societal values. Their expertise and authority enable them to set agendas in media, academia, and policy discussions, often directing the flow of information to the common people. By bridging specialized knowledge with public discourse, intellectual elites contribute to the formation of informed opinions and cultural norms.
Bridging the Gap: Dialogue and Mutual Understanding
Common people and the intellectual elite often experience a communication divide rooted in differences in education, language, and worldview. Bridging this gap requires fostering open dialogue where both groups actively listen and respect diverse perspectives, promoting empathy and reducing misconceptions. Initiatives such as community forums, inclusive education programs, and collaborative projects cultivate mutual understanding and empower collective problem-solving.
Future Trends: Evolving Dynamics Between Classes
Emerging trends indicate a shift in power dynamics as technology-driven innovation increasingly democratizes access to information, enabling common people to challenge traditional intellectual elite dominance. Data reveals a rise in digital literacy and participatory platforms that facilitate grassroots knowledge creation, diminishing the exclusivity of elite expertise. Future societal structures are likely to reflect a blend of collaborative intelligence where class boundaries blur, driven by AI-enhanced education and diversified economic opportunities.
Common people Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com