Surface structure refers to the outward appearance or form of a linguistic expression as opposed to its underlying meaning or deep structure. Understanding surface structure is essential for analyzing how language conveys information and how meaning is constructed from syntax. Discover how mastering surface structure can enhance your language comprehension by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
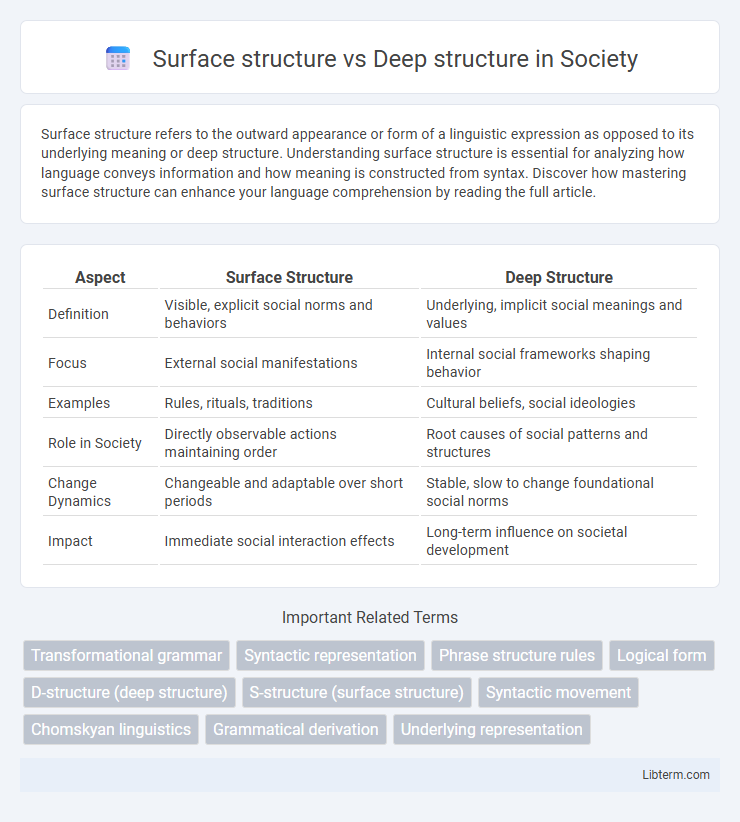
| Aspect | Surface Structure | Deep Structure |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Visible, explicit social norms and behaviors | Underlying, implicit social meanings and values |
| Focus | External social manifestations | Internal social frameworks shaping behavior |
| Examples | Rules, rituals, traditions | Cultural beliefs, social ideologies |
| Role in Society | Directly observable actions maintaining order | Root causes of social patterns and structures |
| Change Dynamics | Changeable and adaptable over short periods | Stable, slow to change foundational social norms |
| Impact | Immediate social interaction effects | Long-term influence on societal development |
Introduction to Surface Structure and Deep Structure
Surface structure represents the outward form of a sentence as it appears in spoken or written language, reflecting the linear arrangement of words and phrases. Deep structure refers to the underlying syntactic relationships and semantic meaning that form the basis for the surface structure. Understanding the distinction between surface and deep structure is crucial for analyzing how sentences convey meaning and how transformations in syntax affect interpretation.
Definition of Surface Structure
Surface structure refers to the outward form of a sentence, including the specific words and syntax used in communication. It represents the literal arrangement of linguistic elements as they appear in spoken or written language. Surface structure contrasts with deep structure, which involves the underlying meaning or semantic representation of the sentence.
Definition of Deep Structure
Deep structure refers to the underlying, abstract syntactic representation of a sentence that conveys its core semantic meaning, distinct from its surface structure, which represents the actual spoken or written form. It captures the fundamental relationships between elements in a sentence, such as subjects, predicates, and objects, before transformation rules generate the surface form. Understanding deep structure is essential in generative grammar for explaining how different surface structures can share the same meaning or how a single deep structure can produce multiple surface variations.
Historical Background and Development
The concepts of surface structure and deep structure were first introduced by Noam Chomsky in the 1950s as part of transformational-generative grammar theory, revolutionizing the understanding of syntax and language processing. Surface structure refers to the literal arrangement of words in a sentence, while deep structure represents the underlying syntactic and semantic relationships that determine meaning. Over time, this distinction has influenced linguistic research, cognitive science, and language acquisition studies by providing a framework for analyzing how humans comprehend and produce complex sentences.
Key Differences Between Surface and Deep Structures
Surface structure represents the outward form of a sentence--the word order and syntax that are immediately visible. Deep structure reflects the underlying semantic meaning and relationships between concepts, often captured in theoretical linguistics as an abstract representation. Key differences include surface structure's focus on linguistic form, while deep structure emphasizes meaning and interpretation within transformational grammar frameworks.
Importance in Linguistic Theory
Surface structure represents the literal arrangement of words in a sentence, while deep structure conveys the underlying semantic relationships and meaning. Understanding the distinction between these structures is crucial in linguistic theory for analyzing syntax and interpreting meaning across different languages. This concept, introduced by Noam Chomsky, forms the foundation for transformational-generative grammar, enabling the study of language universals and cognitive processes involved in language comprehension.
Role in Syntax and Grammar
Surface structure represents the literal arrangement of words in a sentence, capturing its outward form and syntax. Deep structure encodes the underlying grammatical relationships and semantic meaning, guiding how sentences are interpreted and transformed. The interaction between surface and deep structures enables accurate syntactic parsing and understanding of ambiguous or complex sentences.
Applications in Language Analysis
Surface structure represents the literal arrangement of words in a sentence, while deep structure conveys the core semantic meaning underlying that sentence. In language analysis, understanding both structures facilitates accurate parsing and interpretation of syntactic variations across languages. Applications include natural language processing, syntax-tree generation, and semantic role labeling to improve machine translation and sentiment analysis.
Criticisms and Limitations
Surface structure, representing the outward form of sentences, often fails to capture the underlying meaning accurately, leading to criticisms about its insufficiency in explaining syntactic phenomena. Deep structure, intended to reflect the core semantic relationships, faces limitations due to its abstract nature, making empirical validation and cross-linguistic application challenging. Both concepts have been critiqued for their inability to fully address language variability, ambiguity, and cognitive processing in contemporary linguistic theory.
Conclusion and Future Perspectives
Surface structure and deep structure represent foundational concepts in transformational grammar, highlighting the distinction between the outward form of a sentence and its underlying meaning. Advances in computational linguistics and artificial intelligence increasingly leverage deep structure analysis to improve natural language understanding and machine translation accuracy. Future research aims to refine these models by integrating neural network architectures and semantic representations, enhancing the ability to capture context and ambiguity in human language processing.
Surface structure Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com