Housing vouchers provide financial assistance to eligible low-income individuals and families, helping cover rental costs and increase access to safe, affordable housing. These vouchers are typically issued by government programs and can significantly reduce the burden of housing expenses while promoting stability. Explore the full article to understand how housing vouchers can support your journey to secure a home.
Table of Comparison
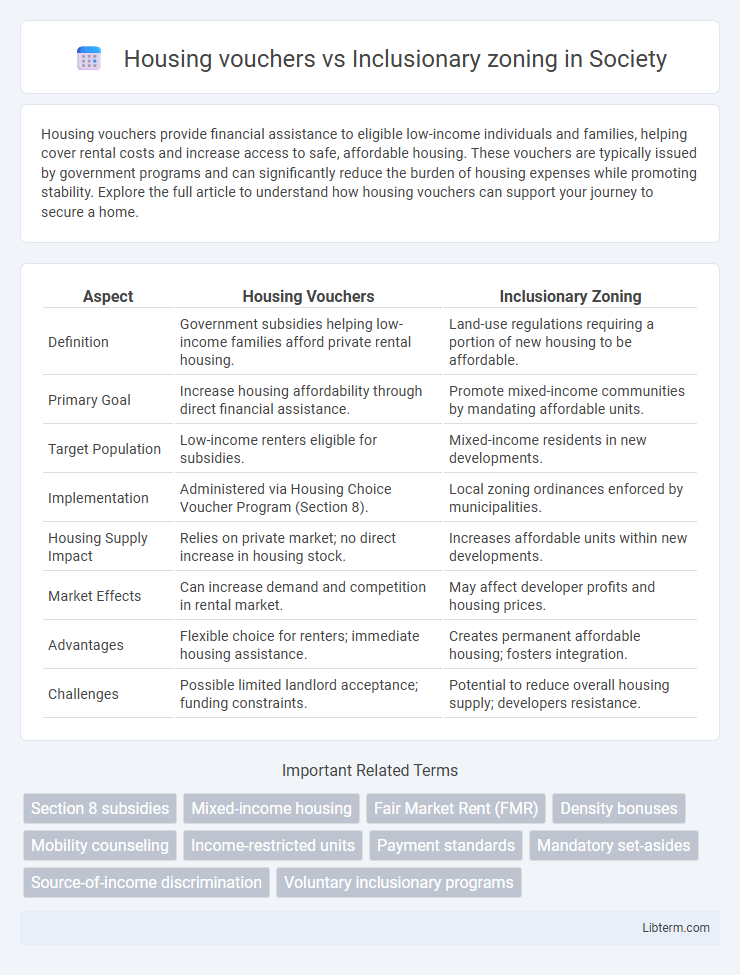
| Aspect | Housing Vouchers | Inclusionary Zoning |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Government subsidies helping low-income families afford private rental housing. | Land-use regulations requiring a portion of new housing to be affordable. |
| Primary Goal | Increase housing affordability through direct financial assistance. | Promote mixed-income communities by mandating affordable units. |
| Target Population | Low-income renters eligible for subsidies. | Mixed-income residents in new developments. |
| Implementation | Administered via Housing Choice Voucher Program (Section 8). | Local zoning ordinances enforced by municipalities. |
| Housing Supply Impact | Relies on private market; no direct increase in housing stock. | Increases affordable units within new developments. |
| Market Effects | Can increase demand and competition in rental market. | May affect developer profits and housing prices. |
| Advantages | Flexible choice for renters; immediate housing assistance. | Creates permanent affordable housing; fosters integration. |
| Challenges | Possible limited landlord acceptance; funding constraints. | Potential to reduce overall housing supply; developers resistance. |
Introduction to Housing Vouchers and Inclusionary Zoning
Housing vouchers provide targeted financial assistance to low-income families, enabling them to afford rent in private-market housing and increase residential mobility. Inclusionary zoning mandates that developers allocate a percentage of new construction units as affordable housing, promoting economic integration within neighborhoods. Both strategies aim to address housing affordability challenges but operate through distinct mechanisms impacting supply and demand.
Defining Housing Vouchers: Key Features
Housing vouchers are government-funded subsidies that help low-income families afford rental housing in the private market by covering a portion of the rent based on income. These vouchers offer flexible housing options without geographical restrictions, enabling recipients to choose any qualifying rental unit. Unlike inclusionary zoning, which mandates affordable units in new developments, housing vouchers directly subsidize tenant costs, promoting housing choice and mobility.
Understanding Inclusionary Zoning Policies
Inclusionary zoning policies require developers to allocate a percentage of new housing units as affordable, directly integrating affordable homes within market-rate projects to promote economically diverse communities. These policies often provide incentives such as density bonuses or expedited permitting to encourage compliance while preserving local housing stock affordability. Housing vouchers, by contrast, subsidize rent for low-income tenants in private markets, but inclusionary zoning ensures long-term affordability tied to the housing supply itself.
Eligibility and Access: Who Benefits?
Housing vouchers primarily benefit low-income families by providing direct financial assistance to access private rental markets, with eligibility often based on income thresholds and family size, ensuring access to safe and affordable housing. Inclusionary zoning benefits a broader community by mandating developers to include a percentage of affordable units in new housing projects, often targeting moderate-income households, though eligibility criteria and access can be more restrictive and location-dependent. Both policies aim to increase housing affordability but differ in scope; vouchers offer personalized support while inclusionary zoning promotes mixed-income neighborhoods.
Impact on Affordable Housing Supply
Housing vouchers increase affordable housing access by subsidizing rents in private market units, enabling low-income households to secure housing immediately without the need for new construction. Inclusionary zoning mandates that a percentage of new residential developments be affordable, directly expanding the affordable housing stock but often facing delays due to development timelines and potential reductions in market-rate units. While vouchers provide flexible and immediate relief for renters, inclusionary zoning contributes to long-term affordable housing supply growth through regulatory requirements.
Cost Effectiveness and Funding Sources
Housing vouchers offer direct financial assistance to low-income families, funded primarily through federal programs like HUD's Housing Choice Voucher program, making them flexible yet reliant on sustained government budgets. Inclusionary zoning requires developers to allocate a percentage of new housing units as affordable, leveraging private investment to create mixed-income communities but often facing higher upfront costs and variable local funding mechanisms. Cost effectiveness varies as vouchers provide immediate relief without new construction costs, whereas inclusionary zoning promotes long-term affordability but may increase housing prices due to developer costs passed to buyers.
Geographic Distribution of Affordable Units
Housing vouchers provide flexible, demand-side subsidies allowing recipients to rent privately-owned units across diverse geographic areas, which can lead to greater spatial integration of affordable housing. Inclusionary zoning mandates developers to include a percentage of affordable units within new residential projects, often concentrating affordable housing in specific neighborhoods with available development opportunities. Geographic distribution of affordable units under inclusionary zoning may be limited by zoning laws and market dynamics, while vouchers promote broader dispersal but depend on landlord participation and local rent levels.
Socioeconomic Integration and Community Outcomes
Housing vouchers provide low-income families direct access to market-rate rental units, promoting socioeconomic integration by enabling choice and mobility across diverse neighborhoods. Inclusionary zoning mandates a percentage of new developments to be affordable, fostering mixed-income communities and encouraging long-term neighborhood diversity. Both strategies impact community outcomes by addressing affordability, but vouchers often yield greater individual agency while inclusionary zoning supports structural integration within housing markets.
Challenges and Criticisms of Each Approach
Housing vouchers face challenges such as limited acceptance by landlords, which restricts tenant mobility and access to high-opportunity neighborhoods, and funding limitations that affect program reach. Inclusionary zoning often encounters criticism for potentially increasing overall housing costs, discouraging private developers, and producing inconsistent affordability levels across jurisdictions. Both approaches struggle with ensuring long-term affordability and equitable access, highlighting the complexity of addressing housing shortages through any single policy.
Policy Comparisons and Future Directions
Housing vouchers provide direct financial assistance to low-income families, enabling more immediate mobility to various neighborhoods, while inclusionary zoning mandates developers to include affordable units within new developments, promoting socioeconomic integration. Policy comparisons highlight that vouchers offer flexibility but depend heavily on funding and market conditions, whereas inclusionary zoning ensures mixed-income communities but may slow development or increase market-rate prices. Future directions emphasize hybrid models combining vouchers with zoning reforms to enhance affordability, sustainability, and equitable access to high-opportunity areas.
Housing vouchers Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com