Social integration fosters a sense of belonging and strengthens community bonds by promoting inclusivity and mutual respect. It enhances opportunities for individuals to contribute meaningfully to society, improving overall well-being and social cohesion. Discover how social integration impacts your life and the ways to cultivate it effectively in the following article.
Table of Comparison
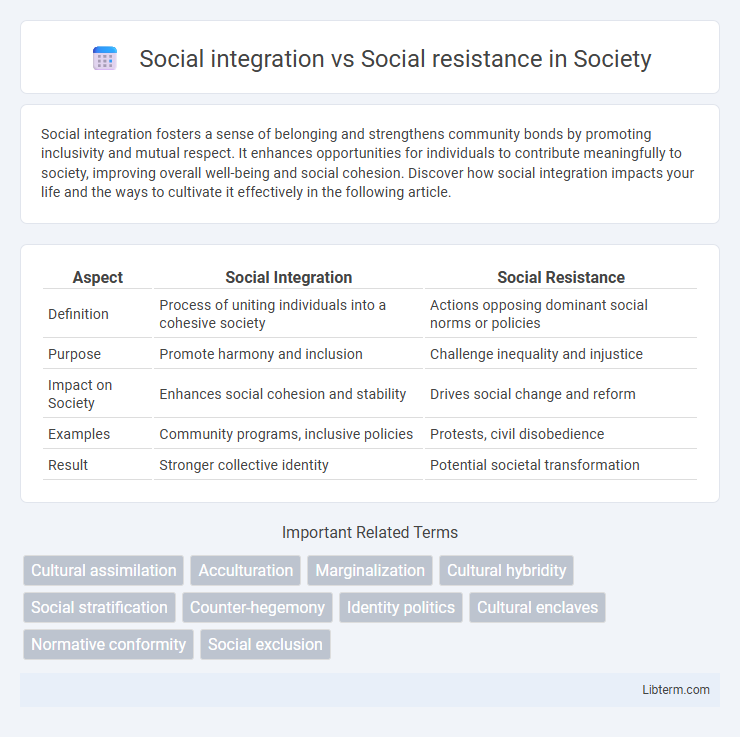
| Aspect | Social Integration | Social Resistance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Process of uniting individuals into a cohesive society | Actions opposing dominant social norms or policies |
| Purpose | Promote harmony and inclusion | Challenge inequality and injustice |
| Impact on Society | Enhances social cohesion and stability | Drives social change and reform |
| Examples | Community programs, inclusive policies | Protests, civil disobedience |
| Result | Stronger collective identity | Potential societal transformation |
Understanding Social Integration
Social integration involves the process of incorporating individuals from diverse backgrounds into a cohesive society by promoting shared values, equal opportunities, and community participation. It enhances social cohesion by reducing inequalities and fostering mutual respect among different social groups. Understanding social integration is crucial for addressing social resistance, which arises when groups oppose changes that threaten their cultural identity or economic status.
Defining Social Resistance
Social resistance refers to the opposition or pushback by individuals or groups against social norms, policies, or changes imposed by dominant social structures. It manifests through protests, boycotts, or passive non-compliance aimed at challenging inequality, marginalization, or cultural domination. Understanding social resistance is crucial for analyzing power dynamics and the agency of marginalized communities within broader social integration processes.
Historical Contexts of Integration and Resistance
Historical contexts of social integration reveal key moments such as the civil rights movement in the United States, where legislative changes like the Civil Rights Act of 1964 fostered the inclusion of African Americans into mainstream society. Conversely, social resistance is exemplified by apartheid in South Africa, where institutionalized racial segregation sparked prolonged global opposition and internal dissent. These historical cases highlight how integration efforts often provoke resistance rooted in entrenched social, political, and economic structures.
Key Factors Influencing Social Integration
Key factors influencing social integration include shared values, effective communication, and inclusive social policies that promote equality and participation. Economic stability and access to education also play crucial roles in fostering a sense of belonging among diverse groups. Conversely, social resistance often arises from cultural differences, discrimination, and unequal resource distribution, which hinder collective cohesion.
Drivers of Social Resistance in Modern Societies
Social resistance in modern societies is primarily driven by factors such as economic inequality, cultural differences, and political polarization. Marginalized groups often resist dominant social norms due to perceived exclusion and lack of representation in decision-making processes. Furthermore, rapid technological changes and globalization can exacerbate feelings of insecurity, fueling social movements that challenge established institutions.
Benefits of Social Integration for Communities
Social integration enhances community cohesion by fostering mutual understanding, reducing social barriers, and promoting inclusivity among diverse groups. It leads to improved economic opportunities, better health outcomes, and increased civic participation, contributing to overall community resilience. Strong social integration encourages collaboration and resource sharing, which helps address social challenges effectively and supports sustainable community development.
Challenges and Consequences of Social Resistance
Social resistance presents significant challenges such as increased social fragmentation, reduced community cohesion, and the perpetuation of inequalities. It often leads to marginalization, social exclusion, and heightened tensions between different groups, undermining efforts toward collective progress. Persistent resistance can also impede policy implementation and economic development, exacerbating disparities within society.
Case Studies: Successful Social Integration
Case studies of successful social integration often highlight community-led initiatives that foster inclusive environments through education, employment opportunities, and cultural exchange programs. For instance, the integration of refugees in Canada demonstrates how coordinated support systems, including language training and workforce integration, reduce social resistance and promote cohesion. Empirical data from these cases reveal increased social capital and reduced instances of discrimination, emphasizing the effectiveness of proactive policies in overcoming social barriers.
Balancing Integration and Resistance in Policy Making
Balancing integration and resistance in policy making requires adaptive strategies that address diverse social needs while preserving cultural identities and values. Effective policies promote social cohesion by facilitating inclusion and equitable resource distribution, yet they must also respect the legitimate concerns of groups resisting integration due to historical, economic, or ideological factors. Data-driven approaches that incorporate stakeholder engagement and continuous evaluation optimize the harmony between social integration efforts and resistance management, fostering sustainable societal development.
Future Perspectives on Social Cohesion
Future perspectives on social cohesion emphasize balancing social integration and social resistance as dynamic forces shaping inclusive societies. Social integration promotes unity and collective identity through shared values and equitable participation, while social resistance challenges injustices and fosters critical dialogue essential for democratic progress. Advancing social cohesion requires adaptive policies that recognize the interplay between integration and resistance to create resilient, diverse, and harmonious communities.
Social integration Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com