Class consciousness shapes how individuals perceive their social position and economic interests within society. It influences collective action by uniting people with shared experiences and goals, often fueling movements for social change. Explore the rest of the article to understand how developing your class consciousness can impact social dynamics and empowerment.
Table of Comparison
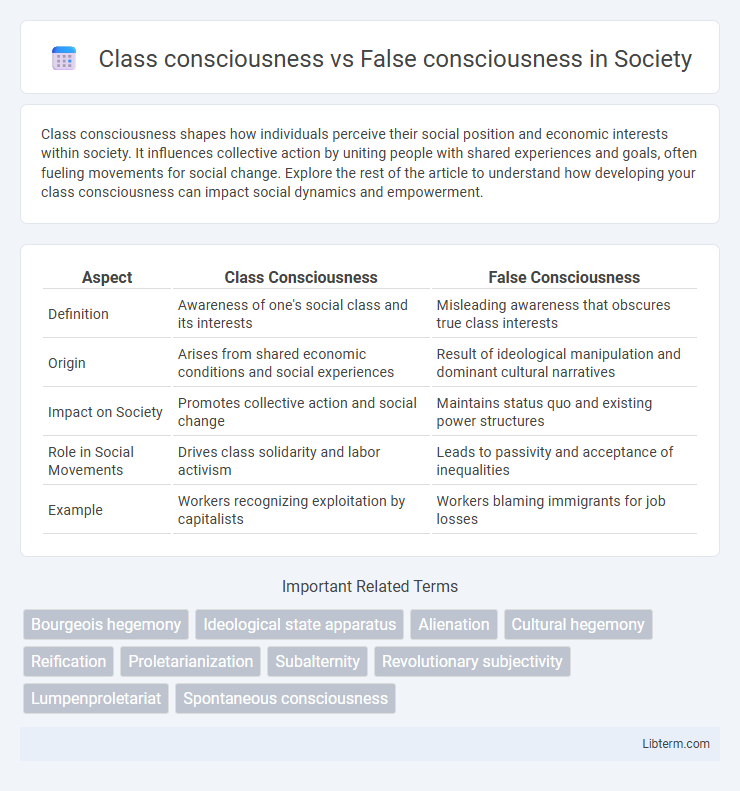
| Aspect | Class Consciousness | False Consciousness |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Awareness of one's social class and its interests | Misleading awareness that obscures true class interests |
| Origin | Arises from shared economic conditions and social experiences | Result of ideological manipulation and dominant cultural narratives |
| Impact on Society | Promotes collective action and social change | Maintains status quo and existing power structures |
| Role in Social Movements | Drives class solidarity and labor activism | Leads to passivity and acceptance of inequalities |
| Example | Workers recognizing exploitation by capitalists | Workers blaming immigrants for job losses |
Understanding Class Consciousness: A Fundamental Overview
Class consciousness refers to the awareness members of a social class have about their shared interests and collective position within the class structure, driving collective action for social change. False consciousness occurs when subordinate classes adopt the ideology of the dominant class, obscuring their real conditions and perpetuating social inequalities. Understanding class consciousness is crucial for analyzing social dynamics, power relations, and the potential for class-based political mobilization.
Defining False Consciousness: Concepts and Origins
False consciousness refers to a distorted understanding of one's social class and the systemic oppression that hinders the proletariat from recognizing their exploitation under capitalism. Rooted in Marxist theory, this concept explains how dominant ideologies shape individuals' beliefs, leading the working class to accept and perpetuate their subjugation. The origins of false consciousness lie in the manipulation of cultural, political, and ideological institutions that mask the realities of class struggle and maintain bourgeois hegemony.
Historical Roots: Marxism and the Development of Consciousness Theories
Class consciousness originates from Marxist theory, describing the awareness of one's social class and its interests in the struggle against exploitation and oppression. False consciousness refers to the distorted understanding that obscures the realities of class relations, often perpetuated by dominant ideologies to maintain the status quo. Historical development of consciousness theories in Marxism emphasizes the transition from false to class consciousness as a critical step in achieving revolutionary change and social emancipation.
Key Differences Between Class Consciousness and False Consciousness
Class consciousness refers to the awareness of one's social class and the collective interests and struggles associated with it, enabling individuals to recognize economic inequalities and mobilize for social change. False consciousness occurs when individuals adopt misleading beliefs that obscure their true class interests, often internalizing dominant ideologies that perpetuate exploitation and hinder collective action. The key difference lies in class consciousness fostering critical awareness and unity among oppressed groups, whereas false consciousness promotes acceptance of existing social hierarchies and prevents collective resistance.
The Role of Ideology in Shaping Social Awareness
Ideology plays a crucial role in shaping class consciousness by influencing how individuals perceive their social position and collective interests. False consciousness arises when dominant ideologies manipulate beliefs, causing workers to misinterpret their exploitation and align with ruling class interests. This distortion hinders the development of true class consciousness necessary for effective social change and collective action.
Media Influence: Propagating False Consciousness
Media influence plays a crucial role in propagating false consciousness by shaping public perception to align with dominant class interests, often masking the realities of exploitation and inequality faced by subordinate classes. Through selective framing, repetition of ideologies, and omission of dissenting perspectives, mass media consolidates support for the status quo, hindering class consciousness development. This manipulation diverts attention from systemic issues, fostering acceptance of social hierarchies as natural and inevitable rather than as constructs that can be challenged.
Education and the Awakening of Class Consciousness
Education plays a crucial role in awakening class consciousness by providing individuals with critical awareness of their socioeconomic conditions and the structural inequalities that shape their lives. False consciousness emerges when education is limited or ideologically skewed, causing individuals to unknowingly accept dominant class interests as their own and overlook systemic exploitation. Developing critical pedagogy and promoting social awareness through inclusive curricula empower oppressed classes to recognize their collective interests and mobilize for socioeconomic change.
Real-World Examples: Manifestations in Contemporary Society
Class consciousness emerges when workers recognize their shared interests and unite to challenge economic inequalities, as seen in recent labor union movements advocating for fair wages and workplace rights globally. False consciousness manifests when individuals mistakenly identify with upper-class values, such as gig economy workers supporting deregulation that ultimately undermines their job security and benefits. Contemporary political polarization often reflects these dynamics, where media influence and consumer culture perpetuate false consciousness, hindering collective action for systemic change.
Overcoming False Consciousness: Pathways to Class Solidarity
Overcoming false consciousness involves raising awareness about the real conditions of socioeconomic inequality and exploitation that shape working-class life. Educational initiatives and critical media literacy empower individuals to recognize their shared interests and resist dominant ideologies that mask class antagonisms. Developing class solidarity requires collective action, fostering unity through labor movements, community organizing, and political engagement that challenge systemic power structures.
The Future of Class Consciousness in a Changing Economic Landscape
The future of class consciousness in a changing economic landscape hinges on the ability of workers to recognize shared interests amid growing economic inequality and labor market fragmentation. Advances in technology and globalization have reshaped class dynamics, making traditional class identities less clear and increasing the risk of false consciousness as individuals internalize dominant ideologies that obscure collective exploitation. Emerging social movements and digital platforms offer new avenues for fostering genuine class awareness by amplifying marginalized voices and challenging dominant economic narratives.
Class consciousness Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com