Frugality means making careful decisions about how you spend your money to maximize savings and avoid waste. Embracing frugality can improve your financial health by encouraging smart budgeting, reducing unnecessary expenses, and fostering long-term financial stability. Explore the article to learn practical tips and strategies to incorporate frugality into your daily life.
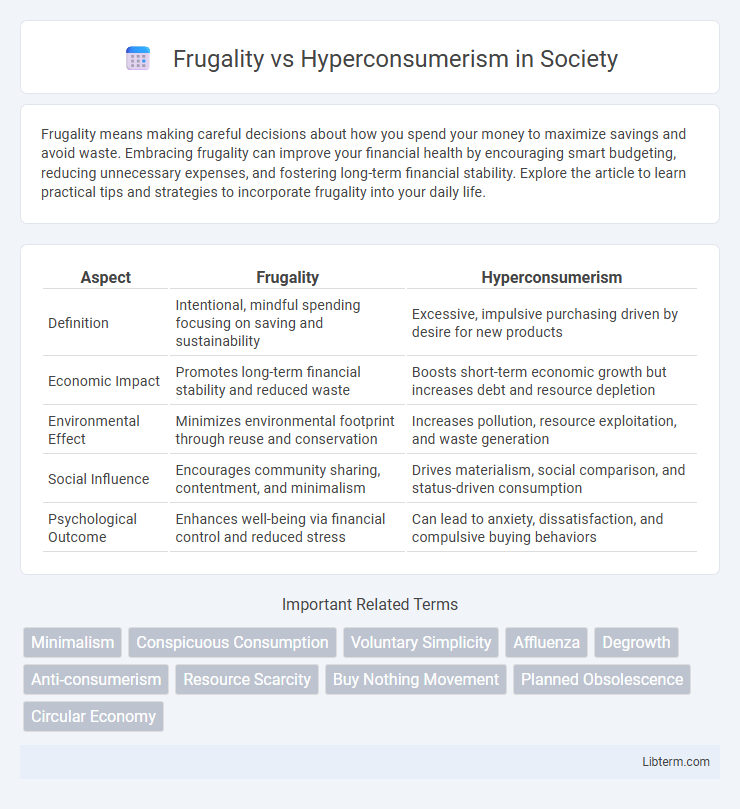
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Frugality | Hyperconsumerism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Intentional, mindful spending focusing on saving and sustainability | Excessive, impulsive purchasing driven by desire for new products |
| Economic Impact | Promotes long-term financial stability and reduced waste | Boosts short-term economic growth but increases debt and resource depletion |
| Environmental Effect | Minimizes environmental footprint through reuse and conservation | Increases pollution, resource exploitation, and waste generation |
| Social Influence | Encourages community sharing, contentment, and minimalism | Drives materialism, social comparison, and status-driven consumption |
| Psychological Outcome | Enhances well-being via financial control and reduced stress | Can lead to anxiety, dissatisfaction, and compulsive buying behaviors |
Understanding Frugality: Philosophy and Practice
Frugality embraces mindful consumption by prioritizing essential needs and sustainable resource use, aiming to reduce waste and financial stress. This philosophy encourages deliberate spending, valuing quality over quantity and cultivating habits that promote long-term savings and environmental responsibility. Practicing frugality often involves detailed budgeting, thoughtful decision-making, and resisting impulsive purchases that characterize hyperconsumerism's excessive consumption patterns.
Hyperconsumerism Defined: Causes and Consequences
Hyperconsumerism is characterized by excessive and compulsive purchasing behavior driven by societal pressures, aggressive advertising, and the constant desire for status and novelty. This phenomenon leads to significant environmental degradation, resource depletion, and increased waste generation, exacerbating global sustainability challenges. Economic consequences include inflated personal debt levels and the perpetuation of materialistic values that undermine long-term financial stability and well-being.
Cultural Drivers Behind Spending and Saving
Cultural drivers behind spending and saving significantly influence frugality and hyperconsumerism, with societal values shaping financial behaviors and priorities. In cultures emphasizing communal well-being and long-term security, frugality becomes a socially reinforced virtue, encouraging saving and mindful consumption. Conversely, consumerist cultures prioritize material success and instant gratification, driving hyperconsumerism through status signaling and aggressive marketing tactics.
Environmental Impact: Frugality vs Hyperconsumerism
Frugality significantly reduces environmental impact by minimizing waste, conserving resources, and lowering carbon emissions through mindful consumption and reuse. Hyperconsumerism drives extensive resource depletion, increased pollution, and higher greenhouse gas emissions due to mass production and excessive waste generation. Adopting frugal habits supports sustainability goals by promoting reduced energy use and less landfill burden compared to the environmentally harmful effects of hyperconsumerist lifestyles.
Mental Health Implications of Each Lifestyle
Frugality promotes mental well-being by fostering mindfulness, reducing financial stress, and encouraging intentional consumption, which leads to greater life satisfaction and decreased anxiety. In contrast, hyperconsumerism often correlates with heightened stress, compulsive buying behaviors, and diminished self-esteem due to constant social comparison and material accumulation. Understanding the mental health implications of these lifestyles highlights the psychological benefits of frugality over the potentially detrimental effects of hyperconsumerist habits.
Social Pressures and Media Influence
Social pressures and media influence significantly shape consumer behavior, often driving hyperconsumerism by promoting material wealth as a status symbol. Advertisements and social media platforms exploit psychological triggers, encouraging impulsive purchases and the constant desire for the latest products. In contrast, frugality emphasizes mindful consumption, resisting societal pressures by valuing long-term financial stability and sustainable living over immediate gratification.
Financial Freedom: Building Wealth vs Chasing Trends
Frugality emphasizes disciplined saving and mindful spending, allowing individuals to accumulate wealth and achieve financial freedom by prioritizing long-term goals over impulsive purchases. Hyperconsumerism, driven by constantly chasing trends and instant gratification, often leads to debt and financial instability due to excessive and unnecessary spending. Building wealth through frugality involves strategic investments and creating sustainable income streams, contrasting sharply with the short-term mindset fueled by consumer culture.
Practical Tips: Embracing Frugal Living
Embracing frugal living involves prioritizing needs over wants by creating a budget that tracks expenses and reduces unnecessary spending. Practical tips include meal planning to minimize food waste, buying quality items that last longer, and utilizing secondhand stores or community swaps. These strategies help build sustainable habits that counteract hyperconsumerism and promote financial stability.
Balancing Enjoyment and Responsibility
Balancing enjoyment and responsibility requires integrating frugality principles with mindful consumption habits, emphasizing quality over quantity to reduce waste and environmental impact. By prioritizing sustainable choices and setting clear financial goals, individuals can enjoy life's pleasures without succumbing to hyperconsumerism's excesses. This balance fosters long-term financial stability and promotes a healthier planet through conscious spending and resourcefulness.
Shaping the Future: Sustainable Choices for a Better World
Frugality emphasizes mindful consumption and resource conservation, directly reducing environmental impact and fostering long-term sustainability. Hyperconsumerism drives excessive demand for short-lived goods, leading to increased waste and depletion of natural resources. Prioritizing frugal habits and sustainable choices can shape a future with healthier ecosystems and more resilient economies.
Frugality Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com