Folkways are informal social norms that guide everyday behavior in communities, reflecting cultural values and traditions without strict enforcement. These unwritten rules influence interactions, dress codes, and manners, shaping social cohesion and identity. Explore the article to understand how your actions are subtly shaped by these powerful cultural forces.
Table of Comparison
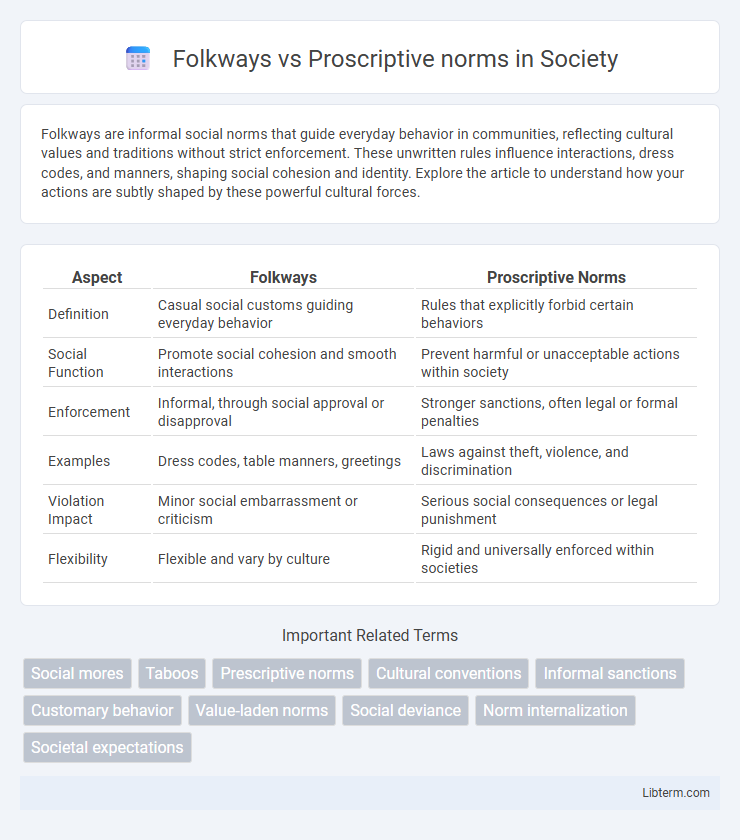
| Aspect | Folkways | Proscriptive Norms |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Casual social customs guiding everyday behavior | Rules that explicitly forbid certain behaviors |
| Social Function | Promote social cohesion and smooth interactions | Prevent harmful or unacceptable actions within society |
| Enforcement | Informal, through social approval or disapproval | Stronger sanctions, often legal or formal penalties |
| Examples | Dress codes, table manners, greetings | Laws against theft, violence, and discrimination |
| Violation Impact | Minor social embarrassment or criticism | Serious social consequences or legal punishment |
| Flexibility | Flexible and vary by culture | Rigid and universally enforced within societies |
Understanding Social Norms: Folkways and Proscriptive Norms
Folkways represent informal social rules that guide everyday behavior, such as dress codes or table manners, reflecting cultural preferences without strict enforcement. Proscriptive norms explicitly forbid certain actions, like theft or violence, and carry clear social sanctions when violated. Understanding social norms involves recognizing how folkways allow flexibility in social interactions, while proscriptive norms maintain essential societal order by preventing harmful behaviors.
Defining Folkways: Everyday Customs in Society
Folkways are informal norms that govern everyday behaviors and customs, reflecting the routine practices accepted by a society without being strictly enforced by law. They guide actions such as greetings, dress codes, and table manners, promoting social cohesion by establishing expected conduct in daily interactions. Unlike proscriptive norms, which explicitly forbid certain behaviors, folkways are more flexible and typically elicit mild social disapproval when violated.
What Are Proscriptive Norms? Rules of Prohibition
Proscriptive norms are societal rules that explicitly forbid certain behaviors to maintain social order and prevent harm, functioning as clear prohibitions within a culture. These norms dictate what individuals should not do, contrasting with folkways that guide routine or customary conduct without severe consequences. Violating proscriptive norms often results in social sanctions or legal penalties, emphasizing their critical role in regulating unacceptable or harmful actions in a community.
Key Differences between Folkways and Proscriptive Norms
Folkways are informal social rules that guide everyday behavior and promote social acceptance without severe consequences for violations, while proscriptive norms explicitly forbid certain actions and impose penalties or sanctions when breached. Folkways primarily regulate routine interactions like dress codes and manners, whereas proscriptive norms address behaviors that are morally or legally unacceptable, such as prohibitions against theft or violence. The key difference lies in enforcement intensity: folkways maintain social order through subtle societal pressure, whereas proscriptive norms rely on formal or informal sanctions to prevent harmful conduct.
Examples of Folkways in Daily Life
Folkways are informal social norms that govern everyday behavior, such as dress codes, table manners, and greetings, reflecting cultural habits without strict enforcement. Examples of folkways include saying "please" and "thank you," holding the door open for others, and dressing appropriately for different occasions, which help maintain social harmony. Unlike proscriptive norms that explicitly forbid certain actions, folkways encourage customary practices that vary across societies.
Examples of Proscriptive Norms in Society
Proscriptive norms explicitly forbid behaviors deemed unacceptable in society, such as laws against theft, prohibitions on assault, and workplace rules against discrimination. These norms guide individuals on actions to avoid to maintain social order and harmony by clearly outlining penalties for violations. Examples include traffic laws forbidding running red lights, school rules banning cheating, and social taboos against public nudity.
The Social Significance of Folkways
Folkways guide everyday social behavior, shaping cultural identity and reinforcing community cohesion through tacit expectations. Their social significance lies in promoting predictable interactions and social harmony without formal sanctions, distinguishing them from proscriptive norms that explicitly forbid certain actions. By normalizing routine practices, folkways sustain group values and facilitate social integration within societies.
Consequences of Violating Proscriptive Norms
Violating proscriptive norms, which dictate behaviors that are forbidden, typically results in more severe social sanctions compared to breaking folkways, such as gossip, ostracism, or legal penalties. These norms are essential for maintaining moral order and social cohesion, so their breach can lead to damaged reputations, loss of trust, or formal punishment. The consequences emphasize the importance society places on prohibiting harmful or unethical actions, highlighting the role of proscriptive norms in regulating behavior.
Folkways vs Proscriptive Norms: Their Role in Social Order
Folkways govern everyday social behaviors and customs, guiding individuals on polite and acceptable conduct without strict enforcement, while proscriptive norms explicitly prohibit certain actions to prevent harm and maintain moral order. The distinction between these norms plays a crucial role in social order by balancing routine social expectations with clear boundaries that protect community welfare. Understanding this balance helps sociologists analyze how societies maintain cohesion through both informal customs and formal prohibitions.
Adapting to Social Change: Evolution of Norms
Folkways represent informal social customs that guide everyday behavior, evolving gradually as societies adapt to cultural shifts and new social trends. Proscriptive norms, which explicitly prohibit certain actions, tend to change more slowly due to their role in maintaining social order and preventing harm. The evolution of both types of norms reflects a dynamic balance between innovation and tradition, as communities negotiate acceptable conduct in response to social change.
Folkways Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com