Sustainable consumption focuses on using resources efficiently to minimize environmental impact while meeting current needs. It encourages you to adopt eco-friendly practices such as reducing waste, choosing sustainable products, and supporting responsible companies. Discover practical tips and insights to transform your habits for a greener future by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
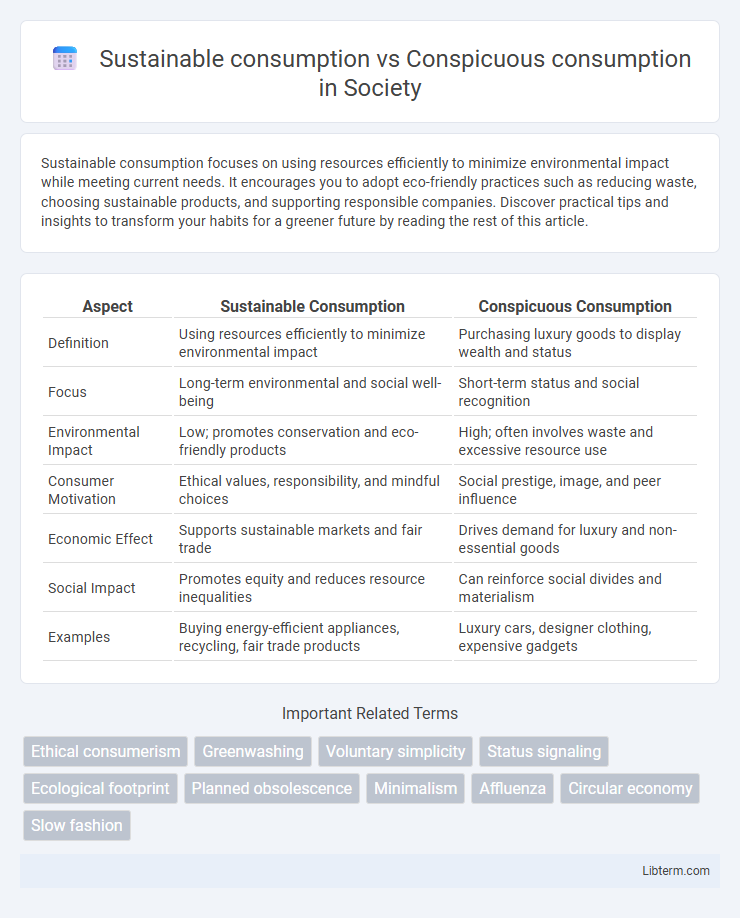
| Aspect | Sustainable Consumption | Conspicuous Consumption |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Using resources efficiently to minimize environmental impact | Purchasing luxury goods to display wealth and status |
| Focus | Long-term environmental and social well-being | Short-term status and social recognition |
| Environmental Impact | Low; promotes conservation and eco-friendly products | High; often involves waste and excessive resource use |
| Consumer Motivation | Ethical values, responsibility, and mindful choices | Social prestige, image, and peer influence |
| Economic Effect | Supports sustainable markets and fair trade | Drives demand for luxury and non-essential goods |
| Social Impact | Promotes equity and reduces resource inequalities | Can reinforce social divides and materialism |
| Examples | Buying energy-efficient appliances, recycling, fair trade products | Luxury cars, designer clothing, expensive gadgets |
Understanding Sustainable Consumption
Sustainable consumption involves using products and resources in ways that minimize environmental impact, conserve natural resources, and promote social equity. It emphasizes durability, energy efficiency, and ethical production practices to reduce waste and pollution. Understanding sustainable consumption is vital for fostering responsible consumer behavior that supports long-term ecological balance and economic resilience.
Defining Conspicuous Consumption
Conspicuous consumption refers to the practice of purchasing goods and services to publicly display wealth and social status rather than for intrinsic value or utility. This behavior often leads to excessive and wasteful spending, prioritizing appearance over sustainability. In contrast, sustainable consumption emphasizes mindful use of resources, minimizing environmental impact and promoting long-term well-being.
Core Differences Between Sustainable and Conspicuous Consumption
Sustainable consumption emphasizes minimizing environmental impact by using resources efficiently, choosing eco-friendly products, and supporting ethical practices, whereas conspicuous consumption prioritizes acquiring luxury goods to display social status and wealth. The core difference lies in the motivation: sustainable consumption focuses on long-term ecological balance and social responsibility, while conspicuous consumption centers on immediate social recognition and materialistic values. Sustainable consumers often prefer durability and resource conservation, contrasting sharply with the wastefulness and excess associated with conspicuous consumer behavior.
Environmental Impact of Consumption Choices
Sustainable consumption reduces environmental impact by minimizing resource depletion and greenhouse gas emissions through thoughtful purchasing of eco-friendly products and services. In contrast, conspicuous consumption drives excessive waste and pollution by prioritizing status and materialism over ecological responsibility. Choosing sustainable options supports conservation efforts and reduces the carbon footprint associated with production and disposal.
Social Consequences of Consumption Behavior
Sustainable consumption promotes social equity by encouraging mindful resource use and reducing environmental harm, fostering community well-being and long-term societal health. Conspicuous consumption often exacerbates social inequality by emphasizing status and materialism, leading to social division and increased pressure to conform to consumerist norms. The contrasting consumption behaviors impact social cohesion, with sustainable practices supporting collective responsibility and conspicuous spending contributing to social stratification.
Role of Marketing in Shaping Consumption Patterns
Marketing strategies heavily influence sustainable consumption by promoting eco-friendly products and ethical brand values, encouraging consumers to prioritize environmental and social responsibility. In contrast, marketing that emphasizes status, luxury, and exclusivity fosters conspicuous consumption by appealing to consumers' desires for social recognition and prestige. The role of marketing in shaping consumption patterns lies in its ability to frame products and lifestyles either as sustainable choices or symbols of wealth and social status.
Economic Implications of Sustainable vs Conspicuous Consumption
Sustainable consumption prioritizes long-term economic resilience by reducing waste, promoting resource efficiency, and supporting circular economies, which can lower costs and create new market opportunities. In contrast, conspicuous consumption often leads to short-term economic stimulation through high-volume, status-driven spending but results in resource depletion, increased environmental costs, and economic inefficiencies. Policymakers aiming for sustainable growth focus on incentivizing sustainable consumption patterns to enhance economic stability and reduce negative externalities associated with conspicuous consumption.
Consumer Psychology and Decision-Making
Sustainable consumption reflects consumer psychology driven by values such as environmental concern and long-term well-being, leading to decisions that prioritize eco-friendly products and resource conservation. Conspicuous consumption, on the other hand, is motivated by social status and identity signaling, where consumers choose luxury or branded goods to display wealth and prestige. Decision-making in these contexts differs as sustainable consumers engage in reflective, ethical evaluation, while conspicuous consumers often rely on emotional and social cues to guide purchases.
Strategies for Promoting Sustainable Consumption
Sustainable consumption strategies emphasize reducing waste, promoting eco-friendly products, and encouraging mindful purchasing behaviors that prioritize long-term environmental benefits. These approaches include implementing educational campaigns, incentivizing green product choices through subsidies or certifications, and fostering circular economy practices such as recycling and product reuse. In contrast to conspicuous consumption, which drives demand through status and luxury appeal, sustainable consumption focuses on responsible resource use and minimizing ecological footprints.
Future Trends in Consumption and Sustainability
Future trends indicate a significant shift toward sustainable consumption driven by increasing environmental awareness and regulatory pressures, prioritizing eco-friendly products and circular economy practices. Conspicuous consumption is expected to evolve, embedding sustainability as a status symbol, where consumers prefer brands demonstrating social responsibility and transparency. Advances in digital technology and data analytics enable personalized sustainable choices, fostering long-term behavioral changes towards reducing waste and resource depletion.
Sustainable consumption Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com