Social norms shape behavior by defining accepted and expected actions within a community or society. These unwritten rules influence how individuals interact, make decisions, and maintain social order. Discover how understanding social norms can enhance your interactions and social awareness in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
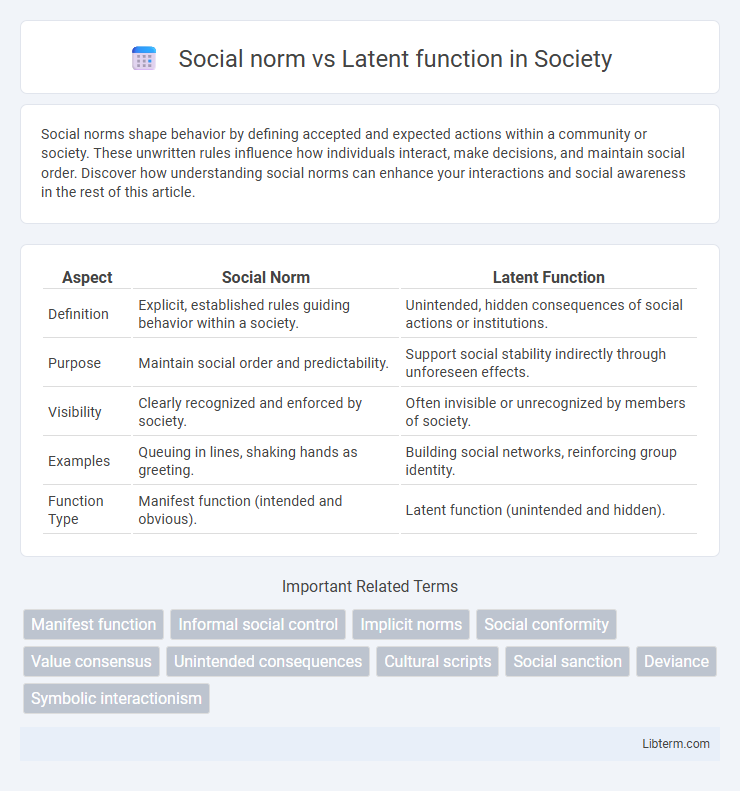
| Aspect | Social Norm | Latent Function |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Explicit, established rules guiding behavior within a society. | Unintended, hidden consequences of social actions or institutions. |
| Purpose | Maintain social order and predictability. | Support social stability indirectly through unforeseen effects. |
| Visibility | Clearly recognized and enforced by society. | Often invisible or unrecognized by members of society. |
| Examples | Queuing in lines, shaking hands as greeting. | Building social networks, reinforcing group identity. |
| Function Type | Manifest function (intended and obvious). | Latent function (unintended and hidden). |
Understanding Social Norms: Definition and Examples
Social norms are established behavioral expectations within a society that guide individuals on acceptable conduct, such as shaking hands when greeting or queuing in public. Latent functions refer to the unintended or hidden consequences of social norms, including the reinforcement of social cohesion or the establishment of power dynamics. Understanding social norms involves examining both their explicit roles and latent effects, which shape social interactions and cultural continuity.
Exploring Latent Functions in Society
Latent functions in society refer to the unintended and often hidden consequences of social norms and institutions that contribute to social stability and cohesion. These functions may include the reinforcement of social networks, the transmission of cultural values, or the creation of social roles that are not explicitly acknowledged. Understanding latent functions helps reveal the deeper social dynamics behind routine behaviors and institutional practices, highlighting how social norms operate beyond their manifest purposes.
Theoretical Foundations: Social Norms vs Latent Functions
Social norms represent the explicit, shared rules that guide individual behavior within a society, reinforcing social order through conformity and collective expectations, as emphasized in structural functionalism. Latent functions, introduced by sociologist Robert K. Merton, refer to the unintended, often hidden consequences of social actions or institutions that contribute to social stability or change without being overtly recognized. While social norms are consciously upheld and directly influence behavior, latent functions operate beneath the surface, revealing deeper, indirect impacts that help maintain the complex dynamics of social systems.
Social Control: How Norms Regulate Behavior
Social norms serve as unwritten rules that guide individual behavior within a society, establishing expectations for conformity and promoting social control through shared values and standards. Latent functions, though unintended, often reinforce these norms by creating indirect social pressures that maintain order and cohesion. Together, social norms and latent functions regulate behavior by sustaining predictable interactions and deterring deviance, essential for societal stability.
Hidden Purposes: Identifying Latent Functions
Latent functions refer to the hidden, unintended purposes of social norms that maintain social stability and cohesion beyond their explicit goals. These underlying effects, such as reinforcing social hierarchies or promoting group solidarity, often remain unnoticed but play a crucial role in societal functioning. Identifying latent functions requires analyzing social behaviors and institutions beyond their manifest intentions to uncover deeper social mechanisms.
Social Norms and Unintended Consequences
Social norms guide individual behavior by establishing shared expectations within a community, promoting social order and predictability. Latent functions refer to the unintended consequences of social actions, where adherence to social norms can lead to unforeseen effects such as reinforcing inequalities or creating resistance to change. Understanding the relationship between social norms and latent functions reveals how routine behaviors may perpetuate social structures beyond their explicit purposes.
Case Studies: Norms and Latent Functions in Everyday Life
Case studies examining social norms and latent functions reveal how everyday behaviors fulfill both explicit expectations and underlying purposes. For example, workplace dress codes enforce visible professionalism (social norm) while also promoting group identity and cohesion (latent function). Similarly, rituals like holiday gatherings uphold cultural traditions and simultaneously strengthen familial bonds and social networks, illustrating the dual impact of norms and latent functions in daily life.
The Role of Institutions in Shaping Social Norms
Institutions play a crucial role in shaping social norms by establishing formal rules and expectations that guide individual behavior within society. Through mechanisms such as laws, educational systems, and religious organizations, institutions reinforce both explicit social norms and latent functions, which are unintended, often hidden consequences of social actions. The interplay between institutional frameworks and social norms ensures social order, stability, and the gradual evolution of cultural practices.
Comparing Manifest and Latent Functions in Social Contexts
Social norms represent explicit, recognized behaviors that guide societal interactions, aligning closely with manifest functions, which are the intended and obvious consequences of social actions. Latent functions, by contrast, involve unintended or hidden outcomes that emerge from social norms, influencing group cohesion or social stability without being openly acknowledged. Comparing manifest and latent functions highlights how social norms simultaneously fulfill overt social purposes while producing subtle, often unrecognized effects that shape social dynamics.
Implications for Social Change and Policy
Social norms, as explicit behavioral expectations, directly shape community interactions and influence policy frameworks by promoting stability and conformity, while latent functions reveal unintended consequences that can either hinder or facilitate social change. Understanding latent functions allows policymakers to anticipate hidden social dynamics, enabling the design of adaptive interventions that address underlying issues beyond surface-level behaviors. Integrating insights about both social norms and latent functions enhances the capacity to craft effective policies that foster sustainable social transformation.
Social norm Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com