Kinship and friendship both play vital roles in shaping social bonds and emotional support systems within human relationships. Kinship often involves familial ties defined by blood or legal connections, while friendship is based on mutual affection and trust beyond family. Discover how understanding these dynamics can enrich Your relationships by exploring the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
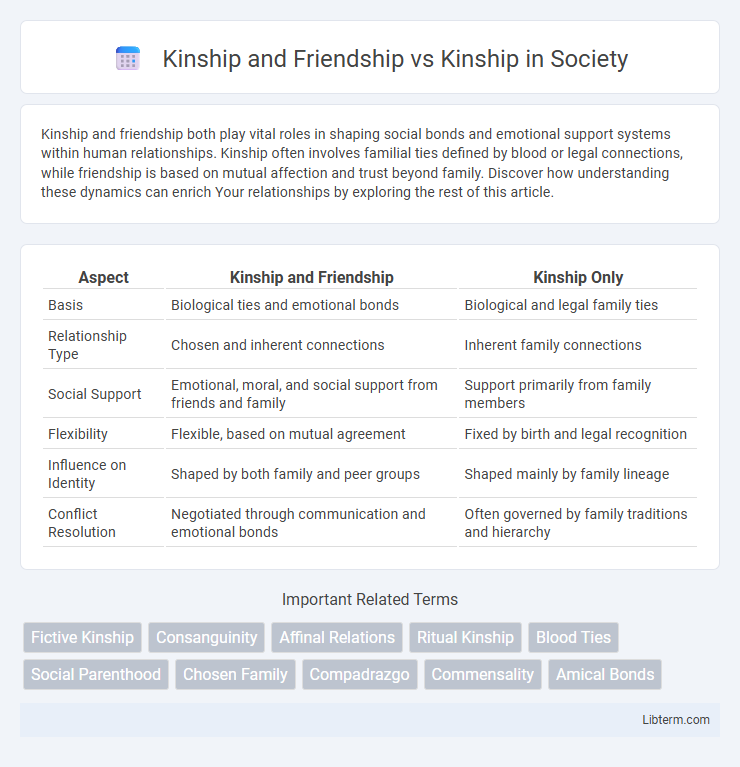
| Aspect | Kinship and Friendship | Kinship Only |
|---|---|---|
| Basis | Biological ties and emotional bonds | Biological and legal family ties |
| Relationship Type | Chosen and inherent connections | Inherent family connections |
| Social Support | Emotional, moral, and social support from friends and family | Support primarily from family members |
| Flexibility | Flexible, based on mutual agreement | Fixed by birth and legal recognition |
| Influence on Identity | Shaped by both family and peer groups | Shaped mainly by family lineage |
| Conflict Resolution | Negotiated through communication and emotional bonds | Often governed by family traditions and hierarchy |
Understanding Kinship: Definition and Importance
Kinship refers to the web of social relationships derived from blood ties, marriage, or adoption, forming the foundation of family structures and social organization. Understanding kinship is vital for analyzing inheritance, lineage, and cultural norms within societies, as it influences identity and social obligations. Friendship, while voluntary and based on personal choice, lacks the formalized roles and legal significance embedded in kinship systems.
The Concept of Friendship in Human Relationships
Friendship in human relationships represents a voluntary bond characterized by mutual trust, emotional support, and shared experiences, contrasting with kinship, which is defined by biological or legal connections. Unlike kinship, friendship offers flexibility in social alliances and plays a crucial role in social networking and personal well-being. This distinction highlights friendship as a dynamic and intentional form of kinship that expands social integration beyond hereditary ties.
Distinguishing Kinship from Friendship
Kinship is defined by biological or legal relationships, establishing family bonds through blood, marriage, or adoption, whereas friendship is based on voluntary emotional connections and mutual interests. Kinship often involves obligations and social norms tied to lineage and inheritance, while friendship relies on trust, shared experiences, and personal choice without legal or genetic ties. Distinguishing kinship from friendship highlights the structured, often duty-bound nature of family relationships compared to the fluid, choice-driven dynamics of friendships.
Role of Kinship in Social Structure
Kinship forms the foundation of social structure by establishing recognized family ties that dictate roles, responsibilities, and inheritance within communities. Unlike friendship, which is voluntary and flexible, kinship networks provide stability and continuity through generations, influencing social organization and resource distribution. Kinship systems define lineage, marital alliances, and social status, reinforcing societal cohesion and cultural norms.
The Evolution of Kinship and Friendship Ties
Kinship and friendship ties have evolved distinctly, with kinship rooted in biological and legal connections that historically structured social organization, inheritance, and mutual obligations. Friendship ties, emerging from shared interests, trust, and reciprocity, have expanded social networks beyond kin groups, enabling adaptive cooperation in diverse societies. This evolution reflects the dynamic interplay between inherited social roles and voluntary, affective bonds shaping social cohesion and individual identity.
Mutual Obligations: Kinship vs Friendship
Kinship relationships are defined by strong mutual obligations rooted in biological ties, legal bonds, and cultural expectations, ensuring ongoing support and responsibility among family members. Friendship, while often voluntary and emotionally driven, generally involves flexible mutual obligations based on trust, shared experiences, and personal commitment rather than formal duties. The key distinction lies in kinship's institutionalized responsibilities contrasted with friendship's negotiated and situational support system.
Cultural Perspectives on Kinship and Friendship
Cultural perspectives on kinship emphasize formalized, often blood-based relationships that dictate social roles and obligations, while friendship is typically viewed as a voluntary and flexible bond shaped by personal choice and shared experiences. In many societies, kinship structures influence inheritance, social status, and community cohesion, contrasting with friendship networks that prioritize emotional support and reciprocity. Understanding these distinctions highlights how cultures balance collective family responsibilities with individual social freedoms.
Emotional Bonds: Comparing Kinship and Friendship
Kinship relationships are often characterized by inherent emotional bonds rooted in shared ancestry and familial obligations, providing a foundation of loyalty and support. Friendship, however, is based on mutual affection, trust, and voluntary connection, frequently offering emotional intimacy that can rival or exceed kinship ties. Both kinship and friendship play crucial roles in emotional well-being, with friendships compensating for weaker or absent familial bonds.
Kinship, Friendship, and Community Building
Kinship fosters deep-rooted social ties through biological and familial bonds, establishing a foundation for trust and mutual support within communities. Friendship, based on chosen and voluntary connections, complements kinship by bridging gaps and expanding social networks beyond blood relations. Together, kinship and friendship enhance community building by promoting cooperation, resilience, and shared identity among diverse members.
Modern Changes in Kinship and Friendship Dynamics
Modern changes in kinship and friendship dynamics reflect increasing fluidity in social connections, influenced by globalization and digital communication technologies. Kinship structures have expanded beyond traditional family boundaries to include chosen families and virtual communities, emphasizing emotional bonds over genetic ties. Friendships now play a central role in social support networks, often substituting or complementing kinship relations in both personal and professional contexts.
Kinship and Friendship Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com