Hierarchical connection organizes elements in a structured manner, enabling efficient flow of information and clear relationships between levels. This method enhances understanding and control within systems by establishing a top-down framework that defines authority and responsibility. Explore the rest of the article to discover how hierarchical connection can optimize your organizational and communication strategies.
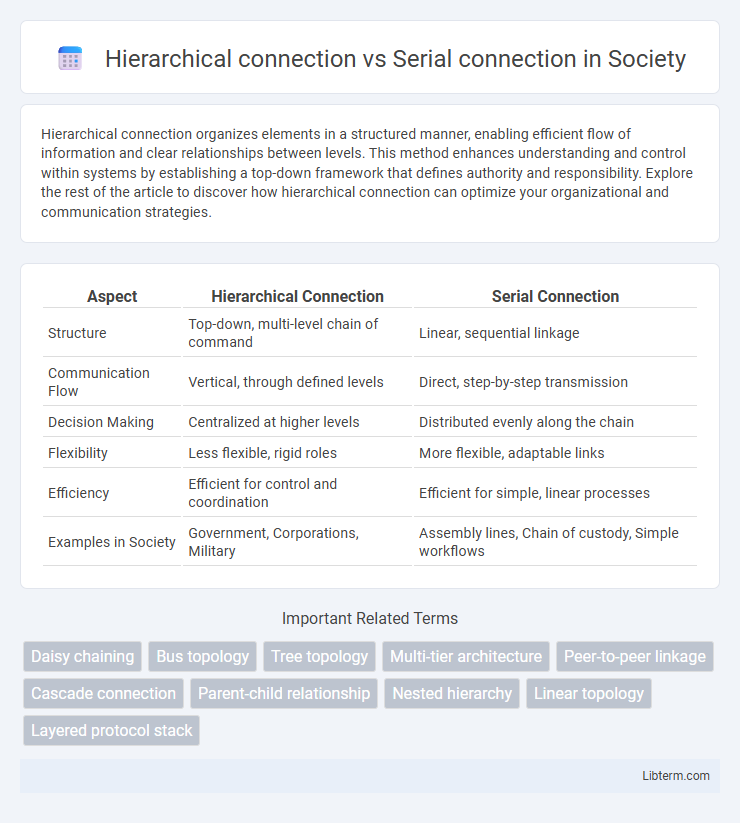
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Hierarchical Connection | Serial Connection |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Top-down, multi-level chain of command | Linear, sequential linkage |
| Communication Flow | Vertical, through defined levels | Direct, step-by-step transmission |
| Decision Making | Centralized at higher levels | Distributed evenly along the chain |
| Flexibility | Less flexible, rigid roles | More flexible, adaptable links |
| Efficiency | Efficient for control and coordination | Efficient for simple, linear processes |
| Examples in Society | Government, Corporations, Military | Assembly lines, Chain of custody, Simple workflows |
Introduction to Hierarchical and Serial Connections
Hierarchical connections organize network components in a multi-level structure, enabling efficient data flow and simplified management by dividing tasks into layers such as core, distribution, and access. Serial connections link devices sequentially, forming a linear pathway where data travels step-by-step from one node to the next, commonly used in point-to-point communications and simple device chains. Both connection types are fundamental in network design, with hierarchical models enhancing scalability and serial connections offering straightforward implementations for specific applications.
Defining Hierarchical Connection
Hierarchical connection refers to a system architecture where elements are organized in a multi-level structure, establishing superior-subordinate relationships to enhance control and communication efficiency. Unlike serial connections that link components linearly, hierarchical connections prioritize data flow through different levels, optimizing management and scalability in complex networks. This structure is commonly used in organizational charts, computer networks, and database systems to facilitate clear authority and systematic information processing.
Understanding Serial Connection
Serial connection involves linking devices or components end-to-end in a single pathway, allowing data to flow sequentially from one element to the next. This method simplifies wiring and reduces the number of communication lines required, making it ideal for systems where data transmission speed is less critical. Understanding serial connection is essential for designing efficient communication protocols in applications like UART, SPI, and I2C interfaces.
Key Differences Between Hierarchical and Serial Connections
Hierarchical connections organize devices or nodes in a multi-level structure where each level controls the next, enabling efficient management and scalability in complex systems. Serial connections link devices end-to-end in a single line, ensuring straightforward data transfer but limited scalability and increased latency as the number of devices grows. Key differences include the complexity, scalability, and data flow control, with hierarchical connections offering better control and expansion capabilities compared to the simple, linear nature of serial connections.
Advantages of Hierarchical Connection
Hierarchical connections offer improved scalability and efficient data management by organizing nodes in multiple layers, reducing bottlenecks commonly found in serial connections. This topology enhances fault tolerance, as failures in lower levels do not necessarily disrupt the entire network, unlike serial connections where a single failure can halt communication. Hierarchical structures also enable faster data transmission and better resource allocation, optimizing overall network performance compared to the linear flow of serial connections.
Advantages of Serial Connection
Serial connection offers significant advantages in simplifying wiring complexity by using a single communication line for multiple devices, which reduces installation costs and minimizes potential signal interference. This connection type enhances scalability and ease of troubleshooting, allowing for straightforward addition or removal of devices without disrupting the entire system. Serial connections are highly effective in long-distance data transmission, providing reliable, synchronized communication that maintains data integrity across extended networks.
Common Use Cases for Hierarchical Connections
Hierarchical connections are commonly used in organizational structures, computer networks, and database management systems where a parent-child relationship is essential for data flow and control. They enable efficient access control, simplified troubleshooting, and optimized resource allocation in complex environments such as corporate intranets, cloud computing architectures, and file directory systems. In contrast to serial connections, hierarchical setups better support scalability and structured decision-making processes.
Popular Applications of Serial Connections
Serial connections are widely utilized in popular applications such as USB interfaces, RS-232 communication, and SPI protocols, offering efficient data transfer between devices in a linear sequence. Unlike hierarchical connections, which organize devices in layered structures with parent-child relationships, serial connections prioritize simplicity and cost-effectiveness for point-to-point communication. This makes serial connections ideal for peripherals like keyboards, mice, and modems, where streamlined communication is essential.
Choosing Between Hierarchical and Serial Connections
Choosing between hierarchical and serial connections depends on system complexity and scalability requirements. Hierarchical connections offer structured, multi-level organization ideal for large networks needing efficient data management and fault isolation. Serial connections suit simpler setups with straightforward data flow, prioritizing ease of implementation and minimizing wiring complexity.
Future Trends in Connection Architectures
Future trends in connection architectures emphasize the integration of hierarchical connection models with serial connection techniques to enhance scalability and fault tolerance in complex systems. Emerging network designs leverage hierarchical layers to optimize data flow and reduce latency, while serial connections simplify hardware interfaces and improve modularity. Advances in AI-driven network management and edge computing are expected to further refine these hybrid architectures, enabling dynamic reconfiguration and adaptive communication protocols.
Hierarchical connection Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com