Groups play a crucial role in shaping social interactions and fostering collaboration among members. Understanding the dynamics and types of groups can enhance your ability to work effectively within teams and build stronger relationships. Explore the rest of this article to learn how different groups function and impact your everyday life.
Table of Comparison
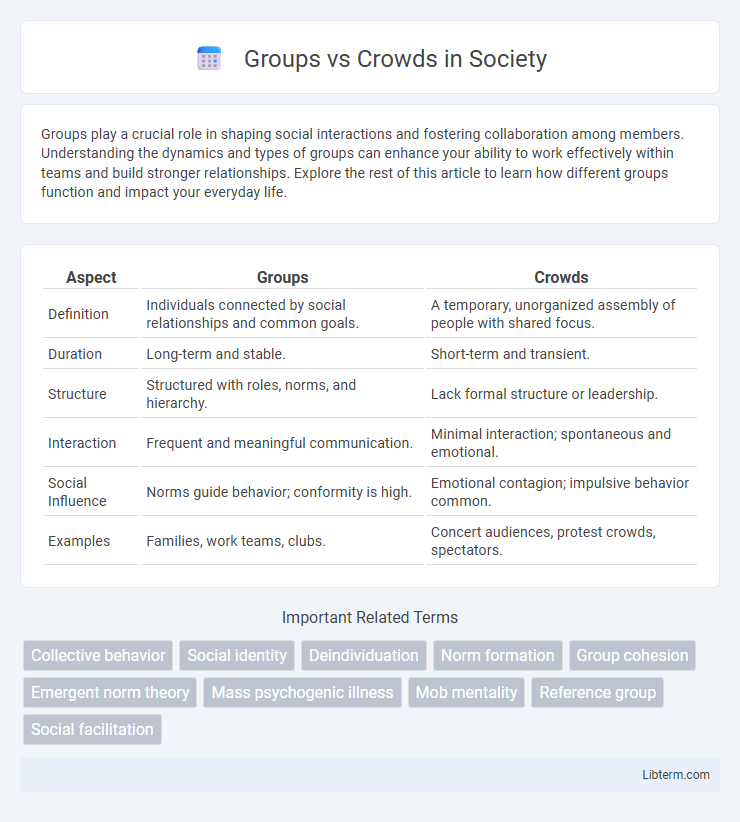
| Aspect | Groups | Crowds |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Individuals connected by social relationships and common goals. | A temporary, unorganized assembly of people with shared focus. |
| Duration | Long-term and stable. | Short-term and transient. |
| Structure | Structured with roles, norms, and hierarchy. | Lack formal structure or leadership. |
| Interaction | Frequent and meaningful communication. | Minimal interaction; spontaneous and emotional. |
| Social Influence | Norms guide behavior; conformity is high. | Emotional contagion; impulsive behavior common. |
| Examples | Families, work teams, clubs. | Concert audiences, protest crowds, spectators. |
Introduction: Defining Groups and Crowds
Groups are structured social units characterized by stable, recurring interactions and shared goals, often involving defined roles and established norms. Crowds consist of loosely connected individuals gathered temporarily, typically driven by a common focus or event without enduring social bonds. Understanding these distinctions highlights how groups foster long-term cohesion while crowds demonstrate collective but transient social behavior.
Key Characteristics of Groups
Groups exhibit defined structures with clear roles, established norms, and consistent interaction patterns among members, which foster strong social bonds and shared goals. Key characteristics include sustained communication, mutual influence, and a collective identity that distinguishes the group from a crowd. Unlike crowds, groups maintain stability over time and demonstrate coordinated behavior driven by interpersonal relationships.
Essential Traits of Crowds
Crowds are characterized by high emotional intensity, spontaneous behavior, and temporary aggregation, lacking structured organization or long-term goals. Unlike groups, crowds exhibit collective behavior driven by shared emotions and anonymity, leading to impulsive actions. The essential traits include rapid formation, limited social norms, and a strong sense of collective identity that influences individual behavior.
Group Formation: How and Why They Emerge
Groups form through shared goals, interests, or identities that create cohesion and foster collaboration among members. Social, psychological, and environmental factors such as common values, communication patterns, and interdependence drive group formation and sustain its structure. Unlike crowds, groups develop organized roles and norms that enhance coordinated action and long-term interaction.
Crowd Dynamics: Understanding Collective Behavior
Crowd dynamics examine how individual behavior influences and is influenced by the collective movement and decision-making within large groups, emphasizing patterns such as density, speed, and emotional contagion. Unlike smaller, structured groups with defined roles, crowds often display spontaneous, emergent behaviors driven by local interactions and shared goals. Understanding these dynamics aids in managing mass gatherings, improving safety measures, and predicting collective responses during emergencies.
Communication Patterns: Groups vs Crowds
Groups exhibit structured communication patterns characterized by ongoing, reciprocal interactions and clear roles, enabling collaboration and shared decision-making. Crowds display spontaneous, unstructured communication with minimal interaction among individuals, driven primarily by immediate emotions or stimuli. These distinct communication dynamics affect how information is exchanged, processed, and acted upon within each social formation.
Social Influence and Decision Making
Groups exhibit stronger social influence by fostering shared norms and facilitating collective decision making through direct interaction and accountability among members. Crowds, characterized by anonymity and emotional contagion, often lead to impulsive decisions driven by immediate social cues rather than reflective deliberation. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for predicting behavior outcomes in organizational and social contexts.
Psychological Impacts: Belonging vs Anonymity
Groups foster a strong sense of belonging, enhancing individual identity through shared goals, values, and interpersonal connections, which improves self-esteem and emotional support. Crowds, characterized by anonymity and lack of structured relationships, often lead to diminished personal accountability and increased impulsivity or deindividuation. This contrast in psychological impacts influences behavior, with groups promoting cohesion and responsibility, while crowds may trigger conformity or aggression due to anonymity.
Real-World Examples: Groups and Crowds in Action
Groups, such as project teams at Google, exhibit structured roles, shared goals, and coordinated interactions leading to high productivity and innovation. Crowds, exemplified by Black Friday shoppers, demonstrate spontaneous, unstructured behavior driven by immediate needs, often resulting in unpredictable dynamics and occasional safety concerns. Understanding the distinct behaviors of groups versus crowds helps in managing social interactions effectively across settings like workplaces and public events.
Conclusion: Implications for Society
Groups foster structured interaction, shared goals, and collective identity, enabling coordinated decision-making and sustained social support. Crowds, characterized by spontaneous behavior and emotional intensity, can trigger rapid social change but often lack long-term cohesion. Understanding these dynamics helps societies manage collective actions, mitigate risks of crowd-related chaos, and leverage group solidarity for social progress.
Groups Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com