The cultural frontier represents the boundary where diverse traditions and customs meet, interact, and often blend, creating rich and dynamic social landscapes. Understanding these intersections helps you appreciate the complexities of cultural identities and the evolution of societies. Explore the rest of the article to discover how cultural frontiers shape communities and influence global connections.
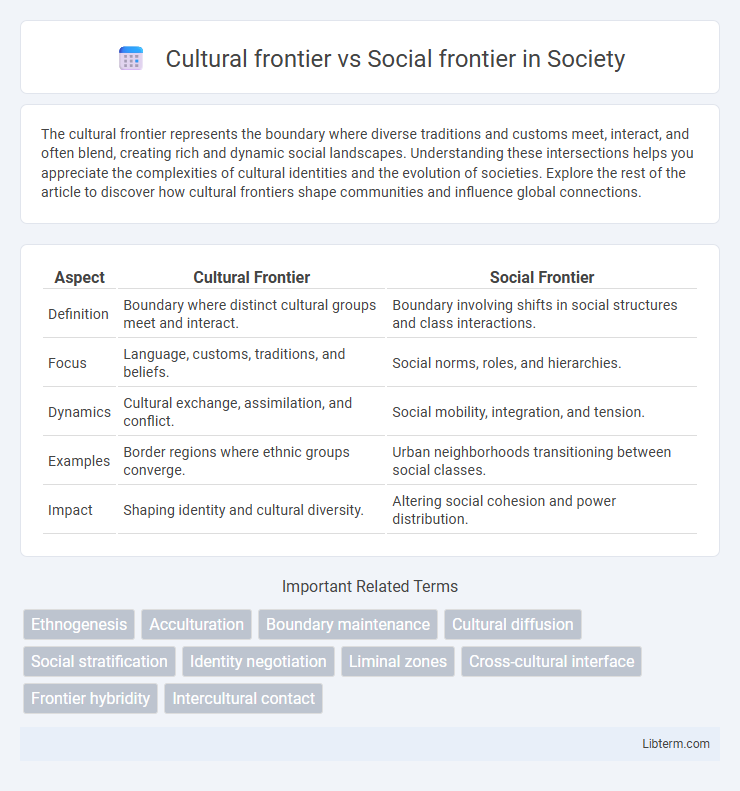
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Cultural Frontier | Social Frontier |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Boundary where distinct cultural groups meet and interact. | Boundary involving shifts in social structures and class interactions. |
| Focus | Language, customs, traditions, and beliefs. | Social norms, roles, and hierarchies. |
| Dynamics | Cultural exchange, assimilation, and conflict. | Social mobility, integration, and tension. |
| Examples | Border regions where ethnic groups converge. | Urban neighborhoods transitioning between social classes. |
| Impact | Shaping identity and cultural diversity. | Altering social cohesion and power distribution. |
Defining the Cultural Frontier
The cultural frontier represents the dynamic boundary where differing cultural groups meet, interact, and influence one another, shaping identities and traditions. It involves the exchange and adaptation of language, beliefs, customs, and values, often leading to hybrid cultural forms. Unlike the social frontier, which centers on societal structures and class interactions, the cultural frontier emphasizes intangible cultural elements and their evolving relationships.
Exploring the Social Frontier
Exploring the social frontier involves examining the evolving dynamics of human relationships, social behaviors, and community structures in response to technological advancements and globalization. This frontier highlights the transformation of communication patterns, social inclusion, and identity formation in increasingly diverse and interconnected societies. Understanding these shifts provides critical insights into addressing social inequality, fostering cohesion, and promoting adaptive social policies in contemporary environments.
Historical Perspectives on Frontiers
Historical perspectives on frontiers reveal cultural frontiers as zones where distinct belief systems, languages, and traditions intersect, often leading to cultural exchange or conflict. Social frontiers, by contrast, emphasize boundaries shaped by class, race, or social status, highlighting power dynamics and social mobility challenges. Analyzing these frontiers helps historians understand how cultural identity and social structures evolved through contact and competition.
Key Differences Between Cultural and Social Frontiers
Cultural frontiers refer to boundaries where distinct cultural groups meet, marked by differences in language, traditions, and belief systems, whereas social frontiers emphasize divisions based on social structure, class, or economic status within or between communities. The key difference lies in cultural frontiers highlighting ethnic and cultural identity contrasts, while social frontiers focus on stratification and social mobility constraints. Understanding these distinctions aids in analyzing how cultural interactions and social inequalities shape group dynamics and conflict.
Overlapping Boundaries: Intersection of Culture and Society
Cultural frontiers represent the zones where distinct beliefs, practices, and values converge, shaping identity and tradition, while social frontiers delineate the boundaries of social organization, roles, and institutions. Overlapping boundaries occur when cultural norms influence social structures, leading to dynamic interactions between collective identity and societal roles. The intersection of culture and society highlights the fluid exchange where cultural heritage informs social behavior, and social frameworks reinforce cultural continuity.
The Role of Identity in Frontier Formation
Cultural frontier formation hinges on shared identity markers such as language, religion, and traditions, which delineate group boundaries and reinforce collective belonging. Social frontiers emerge from socioeconomic disparities and access to resources, shaping identity through class, occupation, and social roles. Identity acts as a critical driver in both frontiers by cultivating in-group cohesion and out-group differentiation, influencing how communities define and defend their borders.
Challenges at Cultural and Social Frontiers
Challenges at cultural frontiers include maintaining identity amidst globalization, navigating language barriers, and reconciling traditional values with modern influences. Social frontiers face issues such as inequality, access to resources, and integration of diverse communities within urban or rural settings. Both frontiers demand adaptive strategies to foster coexistence and sustainable development.
Case Studies: Global Examples of Frontier Dynamics
Case studies on cultural and social frontiers reveal distinct dynamics shaping global interactions. The US-Mexico border illustrates a cultural frontier where bilingualism and hybrid identities emerge from overlapping traditions and norms. In contrast, the Rwandan post-genocide reconciliation process exemplifies a social frontier, emphasizing rebuilding trust and social cohesion amid deep ethnic divisions.
Impact on Globalization and Innovation
Cultural frontiers shape globalization by influencing the exchange and adaptation of ideas, traditions, and values across diverse societies, fostering cross-cultural innovation and creative collaboration. Social frontiers, defined by socio-economic divides and inequalities, impact access to technological advancements and global networks, thereby affecting who benefits from globalization and drives innovation. Understanding these frontiers is crucial for developing inclusive policies that enhance global connectivity and promote equitable innovation ecosystems.
Future Trends in Cultural and Social Frontiers
Future trends in cultural frontiers emphasize technological integration and cross-cultural exchanges driven by globalization, fostering hybrid identities and innovative artistic expressions. Social frontiers are shifting towards inclusive policies and digital activism, reshaping community dynamics and challenging traditional social hierarchies. Advances in artificial intelligence and virtual reality will further blur the boundaries between cultural experiences and social interactions, creating new frontiers in human connectivity.
Cultural frontier Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com