Routine-based change harnesses the power of small, consistent adjustments in daily habits to drive significant long-term improvements. By embedding new behaviors into your regular activities, transformation becomes more sustainable and less overwhelming. Explore the article to discover practical strategies for integrating routine-based change into your life effectively.
Table of Comparison
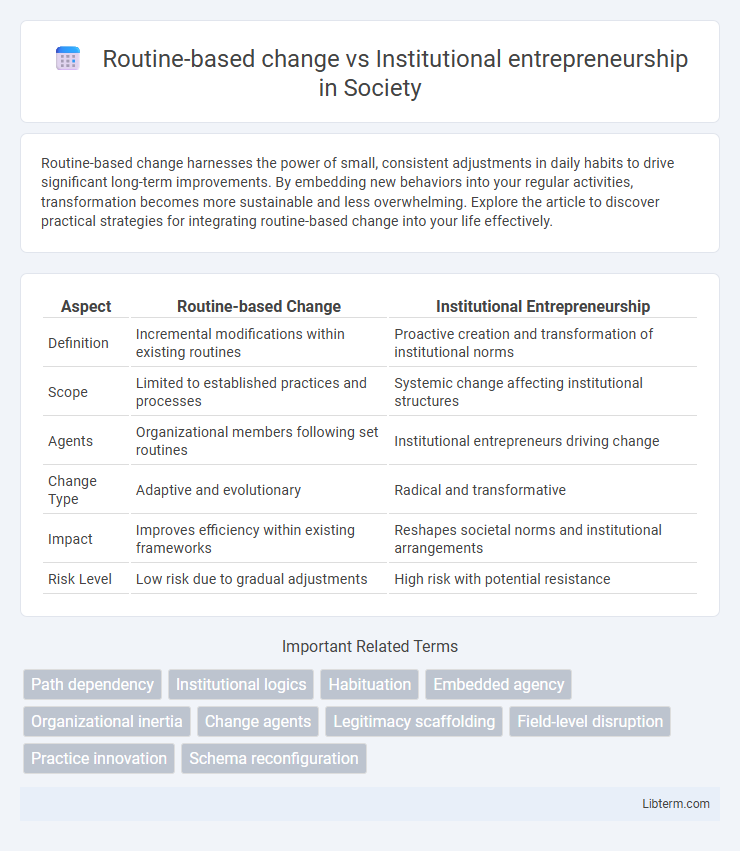
| Aspect | Routine-based Change | Institutional Entrepreneurship |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Incremental modifications within existing routines | Proactive creation and transformation of institutional norms |
| Scope | Limited to established practices and processes | Systemic change affecting institutional structures |
| Agents | Organizational members following set routines | Institutional entrepreneurs driving change |
| Change Type | Adaptive and evolutionary | Radical and transformative |
| Impact | Improves efficiency within existing frameworks | Reshapes societal norms and institutional arrangements |
| Risk Level | Low risk due to gradual adjustments | High risk with potential resistance |
Understanding Routine-Based Change
Understanding routine-based change involves analyzing how established organizational practices evolve through minor adaptations and improvisations without disrupting core routines. This change is incremental, emerging from continuous interactions within existing workflows rather than from radical innovation or leadership-driven initiatives. Routine-based change emphasizes the role of daily activities and collective behaviors in shaping organizational development over time.
Defining Institutional Entrepreneurship
Institutional entrepreneurship refers to the activities of actors who leverage resources and agency to create, transform, or disrupt institutions, challenging established norms and structures. Routine-based change emphasizes incremental adjustments within existing institutional frameworks, while institutional entrepreneurship involves strategic, often radical initiatives that redefine institutional logics. This concept highlights the role of individual or collective actors as catalysts for institutional evolution, enabling significant organizational and social transformations.
Key Differences Between Routine and Entrepreneurial Approaches
Routine-based change emphasizes incremental improvements within established processes, relying on repetition and stability to achieve efficiency. Institutional entrepreneurship involves proactive efforts to create or transform institutions by challenging existing norms and mobilizing resources for innovation. The key difference lies in routine change maintaining continuity while institutional entrepreneurship drives radical transformation and systemic shifts.
Drivers of Routine-Based Change
Routine-based change is primarily driven by incremental adaptations within existing organizational practices, focusing on efficiency improvements and error reduction. Key drivers include habitual actions, repeated interactions, and local problem-solving that gradually evolve routines without altering core structures. This contrasts with institutional entrepreneurship, which relies on deliberate, often disruptive innovations led by actors seeking to transform established institutions.
Motivators Behind Institutional Entrepreneurship
Motivators behind institutional entrepreneurship often include identifying opportunities for innovation, addressing inefficiencies in existing systems, and leveraging social or economic capital to drive transformational change. Unlike routine-based change, which focuses on incremental improvements within established frameworks, institutional entrepreneurship seeks to disrupt and reshape institutional norms and structures. Key drivers include visionary leadership, resource mobilization, and the pursuit of legitimacy within broader institutional fields.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Routine-Based Change
Routine-based change enhances organizational efficiency by leveraging existing processes and minimizing disruption, fostering incremental improvements and employee familiarity. However, it can lead to organizational inertia, limiting innovation and the ability to respond to radical environmental shifts. This approach often struggles to address complex challenges because it relies heavily on established patterns rather than transformative, entrepreneurial actions.
Advantages and Challenges of Institutional Entrepreneurship
Institutional entrepreneurship enables organizations to drive transformative change by identifying and leveraging opportunities within existing structures, fostering innovation beyond routine-based adaptations. Advantages include the ability to influence institutional norms and create long-term competitive advantages through strategic agency. Challenges involve overcoming resistance from entrenched interests, managing uncertainty in novel initiatives, and mobilizing resources without established support systems.
Case Studies: Routine-Based vs Institutional Entrepreneurship
Case studies comparing routine-based change and institutional entrepreneurship reveal distinct mechanisms of organizational transformation. Routine-based change emphasizes incremental adaptations within existing practices, whereas institutional entrepreneurship involves actors leveraging their agency to disrupt and reshape institutional norms. Empirical evidence highlights that successful institutional entrepreneurs mobilize resources and create new institutional logics, contrasting with the gradual, practice-centered evolution seen in routine-based change scenarios.
Impact on Organizational Culture and Innovation
Routine-based change reinforces existing organizational culture by emphasizing incremental improvements within established processes, which can enhance operational stability but may limit radical innovation. Institutional entrepreneurship drives transformative shifts by challenging norms and introducing novel practices, fostering a culture of creativity and adaptive innovation. The interplay between these approaches determines how organizations balance sustaining core values with embracing disruptive change to maintain long-term competitiveness.
Choosing the Right Approach for Sustainable Transformation
Routine-based change leverages existing organizational practices to implement incremental improvements, enhancing sustainability through gradual adaptation and minimizing resistance. Institutional entrepreneurship drives transformative change by mobilizing resources and challenging established norms to create new frameworks, enabling long-term impact and innovation. Selecting the right approach depends on organizational capacity, urgency of change, and the scope of transformation desired to ensure effective and lasting sustainability outcomes.
Routine-based change Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com