Social autonomy empowers individuals to make independent decisions within their community, fostering a sense of personal freedom and responsibility. It enhances self-confidence and promotes collaboration by encouraging diverse perspectives in social interactions. Explore the rest of the article to understand how social autonomy can transform your relationships and community engagement.
Table of Comparison
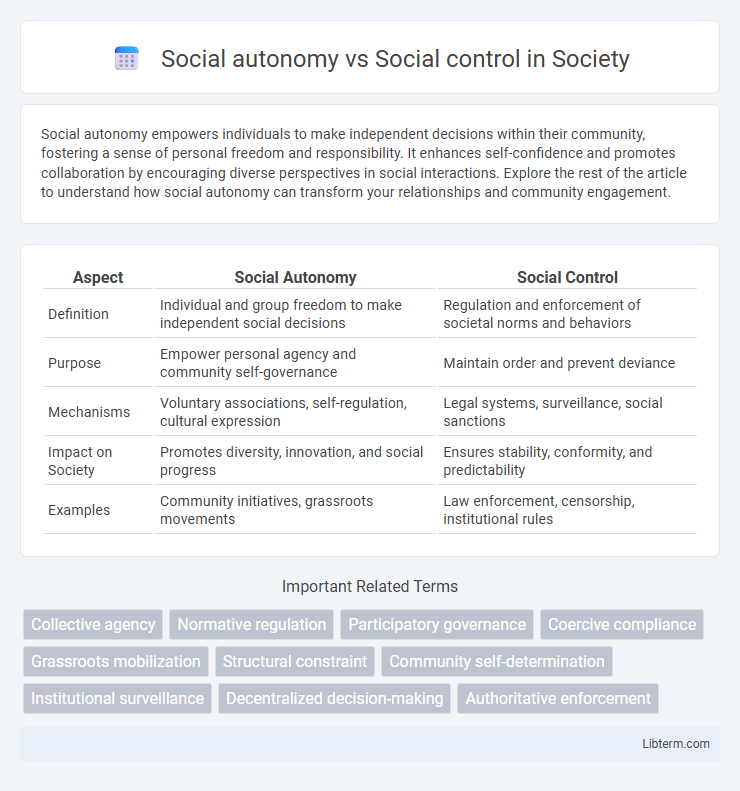
| Aspect | Social Autonomy | Social Control |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Individual and group freedom to make independent social decisions | Regulation and enforcement of societal norms and behaviors |
| Purpose | Empower personal agency and community self-governance | Maintain order and prevent deviance |
| Mechanisms | Voluntary associations, self-regulation, cultural expression | Legal systems, surveillance, social sanctions |
| Impact on Society | Promotes diversity, innovation, and social progress | Ensures stability, conformity, and predictability |
| Examples | Community initiatives, grassroots movements | Law enforcement, censorship, institutional rules |
Understanding Social Autonomy: Definition and Scope
Social autonomy refers to the capacity of individuals or groups to make independent decisions and govern themselves without external interference, emphasizing self-determination within social contexts. It encompasses the ability to assert personal or collective choices in cultural, political, and economic domains while maintaining social responsibility. Understanding its scope involves examining the balance between personal freedom and societal norms, highlighting how autonomy promotes empowerment and diversity in social interactions.
Exploring Social Control: Key Mechanisms and Purposes
Social control operates through mechanisms such as laws, norms, and institutions to regulate individual and group behavior within society. These systems enforce conformity and maintain order by sanctioning deviance and promoting shared values. Understanding social control reveals its purpose in stabilizing social structures and facilitating cooperation among diverse populations.
Historical Perspectives on Social Autonomy and Control
Historical perspectives on social autonomy and social control reveal a dynamic tension between individual freedoms and regulatory mechanisms within societies. Early Greek city-states emphasized citizen participation and autonomy, while later periods, such as the Middle Ages, saw increased social control through religious and feudal institutions. The rise of modern nation-states introduced codified laws and bureaucratic systems that balanced personal liberties with collective order, shaping contemporary debates on governance and civil rights.
The Role of Culture in Shaping Autonomy and Control
Culture profoundly shapes the balance between social autonomy and social control by influencing norms, values, and behavioral expectations within societies. Collectivist cultures often emphasize social control through conformity and interdependence, while individualistic cultures promote autonomy by encouraging personal freedom and self-expression. These cultural frameworks determine how individuals navigate their rights and responsibilities, directly impacting social structures and governance.
Education Systems: Promoting Autonomy or Enforcing Control?
Education systems often balance between promoting social autonomy and enforcing social control, shaping students' ability to think independently while maintaining societal norms. Curricula emphasizing critical thinking and self-directed learning foster autonomy, whereas standardized testing and strict discipline reinforce control. Educational policies that integrate student choice with accountability tend to create environments where autonomy supports social cohesion rather than undermines it.
Impact of Technology on Social Autonomy and Control
Advancements in digital platforms and surveillance technologies have intensified the tension between social autonomy and social control, enabling unprecedented levels of data collection and behavioral monitoring. Algorithms and artificial intelligence shape social interactions by curating content and influencing decision-making, often reducing individual agency while enhancing collective oversight. The proliferation of smart devices and real-time analytics facilitates both personalized autonomy and centralized governance, raising critical questions about privacy, consent, and power dynamics in contemporary society.
Legal Frameworks: Balancing Individual Freedom and Social Order
Legal frameworks play a crucial role in balancing social autonomy and social control by defining the limits of individual freedom while maintaining public order. Laws establish rights and responsibilities that protect personal liberties such as freedom of expression and privacy, yet impose restrictions to prevent harm and ensure collective security. Effective legal systems continuously adapt to evolving social values, striving to uphold human rights alongside social cohesion.
Social Movements: Challenging Control, Advocating Autonomy
Social movements play a critical role in challenging social control by advocating for increased social autonomy, emphasizing the right of individuals and communities to self-governance and participatory decision-making. Historical examples such as the Civil Rights Movement and contemporary climate activism illustrate how collective action disrupts institutional power structures, promoting reforms that expand freedoms and reduce oppressive regulations. These movements utilize strategic protests, grassroots organizing, and digital campaigns to contest social norms and policies, driving societal change towards greater autonomy and justice.
Psychological Impacts: Autonomy versus Obedience
Social autonomy fosters psychological well-being by promoting self-determination, intrinsic motivation, and a stronger sense of identity, leading to enhanced mental health and resilience. In contrast, social control often enforces obedience through external pressures and conformity, which can result in stress, diminished self-esteem, and increased anxiety. Balancing autonomy and control is crucial for maintaining psychological equilibrium, as excessive obedience may suppress creativity and personal growth.
Future Trends: The Evolving Landscape of Social Autonomy and Control
Emerging technologies and AI-driven surveillance systems are reshaping the balance between social autonomy and social control, enabling governments and corporations to exert unprecedented influence over individual behavior and societal norms. Privacy-enhancing tools and decentralized platforms are gaining prominence as countermeasures, fostering greater personal freedom and data sovereignty amid increasing regulatory scrutiny. The future landscape will be defined by a dynamic interplay between innovation in control mechanisms and advocacy for enhanced social autonomy, prompting ongoing ethical and legal debates.
Social autonomy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com