Structural transformation reshapes an economy by shifting resources from low-productivity sectors like agriculture to higher-productivity industries and services, driving sustainable economic growth. This process boosts innovation, enhances employment opportunities, and improves overall living standards by fostering industrialization and modernization. Explore the rest of the article to understand how structural transformation can impact your economic future and development strategies.
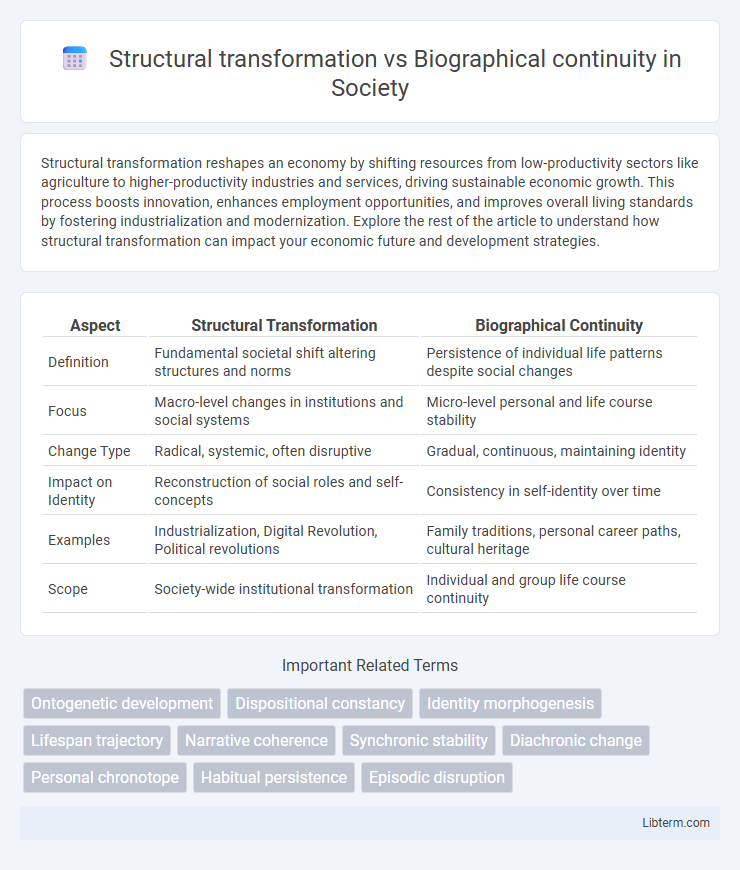
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Structural Transformation | Biographical Continuity |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Fundamental societal shift altering structures and norms | Persistence of individual life patterns despite social changes |
| Focus | Macro-level changes in institutions and social systems | Micro-level personal and life course stability |
| Change Type | Radical, systemic, often disruptive | Gradual, continuous, maintaining identity |
| Impact on Identity | Reconstruction of social roles and self-concepts | Consistency in self-identity over time |
| Examples | Industrialization, Digital Revolution, Political revolutions | Family traditions, personal career paths, cultural heritage |
| Scope | Society-wide institutional transformation | Individual and group life course continuity |
Understanding Structural Transformation
Structural transformation involves significant shifts in economic, social, and institutional frameworks that redefine production patterns, labor markets, and societal roles over time. Understanding structural transformation requires analyzing changes in industrial composition, technological advancements, and policy reforms that drive the transition from agrarian to industrial or service-based economies. This process reshapes social norms and power structures, distinguishing it fundamentally from biographical continuity, which emphasizes individual life course stability amidst broader changes.
Defining Biographical Continuity
Biographical continuity refers to the persistence of core aspects of an individual's identity, values, and life narrative despite changes in external circumstances or social roles. It emphasizes the coherence and stability of the self over time, allowing individuals to maintain a consistent sense of purpose and meaning across different phases of life. This concept contrasts with structural transformation, which highlights shifts in social positions or economic conditions that may disrupt or redefine one's life trajectory.
Historical Contexts: Change and Constancy
Structural transformation emphasizes shifts in societal institutions and economic systems, reflecting broad historical changes such as industrialization and modernization. Biographical continuity focuses on the persistence of individual life courses and social identities despite these macro-level changes. Historical contexts reveal how structural shifts alter social roles while biographical continuity maintains personal and cultural stability.
Key Theories and Frameworks
Structural transformation theory explores shifts in economic and social systems driven by industrialization, urbanization, and technological innovation, emphasizing macro-level changes and their impact on labor markets and social stratification. Biographical continuity theory centers on the stability of individual identity and life course across changing social contexts, highlighting micro-level processes such as personal narratives, role continuity, and intergenerational transmission. Key frameworks include W.W. Rostow's stages of economic growth for structural transformation and Glen H. Elder Jr.'s life course perspective for biographical continuity, both integrating sociological and economic dimensions to explain patterns of social stability and change.
Drivers of Structural Transformation
Drivers of structural transformation primarily include technological advancements, industrialization, and urbanization, which shift economic activities from agriculture to manufacturing and services. Investment in infrastructure, education, and innovation enhances productivity and facilitates labor mobility, accelerating changes in economic structure. Globalization and policy reforms also play crucial roles by enabling market expansions and improving institutional frameworks, fostering sustained economic development.
Factors Sustaining Biographical Continuity
Factors sustaining biographical continuity include stable social roles, consistent personal values, and enduring relationships that provide emotional support. Cognitive frameworks such as memory and identity narratives enable individuals to maintain a coherent sense of self despite external changes. Environmental stability, including steady employment and community ties, also plays a critical role in preserving continuous life stories amid structural transformations.
Comparing Individual and Societal Perspectives
Structural transformation involves broad societal changes altering economic, political, and social frameworks, impacting individuals collectively through shifts in institutions and cultural norms. Biographical continuity emphasizes personal identity stability amid change, highlighting how individuals maintain consistent self-narratives despite external transformations. Comparing these perspectives reveals how societal-level shifts reconfigure opportunities and constraints, while individual biographical continuity supports resilience and adaptive identity in evolving social contexts.
Case Studies: Balancing Change and Continuity
Case studies in structural transformation emphasize shifts in social, economic, and organizational frameworks while highlighting the importance of biographical continuity in maintaining individual and community identities. Detailed analyses reveal how individuals adapt to systemic changes without losing core aspects of their life narratives, ensuring psychological resilience and cultural coherence. Balancing change and continuity allows for sustainable development by integrating transformation with personal and collective historical contexts.
Implications for Social Policy and Practice
Structural transformation reshapes economic and social institutions, necessitating policies that address shifts in employment patterns, education, and social services to support affected populations. Biographical continuity emphasizes individuals' life courses, highlighting the importance of tailored social interventions that respect personal histories and identities. Social policy and practice must balance these frameworks by creating adaptable support systems that integrate macro-level changes with individual experiences to promote social cohesion and equity.
Future Directions in Sociological Research
Future directions in sociological research on structural transformation emphasize the analysis of macro-level changes such as globalization, technological innovation, and economic shifts influencing social institutions. Investigations into biographical continuity prioritize understanding individual life course stability amid these transformations by integrating longitudinal data and mixed-method approaches. Recent studies advocate for a synthesized framework that links structural dynamics with personal narratives to better capture the interplay between societal change and identity formation.
Structural transformation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com