Social integration fosters a sense of belonging and community by connecting individuals from diverse backgrounds through shared values and experiences. It enhances social cohesion, reduces inequalities, and promotes equal participation in societal activities. Discover how social integration can transform your community and improve collective well-being in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
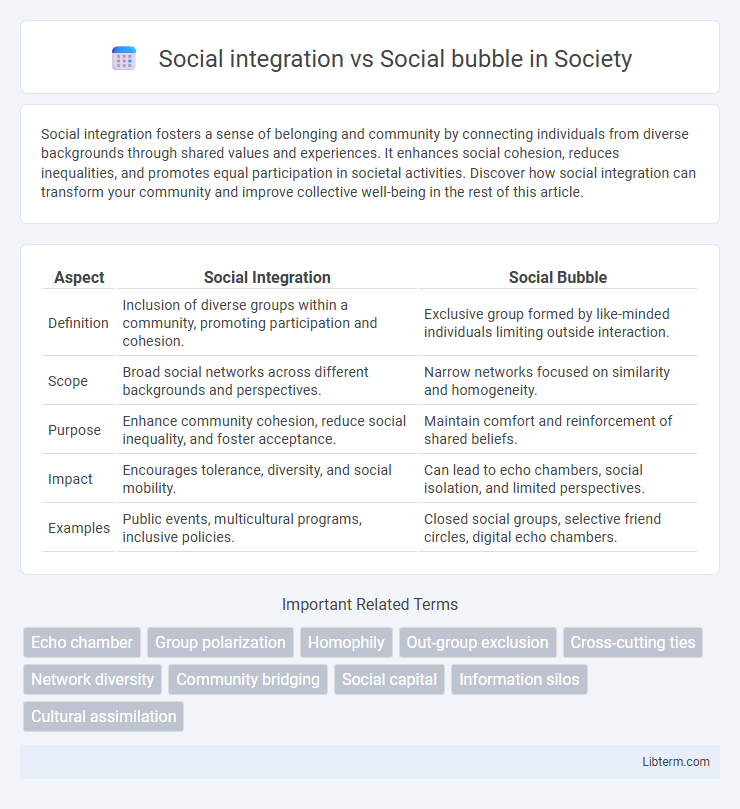
| Aspect | Social Integration | Social Bubble |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Inclusion of diverse groups within a community, promoting participation and cohesion. | Exclusive group formed by like-minded individuals limiting outside interaction. |
| Scope | Broad social networks across different backgrounds and perspectives. | Narrow networks focused on similarity and homogeneity. |
| Purpose | Enhance community cohesion, reduce social inequality, and foster acceptance. | Maintain comfort and reinforcement of shared beliefs. |
| Impact | Encourages tolerance, diversity, and social mobility. | Can lead to echo chambers, social isolation, and limited perspectives. |
| Examples | Public events, multicultural programs, inclusive policies. | Closed social groups, selective friend circles, digital echo chambers. |
Understanding Social Integration
Understanding social integration involves recognizing the process through which individuals or groups are incorporated into the larger social fabric, fostering connections, participation, and shared identities that promote cohesion. Social integration emphasizes inclusivity, active engagement, and the breakdown of social barriers, contrasting sharply with social bubbles that often reinforce homogeneity and limit exposure to diverse perspectives. Effective social integration leads to more resilient communities by encouraging mutual respect and broadening social networks beyond insular groups.
Defining the Social Bubble
The social bubble refers to a selective group of individuals with whom a person interacts regularly, sharing common interests, values, or social identity, often limiting exposure to diverse perspectives. Unlike social integration, which emphasizes broader inclusion and participation in the wider community, the social bubble creates a confined social environment that may reinforce existing beliefs and reduce social diversity. Understanding the dynamics of social bubbles is crucial in analyzing how social networks influence behavior, opinions, and cultural norms.
Key Differences Between Social Integration and Social Bubble
Social integration refers to the process by which individuals from diverse backgrounds come together to create a cohesive, inclusive society, promoting equal participation and reducing social isolation. In contrast, a social bubble consists of a small, exclusive group of people who interact primarily within their own circle, often limiting exposure to differing perspectives and wider community networks. The key differences lie in the scope and inclusivity; social integration emphasizes broad societal engagement and diversity, while social bubbles focus on close-knit, homogeneous interactions.
Benefits of Social Integration
Social integration fosters diverse connections that enhance empathy, collaboration, and access to resources, promoting overall psychological well-being and societal cohesion. Unlike social bubbles that limit interactions to similar viewpoints, integration encourages exposure to different cultures and ideas, enriching personal growth and community resilience. Studies reveal that integrated social networks reduce feelings of isolation and support mental health by providing a broader support system and increasing opportunities for meaningful engagement.
Risks of Living in a Social Bubble
Living in a social bubble increases risks of echo chambers and confirmation bias, limiting exposure to diverse perspectives and reinforcing stereotypes. This isolation can hinder social integration by reducing empathy and understanding across different communities. Over time, social bubbles undermine social cohesion and contribute to polarization within society.
Psychological Effects of Both Phenomena
Social integration enhances psychological well-being by fostering a sense of belonging, increasing self-esteem, and reducing feelings of loneliness and depression through diverse social networks. In contrast, social bubbles can create psychological comfort and safety by limiting social interactions to familiar groups but may increase anxiety and stress when faced with external social situations due to reduced exposure and support diversity. Both phenomena significantly influence mental health, with social integration promoting resilience and adaptability, while social bubbles may lead to social anxiety and cognitive biases due to restricted social experiences.
Social Integration and Community Building
Social integration fosters a sense of belonging by encouraging meaningful interactions and inclusivity within diverse communities, promoting mutual respect and shared values. Community building strengthens these social bonds through collaborative activities and support networks that enhance collective well-being and resilience. This process contrasts with social bubbles, which limit interactions to homogenous groups, reducing exposure to diverse perspectives and opportunities for growth.
The Role of Technology in Shaping Social Bubbles
Technology plays a pivotal role in shaping social bubbles by creating algorithms that curate content and connections based on user preferences, which often reinforces existing beliefs and limits exposure to diverse perspectives. Social media platforms use data-driven personalization to maintain engagement, thereby intensifying echo chambers and reducing opportunities for social integration across different groups. This algorithmic filtering fosters environments where individuals interact primarily within homogeneous communities, challenging broader social integration efforts.
Strategies to Foster Social Integration
Strategies to foster social integration include creating inclusive community programs that encourage interaction among diverse groups, promoting equitable access to education and employment opportunities, and facilitating open dialogue to reduce prejudice and build mutual understanding. Emphasizing cross-cultural events and collaborative projects helps break down social bubbles by connecting individuals beyond homogeneous networks. Implementing policies that support social cohesion and reduce segregation enhances overall societal well-being and resilience.
Breaking Out of the Social Bubble: Practical Steps
Breaking out of the social bubble requires intentional exposure to diverse perspectives by engaging with different communities, attending cultural events, and actively seeking conversations beyond familiar networks. Social integration involves building genuine, inclusive connections that bridge gaps between distinct social groups, fostering empathy and mutual understanding. Practical steps include participating in cross-cultural activities, joining diverse social clubs, and practicing open-minded communication to challenge personal biases.
Social integration Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com