Integration streamlines business operations by connecting diverse systems and applications into a unified platform, enhancing data flow and reducing redundancy. Efficient integration supports real-time analytics and improves decision-making, driving innovation and competitive advantage. Discover how integration can transform your organization by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
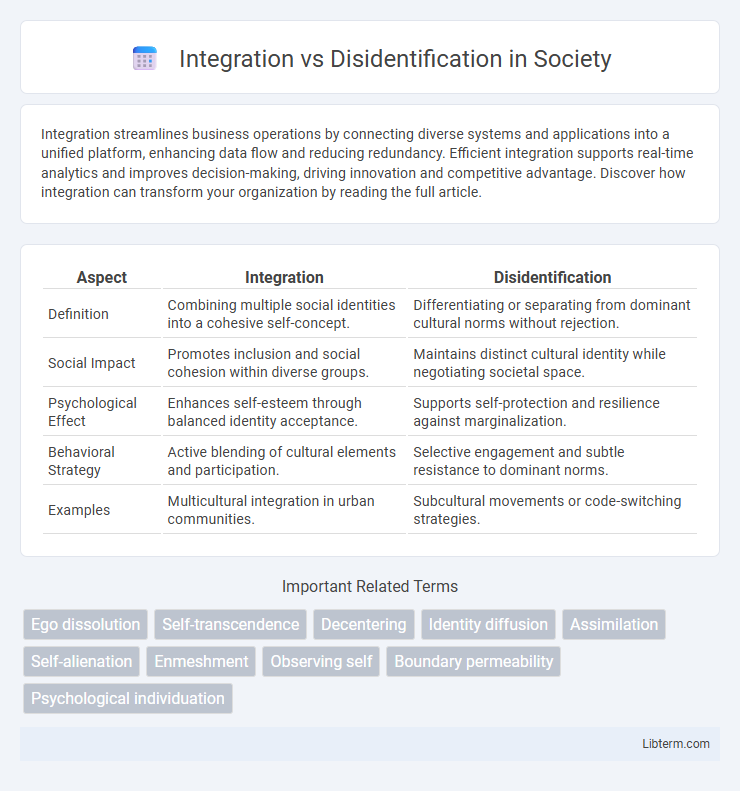
| Aspect | Integration | Disidentification |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Combining multiple social identities into a cohesive self-concept. | Differentiating or separating from dominant cultural norms without rejection. |
| Social Impact | Promotes inclusion and social cohesion within diverse groups. | Maintains distinct cultural identity while negotiating societal space. |
| Psychological Effect | Enhances self-esteem through balanced identity acceptance. | Supports self-protection and resilience against marginalization. |
| Behavioral Strategy | Active blending of cultural elements and participation. | Selective engagement and subtle resistance to dominant norms. |
| Examples | Multicultural integration in urban communities. | Subcultural movements or code-switching strategies. |
Understanding Integration and Disidentification
Understanding integration involves recognizing how individuals incorporate multiple cultural identities into a unified sense of self, promoting psychological well-being and social harmony. Disidentification refers to a psychological strategy where individuals distance themselves from negative stereotypes or marginalized identities, protecting self-esteem and reducing internal conflict. Both processes impact identity formation, influencing how people navigate and reconcile cultural influences in diverse social contexts.
Psychological Foundations of Both Processes
Integration involves the psychological process of harmonizing multiple aspects of the self into a coherent identity, supported by cognitive flexibility and emotional regulation. Disidentification, in contrast, entails psychologically distancing oneself from certain social roles or group identities, often as a defense mechanism to preserve self-coherence under threat. Both processes rely on fundamental mechanisms of self-concept maintenance, with integration fostering adaptive coping through synthesis, while disidentification promotes resilience by rejecting conflicting or stigmatized identities.
The Role in Personal Identity Formation
Integration involves merging diverse aspects of the self into a coherent personal identity, fostering psychological well-being and self-consistency. Disidentification functions as a protective mechanism by distancing from certain social roles or identities that conflict with an individual's authentic self or societal expectations. Both processes critically shape personal identity formation by balancing internal coherence and external adaptation.
Benefits of Integration in Mental Health
Integration in mental health fosters a cohesive self-experience by harmonizing conflicting thoughts and emotions, which reduces psychological distress and enhances emotional resilience. This process promotes greater self-awareness and adaptive coping strategies, leading to improved overall well-being and mental stability. Research shows that integrated identity structures correlate with lower anxiety, depression, and increased life satisfaction, highlighting its critical role in effective therapy outcomes.
Challenges and Limitations of Disidentification
Disidentification faces challenges such as internal conflicts stemming from balancing opposition and identification within cultural identities, leading to psychological stress and fragmented self-concepts. It often limits social acceptance and recognition because disidentified individuals reject dominant norms without fully aligning with alternative groups, resulting in marginalization. The lack of clear belonging makes sustaining community support difficult, hindering collective empowerment and long-term identity stability.
Integration vs Disidentification: Key Differences
Integration involves blending new cultural elements with existing identity while maintaining a cohesive self-concept, whereas disidentification is a defensive coping mechanism where individuals neither fully accept nor reject dominant cultural norms. Integration supports psychological well-being by fostering bicultural competence and positive self-esteem, while disidentification often arises from experiences of marginalization or exclusion. Key differences include the level of identity coherence and emotional outcomes, with integration promoting harmony and disidentification often linked to internal conflict and resistance.
Real-Life Examples and Case Studies
Integration involves blending diverse cultural identities into a cohesive self-concept, exemplified by immigrants who maintain their native traditions while adopting the host country's norms, as observed in studies of second-generation Korean Americans thriving academically and socially. Disidentification occurs when individuals neither fully accept nor reject their cultural identities, often as a coping mechanism against discrimination, illustrated by African American youths who disengage from both mainstream and ethnic group expectations to navigate social pressures. Case studies highlight that integration fosters psychological well-being and social harmony, whereas disidentification can lead to identity confusion and decreased group affiliation.
When to Choose Integration or Disidentification
Choose integration when aligning new experiences with existing identity enhances psychological coherence and promotes growth, especially in multicultural or dynamic environments. Opt for disidentification when separation from an identity threatens well-being or when rejecting imposed roles preserves autonomy and self-concept stability. Assess the context by evaluating identity compatibility, psychological resilience, and long-term goals to determine the most adaptive strategy.
Impacts on Relationships and Social Dynamics
Integration fosters deeper connections and trust by encouraging acceptance of diverse identities, leading to more cohesive and inclusive social networks. Disidentification can create emotional distance and misunderstandings, often resulting in fragmented relationships and social isolation. The balance between these processes significantly influences group dynamics, communication patterns, and overall social harmony.
Moving Forward: Blending Both Approaches
Combining integration and disidentification approaches enhances personal growth by allowing individuals to embrace valued aspects of their identity while critically distancing from limiting or negative labels. This blended strategy promotes mental flexibility, improving resilience and well-being through balanced self-conceptualization. Utilizing both methods acknowledges the complexity of identity, facilitating continuous adaptation and healthier social interactions.
Integration Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com