Organizational citizenship refers to voluntary, extra-role behaviors employees engage in that contribute to the overall effectiveness and positive work environment of their organization. These actions, such as helping colleagues and showing initiative, are not formally rewarded but significantly enhance teamwork and organizational success. Discover how fostering organizational citizenship can transform your workplace by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
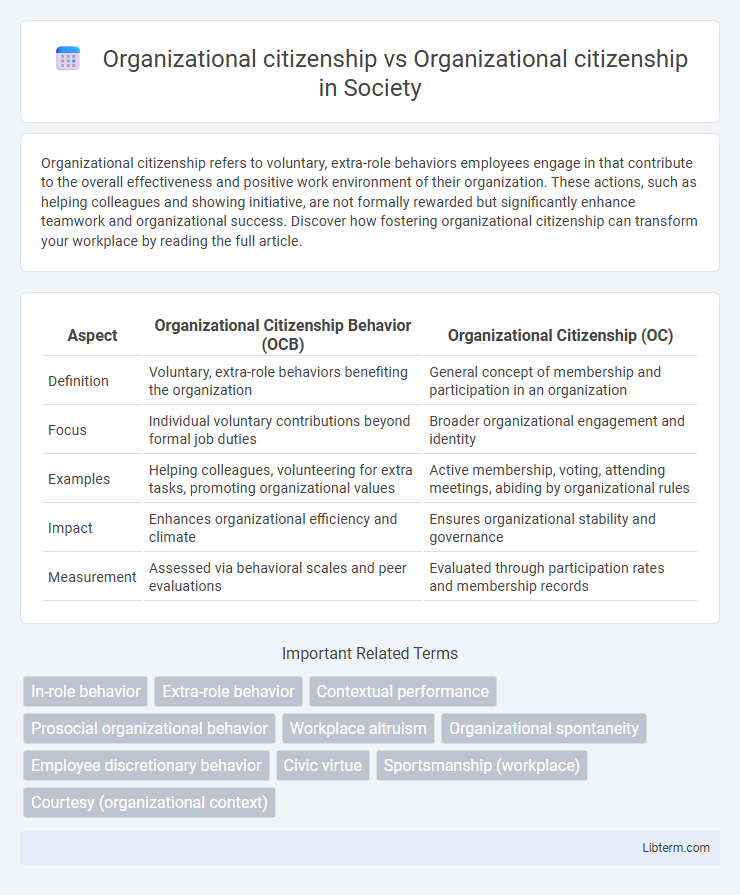
| Aspect | Organizational Citizenship Behavior (OCB) | Organizational Citizenship (OC) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Voluntary, extra-role behaviors benefiting the organization | General concept of membership and participation in an organization |
| Focus | Individual voluntary contributions beyond formal job duties | Broader organizational engagement and identity |
| Examples | Helping colleagues, volunteering for extra tasks, promoting organizational values | Active membership, voting, attending meetings, abiding by organizational rules |
| Impact | Enhances organizational efficiency and climate | Ensures organizational stability and governance |
| Measurement | Assessed via behavioral scales and peer evaluations | Evaluated through participation rates and membership records |
Defining Organizational Citizenship
Organizational Citizenship refers to voluntary, discretionary behaviors by employees that are not part of formal job requirements but contribute to organizational effectiveness. These behaviors include helping colleagues, showing initiative, and adhering to company norms, fostering a positive workplace environment. Understanding Organizational Citizenship helps differentiate it from in-role performance by emphasizing extra-role contributions that enhance overall organizational functioning.
Origins of the Organizational Citizenship Concept
The concept of Organizational Citizenship Behavior (OCB) originated from the seminal work of Dennis Organ in the early 1980s, emphasizing discretionary behaviors that go beyond formal job requirements. This concept builds on earlier psychological theories of prosocial behavior and role theory, linking employee actions to organizational effectiveness. Early research highlighted the importance of voluntary, non-rewarded activities that enhance workplace cooperation and productivity.
Key Dimensions of Organizational Citizenship
Organizational citizenship behavior (OCB) comprises voluntary, non-rewarded actions that support an organization's social and psychological environment, with key dimensions including altruism, conscientiousness, sportsmanship, courtesy, and civic virtue. These dimensions enhance teamwork, organizational efficiency, and employee morale by promoting proactive cooperation beyond formal job responsibilities. Distinguishing from formal organizational roles, OCB reflects discretionary behaviors essential for fostering positive workplace culture and sustained organizational performance.
Organizational Citizenship vs. Organizational Commitment
Organizational Citizenship Behavior (OCB) refers to voluntary, extra-role actions employees take to benefit their organization, such as helping colleagues and promoting a positive work environment. Organizational Commitment, on the other hand, measures the emotional attachment and loyalty an employee feels toward their organization, influencing retention and job satisfaction. While OCB emphasizes discretionary behavior beyond formal job duties, organizational commitment highlights an employee's psychological alignment and long-term dedication to the company.
Antecedents of Organizational Citizenship
Antecedents of Organizational Citizenship Behavior (OCB) encompass individual traits such as conscientiousness and agreeableness, alongside job satisfaction and perceived organizational support, which collectively enhance employees' voluntary contributions beyond formal roles. Organizational Justice, comprising distributive, procedural, and interactional fairness, significantly predicts OCB by fostering trust and commitment within the workplace. Leadership style, particularly transformational leadership, plays a critical role in motivating employees to exhibit citizenship behaviors by aligning individual values with organizational goals.
Impact of Organizational Citizenship on Performance
Organizational citizenship behavior (OCB) significantly enhances individual and organizational performance by fostering a cooperative and motivated work environment. Employees exhibiting high levels of OCB engage in discretionary actions beyond formal job requirements, leading to improved team cohesion, reduced turnover, and increased productivity. Organizations with strong OCB cultures experience better overall effectiveness, as these behaviors facilitate smoother coordination and contribute to achieving strategic goals.
Organizational Citizenship at Individual and Group Levels
Organizational citizenship behavior (OCB) at the individual level refers to personal voluntary actions that go beyond formal job requirements, such as helping colleagues and showing initiative. At the group level, OCB manifests as collective cooperation, shared support, and coordinated efforts that enhance overall team performance and workplace harmony. Both levels contribute to improved organizational effectiveness, with individual OCB fostering personal accountability and group OCB strengthening team cohesion.
Factors Influencing Organizational Citizenship Behaviors
Factors influencing Organizational Citizenship Behaviors (OCB) include job satisfaction, organizational commitment, and perceived organizational support, each significantly enhancing employees' voluntary contributions beyond their formal roles. Leadership style, particularly transformational and ethical leadership, fosters higher levels of OCB by promoting trust and motivation among employees. Work environment variables such as team cohesion and positive communication patterns also play crucial roles in encouraging discretionary behaviors that benefit the organization.
Measuring Organizational Citizenship Effectively
Measuring organizational citizenship behavior (OCB) requires accurate assessment tools like employee surveys and peer evaluations to capture voluntary, extra-role actions that contribute to workplace effectiveness. Reliable metrics focus on dimensions such as altruism, conscientiousness, and civic virtue, ensuring objective evaluation of positive employee contributions beyond formal job requirements. Consistent measurement of OCB aids in identifying behaviors that enhance organizational performance and promote a collaborative culture.
Enhancing Organizational Citizenship in the Workplace
Enhancing organizational citizenship in the workplace involves fostering behaviors such as altruism, conscientiousness, and civic virtue that go beyond formal job requirements. Encouraging open communication, recognizing employee contributions, and promoting a supportive culture increases voluntary cooperation and commitment. Implementing training programs and leadership practices that emphasize trust and fairness significantly boosts organizational citizenship behaviors, leading to improved team performance and overall organizational effectiveness.
Organizational citizenship Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com