Role exit occurs when individuals disengage from a significant social role that has been central to their identity, such as retiring from a career or ending a long-term relationship. This transition involves complex emotional and social adjustments as you redefine your self-concept and navigate new expectations. Explore the entire article to understand the stages, challenges, and strategies for successfully managing role exit.
Table of Comparison
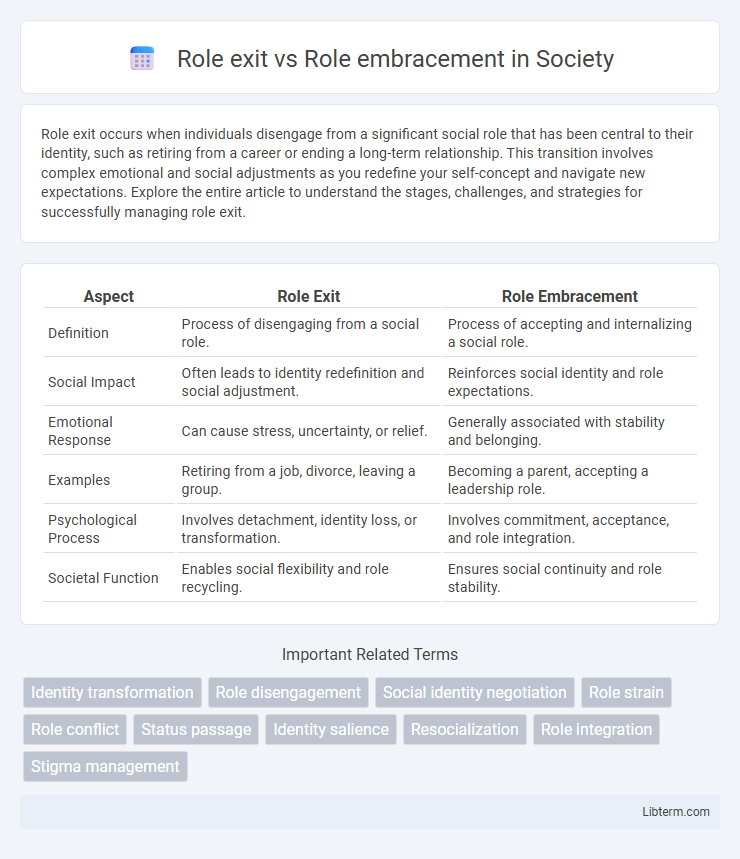
| Aspect | Role Exit | Role Embracement |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Process of disengaging from a social role. | Process of accepting and internalizing a social role. |
| Social Impact | Often leads to identity redefinition and social adjustment. | Reinforces social identity and role expectations. |
| Emotional Response | Can cause stress, uncertainty, or relief. | Generally associated with stability and belonging. |
| Examples | Retiring from a job, divorce, leaving a group. | Becoming a parent, accepting a leadership role. |
| Psychological Process | Involves detachment, identity loss, or transformation. | Involves commitment, acceptance, and role integration. |
| Societal Function | Enables social flexibility and role recycling. | Ensures social continuity and role stability. |
Understanding Role Exit and Role Embracement
Understanding role exit involves recognizing the process individuals undergo when disengaging from a significant social role, often accompanied by identity transformation and changes in behavior. Role embracement, conversely, signifies the acceptance and internalization of a new social role, leading to role-consistent attitudes and actions that align with societal expectations. Both concepts are critical in sociological studies of identity development and social adaptation, highlighting how individuals navigate shifts in social positions and responsibilities.
Theoretical Foundations of Role Dynamics
Role exit and role embracement represent contrasting processes within the theoretical foundations of role dynamics, where role exit involves disengagement from a previously held social role, often accompanied by identity transformation and redefinition. Role embracement, on the other hand, entails the acceptance and internalization of a new or existing role, enabling individuals to align behaviors, expectations, and self-concept with the role's demands. Theoretical frameworks such as symbolic interactionism and identity theory emphasize the negotiation and reconstruction of meanings during these transitions, highlighting how social context and personal agency influence the fluidity of role adoption and abandonment.
Key Differences Between Role Exit and Role Embracement
Role exit involves disengaging from a social role central to one's identity, often leading to a loss of associated status and requiring adjustment to new roles. Role embracement refers to actively accepting and internalizing a role, leading to increased commitment, role performance, and identity reinforcement. Key differences include the direction of identity change--role exit entails detachment and role discontinuity, whereas role embracement involves attachment and role continuity with enhanced social integration.
Factors Influencing Role Exit
Factors influencing role exit include personal dissatisfaction, conflicts between roles, and life transitions such as career change or retirement. Social pressures, changing identities, and the availability of alternative roles also play significant roles in an individual's decision to disengage from a current role. Emotional experiences, such as stress or loss of fulfillment, contribute to the motivation behind role exit processes.
Motivations for Role Embracement
Role embracement occurs when individuals accept and internalize new social roles due to intrinsic motivations such as personal growth, identity alignment, and fulfillment of core values. Motivations for role embracement often include a strong desire for social integration, positive self-concept reinforcement, and commitment to role expectations that enhance psychological well-being. These factors contrast with role exit, where individuals disengage from roles primarily due to dissatisfaction, conflict, or external pressures.
Psychological Impacts of Changing Social Roles
Role exit involves disengaging from a central social role, often causing identity confusion and stress due to loss of status or community, while role embracement reinforces self-concept through acceptance and internalization of new responsibilities. Psychological impacts of role exit include feelings of grief, decreased self-esteem, and uncertainty, whereas role embracement promotes increased self-efficacy, stability, and positive social integration. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for managing transitions such as career changes, divorce, or retirement to support mental health and adaptation.
Societal Reactions to Role Exit and Embracement
Societal reactions to role exit often involve stigma and social sanctions as individuals detach from expected behaviors or identities, leading to potential isolation or loss of social support. In contrast, role embracement is generally met with acceptance and reinforcement, as society rewards conformity by affirming the individual's commitment to the new or sustained role. These differing responses significantly influence the psychological adjustment and social integration of individuals undergoing role changes.
Stages of Role Transition
Role exit involves a process where individuals disengage from a sustained social role, typically passing through stages such as doubt, seeking alternatives, turning points, and creating a new identity. Role embracement, conversely, emphasizes affirming and deepening commitment within a social role, often marked by stages of acceptance, identity consolidation, and increased role investment. Understanding these stages helps clarify how people navigate changes in social identity and group membership dynamics.
Role Identity and Self-Concept in Social Roles
Role exit involves the process of disengaging from a social role that has been central to one's identity, leading to a significant transformation in self-concept as individuals reconstruct their role identity to align with new social expectations. Role embracement occurs when individuals fully internalize and affirm a new or existing social role, reinforcing their self-concept through role-consistent behaviors and attitudes. The dynamics between role exit and role embracement critically influence how social roles shape personal identity, motivation, and social behavior within various contexts.
Real-Life Examples of Role Exit and Role Embracement
Role exit occurs when individuals disengage from a social role central to their identity, such as a firefighter retiring after decades of service; this transition often involves redefining self-concept and social relationships. Role embracement involves actively adopting and internalizing a new role, exemplified by immigrants embracing the identity and cultural practices of their new country to integrate successfully. Both processes highlight the dynamic nature of social identities and the psychological adjustments required during significant life changes.
Role exit Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com