Cultural conformity shapes individual behavior by aligning beliefs, values, and practices with societal norms, promoting social cohesion and predictability. This alignment can influence everything from dress codes and language to ethical judgments and lifestyle choices. Discover how cultural conformity impacts your daily interactions and personal identity throughout the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
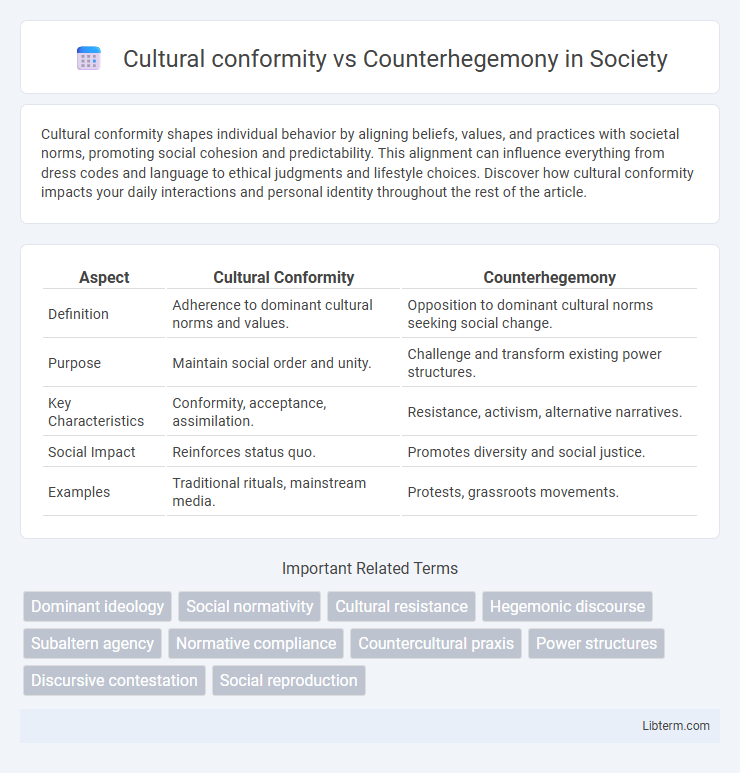
| Aspect | Cultural Conformity | Counterhegemony |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Adherence to dominant cultural norms and values. | Opposition to dominant cultural norms seeking social change. |
| Purpose | Maintain social order and unity. | Challenge and transform existing power structures. |
| Key Characteristics | Conformity, acceptance, assimilation. | Resistance, activism, alternative narratives. |
| Social Impact | Reinforces status quo. | Promotes diversity and social justice. |
| Examples | Traditional rituals, mainstream media. | Protests, grassroots movements. |
Understanding Cultural Conformity
Cultural conformity refers to the adoption of behaviors, norms, and values that align with the dominant societal standards, reinforcing existing power structures and ideologies. Understanding cultural conformity involves analyzing how social institutions, media, and education systems propagate dominant cultural narratives that individuals internalize to maintain social cohesion. This concept is critical in examining the mechanisms through which hegemony operates to stabilize and perpetuate cultural norms.
The Foundations of Counterhegemony
The foundations of counterhegemony lie in challenging dominant cultural norms and power structures imposed by hegemonic forces, aiming to create alternative worldviews and practices that empower marginalized groups. This process involves the critical interrogation of ideology, identity, and social institutions to disrupt the reproduction of hegemonic values and foster transformative social change. Key theorists like Antonio Gramsci emphasize the role of cultural struggle and organic intellectuals in building counterhegemonic movements that resist cultural conformity and advocate for social justice.
Historical Contexts: Tradition vs Transformation
Cultural conformity often reinforces established traditions by promoting shared values and norms that maintain social cohesion within historical contexts. Counterhegemony challenges these traditions through transformative actions and ideologies that seek to disrupt dominant power structures and cultural narratives. Historical movements such as the Civil Rights Movement or anti-colonial struggles exemplify the tension between preserving cultural heritage and pursuing radical societal change.
Power Structures in Culture
Cultural conformity reinforces dominant power structures by promoting hegemonic values that maintain social order and marginalize dissenting voices. Counterhegemony challenges these power dynamics through alternative narratives and practices that disrupt cultural norms and empower oppressed groups. Both frameworks reveal how culture serves as a battleground for ideological control and resistance within society.
Media's Role in Shaping Norms
Media plays a crucial role in reinforcing cultural conformity by perpetuating dominant narratives and social norms through mainstream news outlets, television, and advertising. Alternative media platforms and independent content creators challenge these hegemonic structures by promoting counterhegemonic ideas that question and resist dominant ideologies. The dynamic interplay between mainstream and counterhegemonic media shapes public discourse and influences societal attitudes toward power, identity, and cultural values.
Everyday Acts of Resistance
Everyday acts of resistance challenge cultural conformity by subtly opposing dominant norms through routine behaviors and small-scale defiance. These practices, such as using alternative dialects, creating counter-hegemonic art, or practicing marginalized traditions, disrupt hegemonic power structures embedded in daily life. By embedding resistance in ordinary activities, individuals negotiate identity and power, weakening imposed social controls without overt confrontation.
Marginalized Voices and Representation
Cultural conformity enforces dominant social norms that marginalize minority groups by limiting their visibility and expression within mainstream narratives. Counterhegemony challenges these power structures by amplifying marginalized voices and advocating for authentic representation in media, politics, and culture. Elevating diverse perspectives disrupts hegemonic control and fosters inclusive societies where equity in representation drives social change.
Globalization and Cultural Dynamics
Globalization accelerates cultural conformity by promoting dominant cultural norms through media, trade, and technology, often marginalizing local identities. Counterhegemony emerges as resistant cultural movements that challenge and reshape hegemonic influences, fostering diverse expressions and alternative narratives. These dynamics create ongoing tensions between homogenizing forces and acts of cultural resilience in a globalized world.
Social Movements Challenging Orthodoxy
Social movements challenging orthodoxy often embody counterhegemony by resisting dominant cultural norms and promoting alternative values that disrupt societal conformity. These movements leverage collective action to question established power structures, fostering social change through grassroots activism and cultural redefinition. By rejecting mainstream ideologies, counterhegemonic social movements create spaces for marginalized voices and diverse worldviews, effectively contesting cultural conformity.
Future Trends in Cultural Dissent
Future trends in cultural dissent emphasize the rise of digital platforms as critical spaces for counterhegemonic movements, enabling marginalized voices to challenge dominant cultural norms. The proliferation of decentralized social media networks facilitates grassroots activism, fostering alternative narratives that resist mainstream conformity. Emerging technologies like AI and virtual reality are expected to further amplify diverse cultural expressions, reshaping the dynamics between cultural conformity and resistance.
Cultural conformity Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com