Libertarianism prioritizes individual freedom, advocating minimal government intervention in both personal lives and economic activities. It champions free-market principles and personal responsibility while opposing excessive regulations and state control. Discover how libertarian ideals shape political debates and influence your choices in society by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
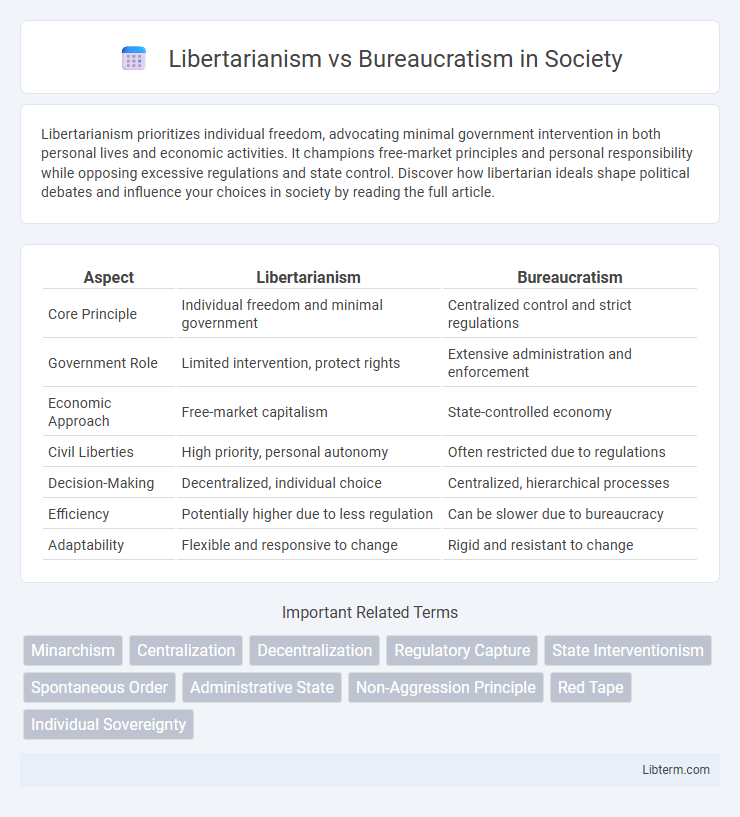
| Aspect | Libertarianism | Bureaucratism |
|---|---|---|
| Core Principle | Individual freedom and minimal government | Centralized control and strict regulations |
| Government Role | Limited intervention, protect rights | Extensive administration and enforcement |
| Economic Approach | Free-market capitalism | State-controlled economy |
| Civil Liberties | High priority, personal autonomy | Often restricted due to regulations |
| Decision-Making | Decentralized, individual choice | Centralized, hierarchical processes |
| Efficiency | Potentially higher due to less regulation | Can be slower due to bureaucracy |
| Adaptability | Flexible and responsive to change | Rigid and resistant to change |
Defining Libertarianism: Core Principles and Values
Libertarianism emphasizes individual liberty, minimal state intervention, and free-market principles as its core values, advocating for personal responsibility and limited government power. It prioritizes property rights, voluntary exchanges, and individual autonomy, opposing bureaucratic control and excessive regulation. This philosophy argues that decentralized decision-making and reduced government bureaucracy enhance economic efficiency and personal freedom.
Understanding Bureaucratism: Structure and Function
Bureaucratism embodies a hierarchical system of authority characterized by standardized rules and procedures designed to ensure consistent decision-making and efficient administration across complex organizations. The structure typically includes multiple levels of management, each with defined roles and responsibilities, facilitating control and coordination of large-scale operations. This organizational framework enables stability and predictability but often faces criticism for rigidity and resistance to innovation compared to the more flexible, individual-focused approach of libertarianism.
Historical Origins: Roots of Libertarianism and Bureaucratism
Libertarianism traces its historical origins to Enlightenment thinkers such as John Locke, emphasizing individual liberty, private property, and limited government intervention. Bureaucratism emerged from the rise of complex administrative states in the 19th and 20th centuries, influenced by Max Weber's theories on rational-legal authority and hierarchical organization. The contrast between libertarian ideals and bureaucratic structures highlights fundamental debates over state power and personal freedom throughout modern political history.
Individual Freedom vs Government Control
Libertarianism champions individual freedom, advocating minimal government interference in personal choices and economic activities, emphasizing self-ownership and voluntary associations. Bureaucratism, by contrast, prioritizes extensive government control and regulation, aiming to organize society through hierarchical administrative systems that often limit personal autonomy. The tension between these ideologies centers on the balance between maximizing individual liberty and enforcing collective order through state authority.
Economic Perspectives: Free Market vs Regulatory Oversight
Libertarianism champions a free market economy where minimal government intervention drives innovation, efficiency, and individual economic freedom. Bureaucratism supports extensive regulatory oversight to ensure market stability, consumer protection, and equitable resource distribution through government agencies. The core economic debate centers on balancing unregulated market dynamics with structured controls to mitigate risks like monopolies and economic inequality.
Political Implications: Governance Models Compared
Libertarianism advocates minimal government intervention, emphasizing individual freedoms and free-market principles, which can lead to decentralized governance and reduced regulatory burdens. Bureaucratism relies on structured, hierarchical government agencies to implement centralized policies, often resulting in increased control and slower decision-making processes. Comparing these governance models highlights the tension between maximizing personal liberty and ensuring organized, consistent public administration.
Social Impact: Community and Personal Responsibility
Libertarianism emphasizes individual autonomy and minimal government intervention, fostering personal responsibility and empowering communities to self-organize without centralized control. Bureaucratism relies on hierarchical structures and regulatory frameworks, which can inhibit grassroots initiative and reduce local accountability by placing decision-making power in distant institutions. The social impact reflects a contrast between promoting individual freedom and community-driven solutions versus prioritizing standardized policies and institutional oversight.
Criticisms and Challenges of Libertarianism
Libertarianism faces criticism for its emphasis on minimal government intervention, which critics argue can lead to insufficient public services and regulatory oversight, potentially exacerbating social inequalities. The challenge of addressing complex societal issues such as healthcare, environmental regulations, and economic disparities often highlights libertarianism's reliance on individual responsibility over collective action. Critics also contend that libertarian policies may weaken essential bureaucratic institutions needed to maintain order and ensure equitable resource distribution in modern states.
Criticisms and Challenges of Bureaucratism
Bureaucratism faces criticism for fostering inefficiency through rigid hierarchies and excessive red tape that stifle innovation and slow decision-making processes. It often breeds a lack of accountability, as complex structures dilute responsibility, leading to mismanagement and corruption risks. Critics argue that bureaucratic systems prioritize procedural adherence over outcomes, which hampers responsiveness to individual needs and dynamic market conditions.
Future Trends: Balancing Libertarianism and Bureaucratism
Emerging future trends in governance emphasize the challenge of balancing libertarianism's emphasis on individual freedom with bureaucratism's structured regulatory frameworks to ensure societal order. Technological advancements such as blockchain and AI-enabled decentralized systems may facilitate greater transparency and efficiency, reducing bureaucratic overhead while preserving personal autonomy. Policy models that integrate adaptive governance, leveraging data-driven decision-making and participatory platforms, will likely shape the evolution toward a hybrid system blending minimal state intervention with strategic regulation.
Libertarianism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com