Social identity shapes how individuals perceive themselves and are perceived within groups, influencing behavior and social interactions. It encompasses factors such as ethnicity, nationality, gender, and social roles that contribute to a person's sense of belonging. Explore the rest of the article to understand how your social identity impacts various aspects of life.
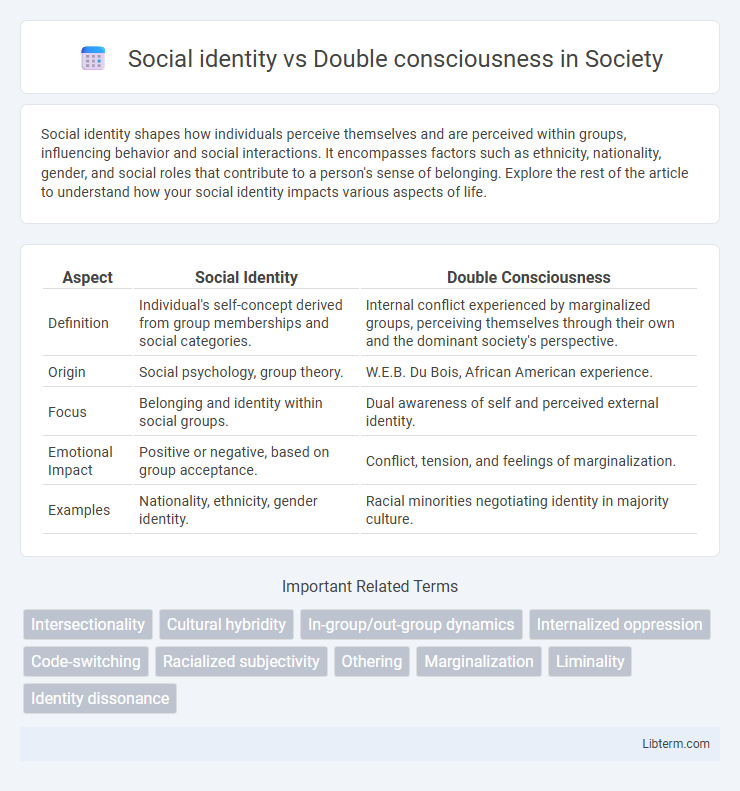
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Social Identity | Double Consciousness |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Individual's self-concept derived from group memberships and social categories. | Internal conflict experienced by marginalized groups, perceiving themselves through their own and the dominant society's perspective. |
| Origin | Social psychology, group theory. | W.E.B. Du Bois, African American experience. |
| Focus | Belonging and identity within social groups. | Dual awareness of self and perceived external identity. |
| Emotional Impact | Positive or negative, based on group acceptance. | Conflict, tension, and feelings of marginalization. |
| Examples | Nationality, ethnicity, gender identity. | Racial minorities negotiating identity in majority culture. |
Understanding Social Identity: Core Concepts
Social identity refers to an individual's self-concept derived from perceived membership in social groups, encompassing aspects such as ethnicity, nationality, and gender. Double consciousness, introduced by W.E.B. Du Bois, describes the internal conflict experienced by marginalized individuals who navigate their own self-perception alongside dominant societal views. Understanding social identity involves analyzing how social categorizations influence behavior, group dynamics, and individual psychology in various social contexts.
The Origins and Evolution of Double Consciousness
Double consciousness originated from W.E.B. Du Bois's analysis of African American identity under systemic racial oppression, describing a dual awareness of self and society. This concept has evolved to articulate the psychological challenge of reconciling internal identity with external societal perceptions, especially in marginalized communities. Unlike broader social identity theory, double consciousness uniquely emphasizes the conflict between personal identity and imposed social narratives in racialized contexts.
Key Differences Between Social Identity and Double Consciousness
Social identity refers to an individual's self-concept derived from perceived membership in social groups such as race, gender, or nationality, emphasizing external classification within society. Double consciousness, a concept introduced by W.E.B. Du Bois, describes an internal conflict experienced by marginalized individuals who see themselves through the eyes of a dominant society while maintaining their own self-awareness. The key difference lies in social identity focusing on group affiliation and collective identity, whereas double consciousness highlights the psychological tension of navigating dual social realities.
Intersectionality: Where Social Identity Meets Double Consciousness
Social identity encompasses the multifaceted aspects of an individual's self-concept derived from group memberships, while double consciousness describes the internal conflict experienced by marginalized individuals navigating dominant societal perceptions. Intersectionality bridges these concepts by highlighting how overlapping social identities--such as race, gender, and class--intensify the lived experience of double consciousness. This framework reveals the complex ways in which systemic inequalities shape both personal identity formation and collective social dynamics.
The Role of Race and Ethnicity in Shaping Identity
Race and ethnicity profoundly influence social identity by shaping individual self-perception and group belonging through shared cultural heritage and lived experiences. Double consciousness, a concept introduced by W.E.B. Du Bois, captures the internal conflict experienced by marginalized racial groups who navigate the tension between their own self-identity and the dominant societal perceptions. This dual awareness highlights the complexities of racial and ethnic identity formation within societies structured by systemic inequalities.
Psychological Impacts of Navigating Multiple Identities
Navigating multiple identities often leads to psychological stress characterized by internal conflict and identity fragmentation, impacting self-esteem and mental health. Social identity theory highlights the need for group belonging and positive self-concept, while double consciousness, as conceptualized by W.E.B. Du Bois, describes the internal struggle of reconciling marginalized identities within dominant societal norms. This complex negotiation can result in heightened anxiety, cognitive dissonance, and a persistent sense of otherness in individuals balancing intersecting identities.
Historical Context: W.E.B. Du Bois and Double Consciousness
W.E.B. Du Bois introduced the concept of double consciousness in the early 20th century to describe the internal conflict experienced by African Americans navigating a racially segregated society. This framework highlights the dual awareness of one's identity and the perception imposed by a dominant culture, shaped by historical events like slavery and Jim Crow laws. Social identity theory, by contrast, broadly examines individual self-concepts derived from group memberships, but Du Bois's double consciousness specifically addresses the unique historical and psychological struggles of African American identity formation.
Social Identity Theory: Frameworks and Applications
Social Identity Theory, developed by Henri Tajfel and John Turner, explains how individuals derive a sense of identity and self-esteem from group memberships, influencing intergroup behavior and social categorization. This framework has practical applications in organizational behavior, marketing, and conflict resolution by addressing in-group favoritism and out-group discrimination. Unlike Du Bois' concept of double consciousness, which highlights an internal conflict of identity experienced by marginalized groups, Social Identity Theory emphasizes the cognitive processes behind group affiliation and social comparison.
Modern Implications in Society and Culture
Social identity shapes individuals' sense of belonging through race, ethnicity, and community affiliations, impacting societal roles and cultural expression. Double consciousness exposes the internal conflict experienced by marginalized groups navigating dominant cultural expectations and their own heritage, influencing identity formation and social interactions. Modern implications include ongoing challenges in multicultural integration, systemic inequality, and efforts to reconcile multiple identities within globalized societies.
Strategies for Resolving Identity Conflicts
Strategies for resolving identity conflicts between social identity and double consciousness involve embracing intersectionality to acknowledge multifaceted personal and group affiliations. Engaging in reflective dialogue and critical self-awareness helps individuals reconcile external social perceptions with internal self-conceptions. Creating inclusive spaces that validate diverse identities supports the negotiation of complex identity experiences and reduces psychological distress.
Social identity Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com