Uncertainty avoidance measures how comfortable individuals or societies are with ambiguity and unstructured situations, influencing decision-making and risk-taking behaviors. Cultures with high uncertainty avoidance prefer clear rules and stability, while those with low avoidance embrace change and innovation. Explore the rest of the article to understand how this dimension impacts your interactions and business strategies globally.
Table of Comparison
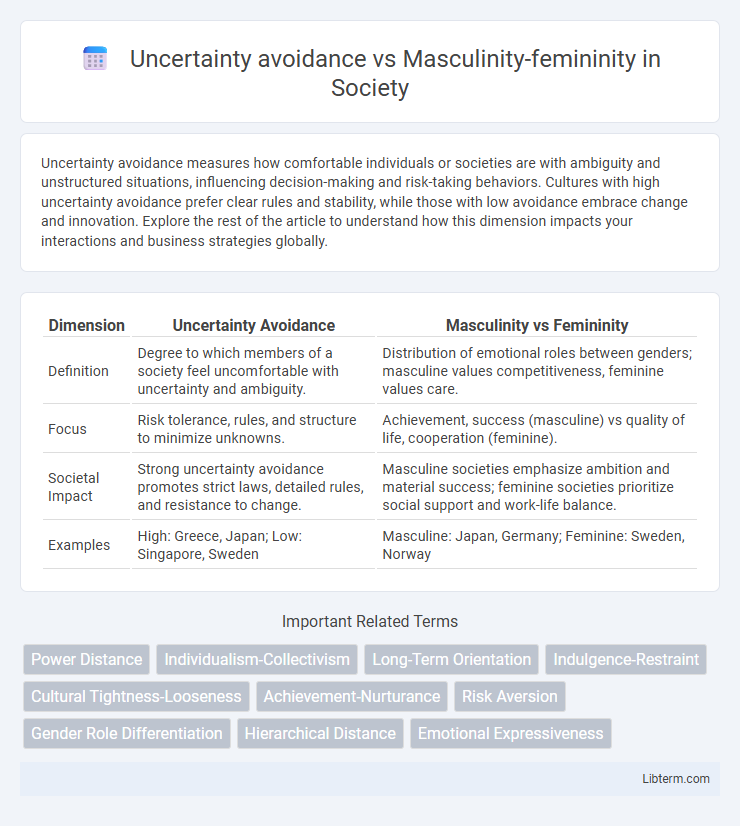
| Dimension | Uncertainty Avoidance | Masculinity vs Femininity |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Degree to which members of a society feel uncomfortable with uncertainty and ambiguity. | Distribution of emotional roles between genders; masculine values competitiveness, feminine values care. |
| Focus | Risk tolerance, rules, and structure to minimize unknowns. | Achievement, success (masculine) vs quality of life, cooperation (feminine). |
| Societal Impact | Strong uncertainty avoidance promotes strict laws, detailed rules, and resistance to change. | Masculine societies emphasize ambition and material success; feminine societies prioritize social support and work-life balance. |
| Examples | High: Greece, Japan; Low: Singapore, Sweden | Masculine: Japan, Germany; Feminine: Sweden, Norway |
Introduction to Cultural Dimensions Theory
Hofstede's Cultural Dimensions Theory identifies uncertainty avoidance and masculinity-femininity as key cultural variables influencing societal behavior and values. Uncertainty avoidance measures a culture's tolerance for ambiguity and risk, affecting decision-making and innovation, while masculinity-femininity reflects gender role differentiation, emphasizing competitiveness versus cooperation. Understanding these dimensions helps interpret cross-cultural interactions and organizational practices worldwide.
Defining Uncertainty Avoidance
Uncertainty avoidance measures a society's tolerance for ambiguity and risk, reflecting the degree to which members feel uncomfortable with unstructured situations. It influences organizational behavior, decision-making, and the preference for established rules and procedures to minimize uncertainty. In contrast, masculinity-femininity relates to the distribution of emotional roles between genders, highlighting values such as competitiveness versus care, rather than attitudes toward ambiguity.
Understanding Masculinity-Femininity
Masculinity-femininity reflects cultural preferences for achievement, assertiveness, and material success versus cooperation, care, and quality of life, shaping workplace dynamics and social roles. High masculinity cultures emphasize competition, ambition, and distinct gender roles, while feminine cultures prioritize empathy, collaboration, and gender equality. Understanding these dimensions aids in interpreting organizational behavior, communication styles, and conflict resolution across different cultural contexts.
Key Differences between the Two Dimensions
Uncertainty avoidance measures a society's tolerance for ambiguity and ambiguity-related stress, while masculinity-femininity reflects the distribution of emotional roles between genders with masculinity emphasizing competitiveness and femininity valuing care and quality of life. High uncertainty avoidance cultures favor structured environments and clear rules, whereas masculine cultures prioritize achievement, success, and assertiveness over cooperation and modesty found in feminine cultures. These dimensions influence workplace behavior, with uncertainty avoidance impacting risk-taking attitudes and masculinity-femininity affecting leadership styles and motivation approaches.
Cultural Implications in the Workplace
High uncertainty avoidance cultures prioritize structured work environments with clear rules and risk mitigation, fostering employee stability but often limiting innovation. Masculine cultures emphasize competitiveness, achievement, and assertiveness, shaping workplace dynamics through goal-oriented leadership and performance-driven incentives. In contrast, feminine cultures value collaboration, quality of life, and employee well-being, promoting cooperative teamwork and supportive management practices that influence organizational behavior and communication styles.
Impact on Communication Styles
Uncertainty avoidance cultures prefer clear rules and structured communication, minimizing ambiguity to reduce anxiety, whereas masculinity-femininity dimensions influence whether communication is more assertive and competitive (masculine) or nurturing and cooperative (feminine). High uncertainty avoidance correlates with formal, precise language to prevent misunderstandings, while masculine cultures favor direct, goal-oriented exchanges contrasting with the empathetic, consensus-driven dialogue found in feminine cultures. Understanding these dimensions aids in adapting communication strategies to improve cross-cultural interactions and reduce friction in multinational teams.
Influence on Decision-Making Process
Uncertainty avoidance influences decision-making by driving preferences for structured procedures and risk minimization, leading to cautious and well-planned approaches. Masculinity-femininity shapes decisions through cultural emphasis on competitiveness and achievement in masculine societies, while feminine cultures prioritize cooperation and consensus-building. The interplay of these dimensions affects whether decisions are made assertively with clear hierarchies or collaboratively with flexible guidelines.
Case Studies: Countries with High Uncertainty Avoidance vs Masculinity
Countries with high uncertainty avoidance, such as Japan and Greece, typically emphasize strict rules and risk minimization in both personal and professional settings, fostering a culture that values stability and predictability. In contrast, nations exhibiting high masculinity, like the United States and Germany, prioritize competition, achievement, and assertiveness, reflecting a societal focus on success and material rewards. Case studies reveal how these cultural dimensions influence management styles, decision-making processes, and interpersonal relationships within organizations, impacting international business strategies and cross-cultural communication.
Navigating Cross-Cultural Interactions
Uncertainty avoidance measures how cultures tolerate ambiguity, impacting decision-making and communication styles, while masculinity-femininity reflects a society's emphasis on competitiveness versus care and collaboration. Navigating cross-cultural interactions requires recognizing that high uncertainty avoidance cultures prefer structured environments, whereas feminine cultures value relationship-building and consensus over assertiveness. Understanding these dimensions helps tailor communication strategies to manage expectations, reduce misunderstandings, and foster effective teamwork across diverse cultural contexts.
Conclusion: Bridging the Gap for Global Success
High uncertainty avoidance cultures emphasize risk minimization and structured environments, while masculinity-femininity dimensions influence values related to competitiveness and nurturing behaviors. Bridging these cultural differences requires adaptive leadership that balances clear guidelines with empathy and collaboration to foster innovation and employee well-being. Leveraging insights from both dimensions enhances global business strategies, promoting effective communication and sustainable success across diverse markets.
Uncertainty avoidance Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com