Ascribed status refers to the social position assigned to individuals based on characteristics such as race, gender, family background, or ethnicity, which they are born into rather than earned. This status can significantly influence a person's opportunities, social interactions, and self-identity within a society. Explore the rest of the article to understand how ascribed status impacts social dynamics and personal experiences.
Table of Comparison
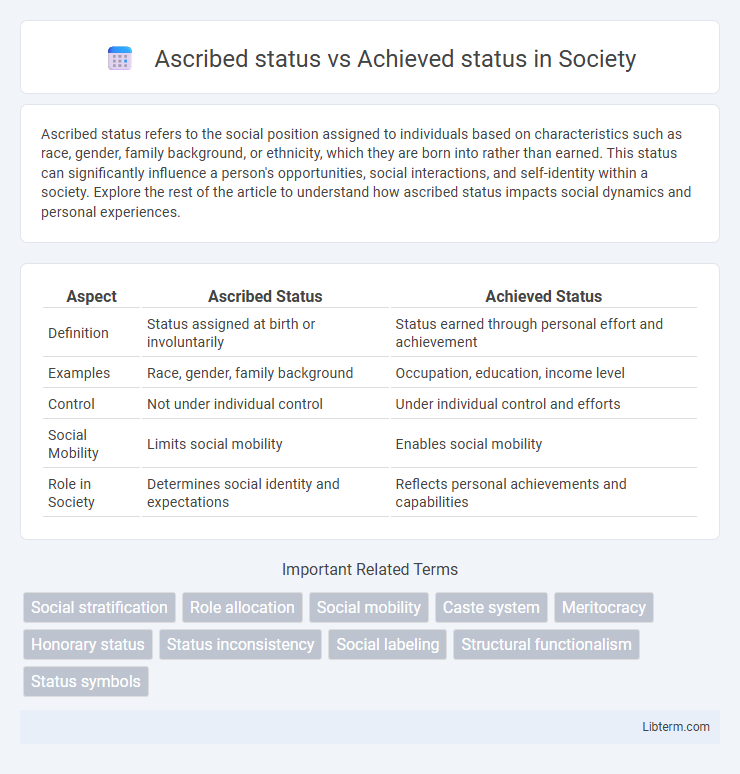
| Aspect | Ascribed Status | Achieved Status |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Status assigned at birth or involuntarily | Status earned through personal effort and achievement |
| Examples | Race, gender, family background | Occupation, education, income level |
| Control | Not under individual control | Under individual control and efforts |
| Social Mobility | Limits social mobility | Enables social mobility |
| Role in Society | Determines social identity and expectations | Reflects personal achievements and capabilities |
Introduction to Social Status
Ascribed status refers to the social position assigned at birth based on characteristics like race, gender, or family heritage, while achieved status is earned through personal efforts such as education, occupation, or skills. Social status influences individual identity and societal interactions, shaping access to resources and power within a community. Understanding the distinction between ascribed and achieved status is crucial in analyzing social mobility and inequality.
Defining Ascribed Status
Ascribed status refers to the social position assigned to an individual at birth or assumed involuntarily later in life, based on characteristics such as race, gender, ethnicity, or family heritage. This status is typically immutable and influences opportunities, social interactions, and individual identity within a society. Unlike achieved status, which is earned through personal effort and accomplishments, ascribed status is predetermined and shapes social expectations and roles without regard to individual merit.
Understanding Achieved Status
Achieved status refers to a social position that individuals earn or accomplish through their actions, skills, education, or efforts, contrasting with ascribed status, which is assigned at birth or involuntarily. This status highlights the role of personal agency and achievement in shaping social identity, impacting opportunities and social mobility within a society. Understanding achieved status is crucial for analyzing social dynamics, as it reflects meritocratic values and influences individual life chances.
Key Differences Between Ascribed and Achieved Status
Ascribed status is assigned at birth based on characteristics such as ethnicity, gender, or family background, while achieved status results from personal effort, skills, or accomplishments. Ascribed status is typically fixed and involuntary, contrasting with achieved status, which is flexible and earned through individual actions. These distinctions affect social mobility, with ascribed status often limiting opportunities, whereas achieved status can provide pathways to higher social positions.
Examples of Ascribed Status in Society
Examples of ascribed status in society include race, ethnicity, gender, and family heritage, which individuals inherit at birth and cannot change. Social class and caste systems also exemplify ascribed status, often determining a person's opportunities and social interactions from an early age. These characteristics shape identity and influence social roles regardless of personal achievements or efforts.
Examples of Achieved Status in Society
Achieved status in society refers to positions earned through individual effort, skill, or accomplishment, such as becoming a doctor, teacher, or athlete. Examples include a person who attains higher education degrees, secures professional employment, or wins a competitive sports championship. These statuses contrast with ascribed statuses, which are assigned at birth and include attributes like race, gender, or family background.
Factors Influencing Ascribed Status
Ascribed status is determined by inherent traits such as race, gender, ethnicity, and family background, which individuals are born into without personal choice. Social and cultural norms, including traditions, caste systems, and hereditary privileges, strongly influence the ascribed status assigned to a person. These factors create a static social position that often impacts access to resources, opportunities, and social mobility in various societies.
Pathways to Attaining Achieved Status
Achieved status is acquired through personal effort, skills, education, and accomplishments, reflecting an individual's agency and ability to influence their social position. Pathways to attaining achieved status often include formal education, professional training, career advancements, and social networking, which enhance one's reputation and socioeconomic standing. Unlike ascribed status, which is assigned at birth and immutable, achieved status allows for social mobility based on merit and individual achievements.
Impact of Status Types on Individual Life Chances
Ascribed status, determined by birth traits like race, gender, or family background, often limits access to resources and opportunities, influencing educational attainment, employment, and social mobility. Achieved status, earned through personal effort such as education, skills, or career success, allows individuals to improve their life chances through merit-based recognition and socioeconomic advancement. The interplay between ascribed and achieved status shapes social inequality, affecting income distribution, health outcomes, and overall quality of life.
Ascribed vs Achieved Status: Contemporary Relevance
Ascribed status refers to social positions assigned at birth based on attributes like race, gender, or family heritage, while achieved status is earned through personal effort, education, or career accomplishments. In contemporary society, the tension between ascribed and achieved status remains significant in discussions on social mobility, inequality, and identity politics. Understanding how ascribed factors influence opportunities despite achievements highlights ongoing challenges in creating equitable systems.
Ascribed status Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com