Self-serving bias influences how individuals attribute their successes to internal factors while blaming external causes for failures, shaping personal accountability and perception. Recognizing this cognitive bias is essential for improving self-awareness and fostering more accurate self-assessment in both personal and professional contexts. Explore the rest of the article to understand how self-serving bias affects your decisions and relationships.
Table of Comparison
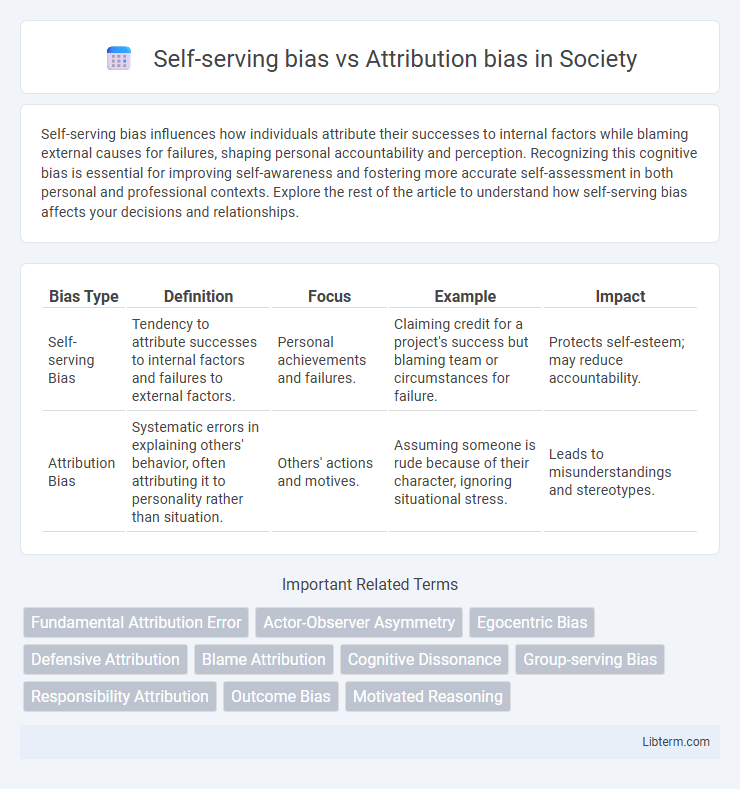
| Bias Type | Definition | Focus | Example | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Self-serving Bias | Tendency to attribute successes to internal factors and failures to external factors. | Personal achievements and failures. | Claiming credit for a project's success but blaming team or circumstances for failure. | Protects self-esteem; may reduce accountability. |
| Attribution Bias | Systematic errors in explaining others' behavior, often attributing it to personality rather than situation. | Others' actions and motives. | Assuming someone is rude because of their character, ignoring situational stress. | Leads to misunderstandings and stereotypes. |
Understanding Self-Serving Bias
Self-serving bias refers to the tendency to attribute personal successes to internal factors such as ability and effort, while blaming external factors for failures. This bias enhances self-esteem by selectively interpreting events to maintain a positive self-image. Understanding self-serving bias is crucial for recognizing how it skews personal accountability and influences interpersonal relationships.
Defining Attribution Bias
Attribution bias refers to the systematic errors individuals make when evaluating the causes of their own and others' behaviors, often leading to distorted judgments. Unlike self-serving bias, which protects self-esteem by attributing successes internally and failures externally, attribution bias encompasses a broader range of misjudgments such as the fundamental attribution error, where people overemphasize personality traits and underestimate situational factors. Understanding attribution bias is crucial for improving interpersonal communication and reducing conflicts arising from misinterpretations of others' actions.
Key Differences Between Self-Serving and Attribution Bias
Self-serving bias involves attributing personal successes to internal factors and failures to external causes, enhancing self-esteem. Attribution bias refers to errors in assigning causes to others' behavior, often misjudging intentions or situational influences. The key difference lies in self-serving bias emphasizing self-protection, while attribution bias concerns broader judgment errors about others' actions.
Psychological Foundations of Both Biases
Self-serving bias arises from the psychological need to maintain self-esteem by attributing successes to internal factors and failures to external circumstances. Attribution bias encompasses various cognitive distortions where individuals misattribute causes of behavior, often influenced by limited information processing and heuristic shortcuts. Both biases stem from fundamental cognitive mechanisms aimed at preserving a coherent self-concept and simplifying social judgments, embedded within the framework of social cognition theory.
Real-Life Examples of Self-Serving Bias
Self-serving bias manifests in real life when athletes attribute wins to their skill but blame losses on external factors like bad referees, highlighting the tendency to preserve self-esteem. Students often exhibit this bias by crediting good grades to their intelligence while blaming poor performance on unfair exams or difficult teachers. In the workplace, employees may take credit for successful projects while blaming failures on team members or management decisions, demonstrating how self-serving bias distorts personal accountability.
Real-Life Examples of Attribution Bias
Attribution bias often manifests in real-life situations such as blaming a coworker's mistake on their carelessness while excusing one's own errors due to external factors like lack of time. In traffic, a driver may attribute another's aggressive behavior to their personality, yet justify their own similar actions by explaining unavoidable circumstances. These examples highlight how attribution bias skews perception by overemphasizing personal traits in others and external conditions in oneself.
Impact of Biases on Decision Making
Self-serving bias and attribution bias significantly distort decision-making by influencing how individuals evaluate outcomes and assign causes to events. Self-serving bias leads people to attribute successes to internal factors while blaming failures on external circumstances, which can hinder learning from mistakes and reduce accountability. Attribution bias, which involves misjudging others' behaviors by attributing them to inherent traits rather than situational factors, often results in flawed judgments and conflicts, negatively affecting interpersonal decisions and organizational dynamics.
Overcoming Self-Serving Bias
Overcoming self-serving bias requires cultivating self-awareness and actively seeking objective feedback to distinguish personal achievements from external influences. Techniques such as reflective journaling and perspective-taking help individuals recognize their role in failures without deflecting blame. Employing attribution retraining encourages attributing outcomes to controllable factors, enhancing responsibility and promoting personal growth.
Reducing Attribution Bias in Daily Life
Reducing attribution bias in daily life involves consciously examining the causes behind others' behaviors, emphasizing situational factors over inherent traits. Practicing empathy and seeking alternative explanations can minimize the tendency to unfairly attribute negative actions to personality flaws. Mindfulness techniques and feedback from diverse perspectives further enhance accuracy in understanding social interactions.
The Importance of Recognizing Cognitive Biases
Recognizing cognitive biases such as self-serving bias and attribution bias is crucial for improving decision-making and interpersonal understanding. Self-serving bias leads individuals to attribute successes to personal factors while blaming external circumstances for failures, whereas attribution bias involves misjudging others' behaviors by oversimplifying their motives. Awareness of these biases enhances objectivity, reduces conflict, and fosters more accurate evaluations in both personal and professional contexts.
Self-serving bias Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com