Counterculture challenges mainstream values by embracing alternative lifestyles, beliefs, and artistic expressions that question societal norms. It often sparks social change by promoting innovation, diversity, and freedom of thought. Discover how counterculture shapes your world and ignites transformation in the full article.
Table of Comparison
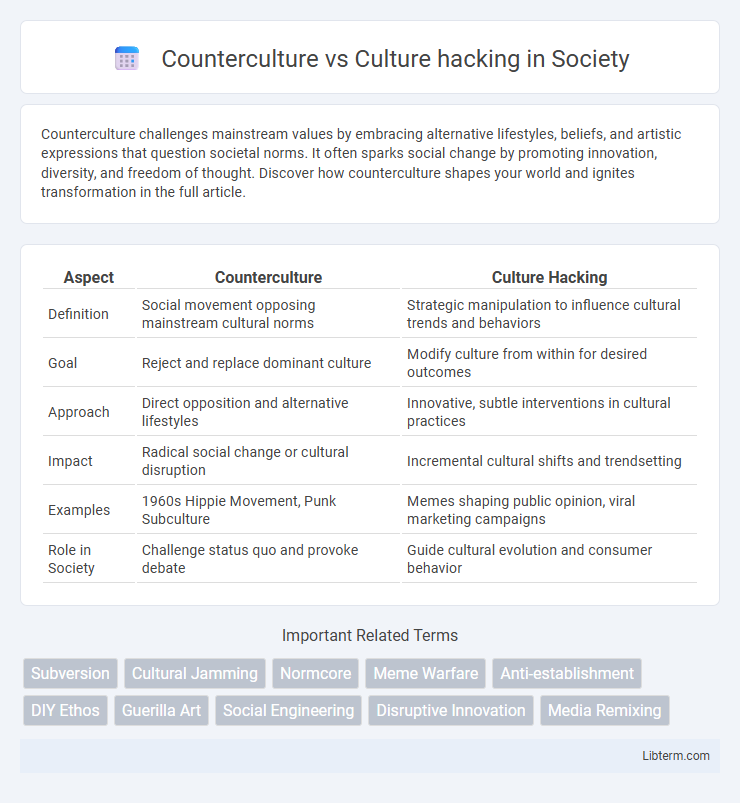
| Aspect | Counterculture | Culture Hacking |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Social movement opposing mainstream cultural norms | Strategic manipulation to influence cultural trends and behaviors |
| Goal | Reject and replace dominant culture | Modify culture from within for desired outcomes |
| Approach | Direct opposition and alternative lifestyles | Innovative, subtle interventions in cultural practices |
| Impact | Radical social change or cultural disruption | Incremental cultural shifts and trendsetting |
| Examples | 1960s Hippie Movement, Punk Subculture | Memes shaping public opinion, viral marketing campaigns |
| Role in Society | Challenge status quo and provoke debate | Guide cultural evolution and consumer behavior |
Introduction to Counterculture and Culture Hacking
Counterculture represents a deliberate rejection of mainstream societal norms, emphasizing alternative lifestyles, values, and artistic expressions that challenge conventional cultural frameworks. Culture hacking involves strategically manipulating cultural symbols, narratives, and practices to subvert, disrupt, or influence dominant cultural systems from within. Both concepts intersect in their focus on transformative social impact, but culture hacking leverages insider tactics, whereas counterculture adopts an oppositional stance outside mainstream culture.
Defining Counterculture: Origins and Evolution
Counterculture emerged in the 1960s as a social movement rejecting mainstream cultural norms, emphasizing values such as anti-establishment views, civil rights, and environmentalism. This evolution of counterculture was deeply influenced by political activism, music, and art that challenged authority and traditional societal structures. Over time, counterculture has shaped modern activism and cultural expression by continuously opposing dominant cultural practices and promoting alternative lifestyles.
Unpacking Culture Hacking: Concept and History
Culture hacking involves strategically altering cultural norms and symbols to influence social behaviors and perceptions, originating from the early hacker movements in the 1960s and 1970s. Unlike counterculture, which rejects mainstream values through opposition and alternative lifestyles, culture hacking works within existing systems to disrupt and reshape societal narratives. This practice has evolved through digital activism, marketing, and art, leveraging technology to engineer cultural change subtly and effectively.
Key Differences: Counterculture vs. Culture Hacking
Counterculture challenges mainstream societal norms by rejecting established values and promoting alternative lifestyles, often resulting in radical social movements. Culture hacking, on the other hand, strategically manipulates cultural symbols and media to subvert or influence dominant narratives without outright rejection of the system. The key difference lies in counterculture's oppositional stance versus culture hacking's adaptive approach to effect change within existing cultural frameworks.
Motivations Behind Counterculture Movements
Counterculture movements emerge from a desire to challenge and dismantle established social norms, often rooted in political, social, or environmental dissatisfaction. These movements are driven by collective motivations to promote alternative values, such as freedom, equality, and anti-consumerism, contrasting mainstream cultural practices. The underlying purpose is to create profound societal change by rejecting dominant ideologies and fostering new ways of thinking and living.
Tools and Methods of Culture Hackers
Culture hackers utilize a variety of digital tools and social engineering methods to subtly infiltrate and influence societal norms from within, often leveraging social media platforms, data analytics, and viral content creation. Their strategies include meme propagation, guerrilla marketing tactics, and algorithm manipulation to spread alternative narratives and challenge mainstream ideas without direct confrontation. These tools enable culture hackers to reshape culture interactively and stealthily, contrasting with countercultural movements that openly reject and oppose prevailing cultural standards.
Impact on Society: Counterculture Movements
Counterculture movements challenge dominant societal norms by promoting alternative lifestyles and values, often leading to significant social change in areas such as civil rights, environmentalism, and artistic expression. These movements inspire shifts in public consciousness and contribute to the diversification of cultural practices, influencing policy and community structures. The impact of counterculture is seen in lasting reforms and the ongoing dialogue about freedom, identity, and social justice within society.
Real-World Examples of Culture Hacking
Culture hacking involves deliberately altering cultural norms within organizations to foster innovation, as seen in Google's 20% time policy encouraging employee creativity. In contrast, counterculture movements reject mainstream cultural norms entirely, such as the Beat Generation's challenge to 1950s American values. Real-world examples of culture hacking include Zappos' integration of Holacracy to disrupt traditional corporate hierarchies and LEGO's use of fan communities to co-create product designs, effectively reshaping company culture from within.
Counterculture and Culture Hacking in the Digital Age
Counterculture in the digital age manifests as online communities and movements that challenge mainstream social norms, leveraging social media platforms to spread alternative ideologies and resist dominant cultural narratives. Culture hacking involves the strategic use of digital tools and platforms to subvert, remix, or reinterpret cultural symbols and practices, creating new meanings and influencing public perception. Both phenomena highlight the power of digital technologies to reshape cultural landscapes by enabling rapid dissemination and transformation of ideas outside traditional media channels.
Future Trends: Synergy or Conflict?
Future trends indicate a complex interplay between counterculture and culture hacking, with potential for both synergy and conflict. Counterculture movements challenge prevailing norms, inspiring cultural shifts that culture hacking techniques can amplify through digital platforms and social engineering. Emerging technologies like AI and blockchain may enable more sophisticated culture hacking strategies, potentially aligning with countercultural goals or intensifying clashes over societal values.
Counterculture Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com