Mass society refers to a large-scale social structure characterized by a high degree of social integration and uniformity, often resulting from industrialization and urbanization. It influences cultural norms, communication patterns, and individual behavior in ways that shape collective identities and social dynamics. Discover how mass society impacts your daily life and the broader implications explored throughout this article.
Table of Comparison
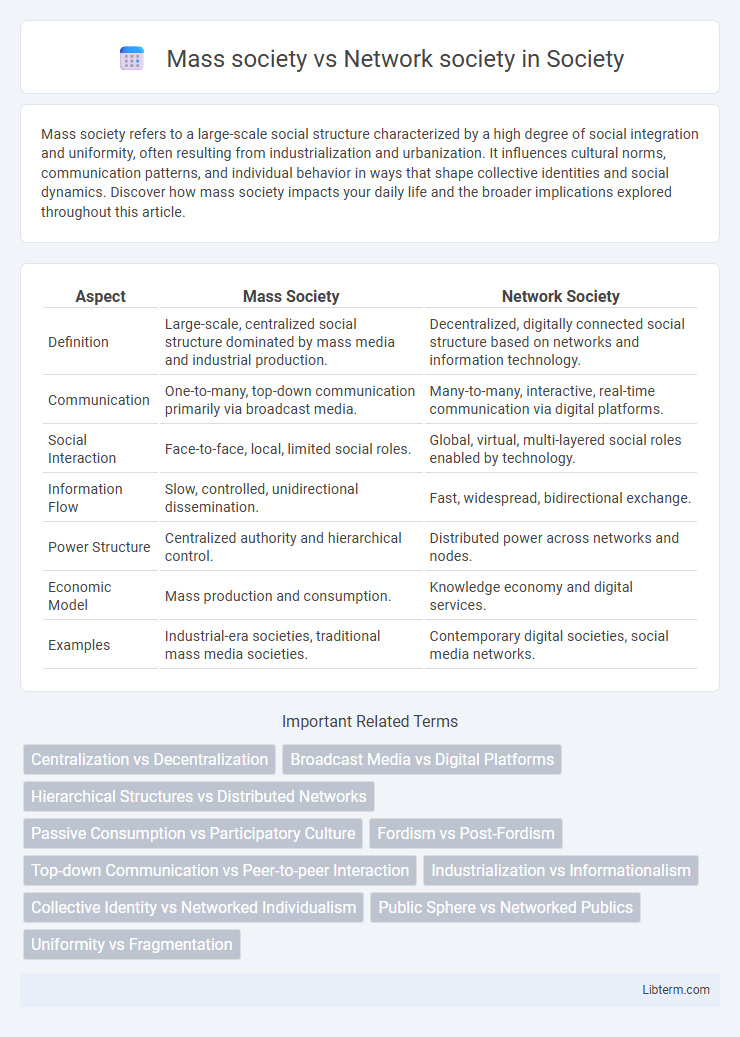
| Aspect | Mass Society | Network Society |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Large-scale, centralized social structure dominated by mass media and industrial production. | Decentralized, digitally connected social structure based on networks and information technology. |
| Communication | One-to-many, top-down communication primarily via broadcast media. | Many-to-many, interactive, real-time communication via digital platforms. |
| Social Interaction | Face-to-face, local, limited social roles. | Global, virtual, multi-layered social roles enabled by technology. |
| Information Flow | Slow, controlled, unidirectional dissemination. | Fast, widespread, bidirectional exchange. |
| Power Structure | Centralized authority and hierarchical control. | Distributed power across networks and nodes. |
| Economic Model | Mass production and consumption. | Knowledge economy and digital services. |
| Examples | Industrial-era societies, traditional mass media societies. | Contemporary digital societies, social media networks. |
Introduction: Understanding Mass Society and Network Society
Mass society refers to a social structure characterized by large-scale, homogeneous populations where mass media and centralized institutions dominate communication and culture. Network society, in contrast, is defined by decentralized, digital networks enabling real-time, multidirectional interactions and personalized information flows. Understanding these concepts highlights the shift from uniform mass communication to fragmented, interconnected digital platforms shaping social dynamics today.
Historical Emergence of Mass Society
The historical emergence of mass society traces back to the Industrial Revolution, which catalyzed urbanization, mass production, and widespread literacy, reshaping social structures and communication patterns. Mass society is characterized by centralized institutions, standardized cultural experiences, and a dominant role of mass media shaped by industrial capitalism. This contrasts with the network society, where digital communication technologies and decentralized information flows enable more diverse and flexible social interactions.
Rise of Network Society in the Digital Age
The rise of the network society in the digital age is defined by the shift from hierarchical mass society structures to decentralized, interconnected networks enabled by the internet, mobile communication, and social media platforms. This transformation emphasizes real-time information exchange, global connectivity, and participatory communication, fostering a dynamic environment for collaboration and innovation across diverse social, economic, and cultural spheres. Key technologies like broadband, cloud computing, and big data analytics drive the proliferation of networks, reshaping social organization, power distribution, and individual identity formation in contemporary society.
Key Characteristics of Mass Society
Mass society is characterized by large-scale, centralized institutions that promote cultural uniformity and social integration through mass media and standardized education. It features hierarchical social structures where communication flows primarily from top-down authorities to passive audiences. The emphasis on homogenization and mass consumption contrasts with the decentralized, interactive networks of network society.
Defining Features of Network Society
Network society is characterized by digital communication technologies that enable decentralized information flow and real-time interaction across global networks. Unlike mass society, which relies on hierarchical media distribution and passive consumption, network society emphasizes active participation, interconnectedness, and the aggregation of social, economic, and cultural activities through internet platforms. Key features include the prominence of information as a resource, the erosion of traditional institutions, and the importance of networked organizations shaping social dynamics.
Media Influence: Broadcast vs. Digital Networks
Mass society is characterized by centralized broadcast media, where information flows from a few powerful sources to a passive audience, reinforcing homogenized cultural norms and limiting individual agency. Network society, driven by digital networks, enables decentralized communication with interactive, user-generated content, fostering diverse perspectives and increased social connectivity. Media influence shifts from one-to-many models to many-to-many dynamics, transforming how information is produced, distributed, and consumed globally.
Social Structures and Power Dynamics
Mass society is characterized by hierarchical social structures with centralized power concentrated in institutions, leading to top-down control and homogenized cultural norms. In contrast, network society features decentralized social structures where power is distributed across interconnected nodes, enabling more fluid, horizontal interactions and diverse cultural expressions. This shift from centralized authority to networked influence transforms social organization by empowering individuals and groups through digital communication technologies.
Communication Patterns in Both Societies
Mass society relies on one-way, top-down communication channels such as television, radio, and newspapers that deliver uniform messages to a broad audience, emphasizing centralized control and limited audience interaction. Network society is characterized by decentralized, multi-directional communication enabled by digital platforms and social media, fostering interactive, participatory exchanges and real-time information flow among diverse, interconnected individuals and groups. These contrasting communication patterns reflect shifts from passive mass consumption to active, collaborative communication shaping social dynamics and information dissemination.
Impacts on Culture, Identity, and Participation
Mass society centralizes cultural production, leading to homogenized identities and passive participation patterns dominated by broadcast media and top-down communication. Network society fosters decentralized, interactive engagement through digital platforms, enabling diverse cultural expressions and fluid identities shaped by peer-to-peer collaboration. This shift enhances participatory culture, empowering individuals to co-create content and influence social dynamics across global networks.
Future Trends: Transition from Mass to Network Society
The transition from mass society to network society is driven by the rapid advancement of digital technologies and the proliferation of the internet, enabling decentralized and interactive communication platforms. Future trends emphasize increased connectivity, personalized information flows, and the rise of social media networks that empower individuals to create and share content globally. This shift fosters more dynamic social structures, transforming traditional mass media patterns into collaborative and participatory networks that reshape cultural, economic, and political landscapes.
Mass society Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com